

上海交通大学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 138-147.doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2021.386
所属专题: 《上海交通大学学报》2023年“船舶海洋与建筑工程”专题
彭晨鑫1, 李明广1,2( ), 甄亮3, 李耀良2, 张哲彬2
), 甄亮3, 李耀良2, 张哲彬2
收稿日期:2021-09-28
修回日期:2021-12-01
接受日期:2021-12-08
出版日期:2023-02-28
发布日期:2023-03-01
通讯作者:
李明广
E-mail:lmg20066028@sjtu.edu.cn.
作者简介:彭晨鑫(1996-),硕士,从事基坑工程方面的研究.
基金资助:
PENG Chenxin1, LI Mingguang1,2( ), ZHEN Liang3, LI Yaoliang2, ZHANG Zhebin2
), ZHEN Liang3, LI Yaoliang2, ZHANG Zhebin2
Received:2021-09-28
Revised:2021-12-01
Accepted:2021-12-08
Online:2023-02-28
Published:2023-03-01
Contact:
LI Mingguang
E-mail:lmg20066028@sjtu.edu.cn.
摘要:
软土地区多含水层系统承压层抽水存在越流现象,地下水渗流和区域地层变形响应规律复杂.基于某超深地下工程承压水抽水试验,采用数值方法研究软土地区多含水层系统第二、第三承压层降水的地质环境响应.建立了三维有限差分模型,考虑流固耦合效应和土体小应变刚度特性,模拟了不同埋深承压含水层抽水试验,对比分析各承压层抽水引起的承压水头降深和深层土体变形时空分布特性.结果表明,第二承压层水位降深较小,但引起的地表沉降更大;第二和第三承压层抽水引起降水层的压缩变形分别占地表沉降的56.18%和77.69%.主要原因为浅部土层压缩性高,相同降深条件下引起的土层竖向压缩量更大;且第二承压层与上部弱透水层的水力联系较强,越流作用明显,导致抽水引起的地下水水位降深在深度方向的影响范围更大.研究成果对后续超深基坑降水施工及环境变形控制具有重要的参考价值.
中图分类号:
彭晨鑫, 李明广, 甄亮, 李耀良, 张哲彬. 上海地区多含水层系统深部承压层降水诱发地层响应规律[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57(2): 138-147.
PENG Chenxin, LI Mingguang, ZHEN Liang, LI Yaoliang, ZHANG Zhebin. Strata Responses Due to Pumping from Deep Confined Aquifers of Multi-Aquifer-Aquitard System in Shanghai[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57(2): 138-147.
表1
抽水试验时间
| 序号 | 时间 | 试验内容 | 抽水井号 | 平均流量/(m3·h-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2017-10-23T10:30—2017-10-29T19:00 | 初始水位观测 | - | - |
| 2 | 2017-12-7T12:20—2017-12-8T12:20 | 11层单井抽水 | K11-1 | 75.30 |
| 3 | 2017-12-10T13:30—2017-12-12T16:30 | ⑨层单井抽水 | K9-2 | 456.00 |
| 4 | 2017-12-20T12:00—2017-12-27T12:00 | 11层群井抽水 | K11-1、K11-2 | 74.36、132.56 |
| 5 | 2018-1-2T 15: 00—2018-1-9T 16:00 | ⑨层群井抽水 | K9-1、K9-2 | 146.70、452.20 |
表2
土层参数取值
| 土层编号 | γ/ (kN·m-3) | c'/ kPa | φ'/ (°) | ψ/ (°) | e |       MPa |       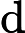 MPa |       MPa |      /MPa | γ0.7 | kh/ (cm·s-1) | kv/ (cm·s-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aq0 | ②1 | 18.5 | 6 | 26.5 | 0 | 0.93 | 5.31 | 4.43 | 31.00 | 124.0 | 2.7×10-4 | 1.19×10-6 | 7.76×10-7 |
| ③ | 17.5 | 2 | 29.6 | 0 | 1.18 | 3.61 | 3.01 | 21.04 | 84.2 | 2.7×10-4 | 1.04×10-6 | 6.78×10-7 | |
| AdI | ④ | 17.0 | 3 | 27.9 | 0 | 1.34 | 2.90 | 2.41 | 16.88 | 67.5 | 2.7×10-4 | 1.94×10-7 | 1.41×10-7 |
| ⑤1 | 17.6 | 4 | 30.5 | 0 | 1.13 | 4.05 | 3.38 | 23.623 | 94.5 | 2.7×10-4 | 3.77×10-7 | 3.12×10-7 | |
| ⑤3 | 17.9 | 5 | 31.6 | 0 | 1.01 | 5.55 | 4.62 | 32.38 | 129.5 | 2.7×10-4 | 2.42×10-6 | 1.47×10-6 | |
| AdII | ⑧1 | 18.0 | 8 | 32.4 | 0 | 1.01 | 5.70 | 4.75 | 33.26 | 133.1 | 2.7×10-4 | 1.15×10-6 | 7.32×10-7 |
| ⑧2 | 18.7 | 8 | 33.1 | 0 | 0.85 | 6.75 | 5.63 | 39.38 | 157.5 | 2.7×10-4 | 3.72×10-6 | 2.31×10-6 | |
| AqII | ⑨1 | 19.6 | 0 | 31.5 | 1.5 | 0.66 | 14.66 | 14.66 | 58.64 | 293.2 | 2.7×10-4 | 3.01×10-4 | 2.03×10-4 |
| ⑨2-1 | 20.4 | 0 | 37.5 | 7.5 | 0.53 | 15.69 | 15.69 | 62.76 | 313.8 | 2.7×10-4 | 1.00×10-4 | 9.61×10-5 | |
| ⑨2-2 | 20.4 | 0 | 36.5 | 6.5 | 0.52 | 17.21 | 17.21 | 68.84 | 344.2 | 2.7×10-4 | 4.98×10-4 | 2.04×10-4 | |
| AdIII | ⑩ | 20.0 | 19 | 31.6 | 0 | 0.64 | 12.51 | 10.42 | 72.95 | 291.8 | 2.7×10-4 | 2.05×10-7 | 8.59×10-8 |
| ⑩夹 | 19.5 | 0 | 32.0 | 0 | 0.71 | 9.25 | 7.70 | 53.93 | 215.7 | 2.7×10-4 | 2.31×10-5 | 3.47×10-6 | |
| ⑩A | 19.5 | 0 | 37.0 | 7.0 | 0.69 | 12.37 | 12.37 | 49.48 | 247.4 | 2.7×10-4 | 3.47×10-4 | 7.98×10-5 | |
| AqIII | 11 | 19.5 | 0 | 36.0 | 6.0 | 0.69 | 15.40 | 15.40 | 61.60 | 308.0 | 2.7×10-4 | 8.45×10-4 | 1.74×10-4 |
| 11T | 19.2 | 0 | 36.0 | 0 | 0.76 | 10.78 | 8.98 | 62.87 | 251.5 | 2.7×10-4 | 8.43×10-6 | 4.68×10-6 | |
| AdIV | 12 | 20.1 | 15 | 30.0 | 0 | 0.62 | 12.20 | 10.17 | 71.19 | 284.8 | 2.7×10-4 | 2.01×10-7 | 1.18×10-7 |
| [1] | 史玉金, 严学新, 陈大平. 上海海陆一体工程地质结构构建及地质条件评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2017, 44(2): 96-101. |
| SHI Yujin, YAN Xuexin, CHEN Daping. Engineering geological structure establishment and conditions assessment integrating land and sea in Shanghai coastal area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(2): 96-101. | |
| [2] | 郑启宇, 夏小和, 李明广, 等. 深基坑降承压水对墙体变形和地表沉降的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2020, 54(10): 1094-1100. |
| ZHENG Qiyu, XIA Xiaohe, LI Mingguang, et al. Influence of dewatering in confined aquifers on wall deformation and ground settlements in deep excavation[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2020, 54(10): 1094-1100. | |
| [3] | 仵彦卿, 张建山, 李哲. 基坑抽水引起周围地面沉降机理及防治措施[J]. 岩土力学, 2005, 26(10): 61-65. |
| WU Yanqing, ZHANG Jianshan, LI Zhe. Mechanism analysis of land subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal and control measures[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(10): 61-65. | |
| [4] |
ZENG C F, WANG S, XUE X L, et al. Evolution of deep ground settlement subject to groundwater drawdown during dewatering in a multi-layered aquifer-aquitard system: Insights from numerical modelling[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 603: 127078.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127078 URL |
| [5] |
ZENG C F, ZHENG G, XUE X L. Responses of deep soil layers to combined recharge in a leaky aquifer[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 260: 105263.
doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105263 URL |
| [6] |
WU Y X, ZHENG Q, ZHOU A N, et al. Numerical evaluation of the ground response induced by dewatering in a multi-aquifer system[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2021, 12(5): 101209.
doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2021.101209 URL |
| [7] | WANG D F, LI M G, CHEN J J, et al. Numerical study on groundwater drawdown and deformation responses of multi-layer strata to pumping in a confined aquifer[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Science), 2019, 24(3): 287-293. |
| [8] |
ZENG C F, SONG W W, XUE X L, et al. Construction dewatering in a metro station incorporating buttress retaining wall to limit ground settlement: Insights from experimental modelling[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2021, 116: 104124.
doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.104124 URL |
| [9] |
CHAI J C, SHEN S L, ZHU H H, et al. Land subsidence due to groundwater drawdown in Shanghai[J]. Géotechnique, 2004, 54(2): 143-147.
doi: 10.1680/geot.2004.54.2.143 URL |
| [10] |
LI M G, CHEN J J, XIA X H, et al. Statistical and hydro-mechanical coupling analyses on groundwater drawdown and soil deformation caused by dewatering in a multi-aquifer-aquitard system[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 589: 125365.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125365 URL |
| [11] |
LI M G, CHEN J J, XU Y S, et al. Effects of groundwater exploitation and recharge on land subsidence and infrastructure settlement patterns in Shanghai[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 282: 105995.
doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.105995 URL |
| [12] |
WU Y X, SHEN S L, WU H N, et al. Environmental protection using dewatering technology in a deep confined aquifer beneath a shallow aquifer[J]. Engineering Geology, 2015, 196: 59-70.
doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.06.015 URL |
| [13] |
ZHANG Y Q, LI M G, WANG J H, et al. Field tests of pumping-recharge technology for deep confined aquifers and its application to a deep excavation[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 228: 249-259.
doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.08.019 URL |
| [14] |
ZHANG Y Q, WANG J H, CHEN J J, et al. Numerical study on the responses of groundwater and strata to pumping and recharge in a deep confined aquifer[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2017, 548: 342-352.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.03.018 URL |
| [15] | 王卫东, 王浩然, 徐中华. 上海地区基坑开挖数值分析中土体HS-Small模型参数的研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(6): 1766-1774. |
| WANG Weidong, WANG Haoran, XU Zhonghua. Study of parameters of HS-Small model used in numerical analysis of excavations in Shanghai area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(6): 1766-1774. | |
| [16] | 王建秀, 吴林高, 朱雁飞, 等. 地铁车站深基坑降水诱发沉降机制及计算方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(5): 1010-1019. |
| WANG Jianxiu, WU Lingao, ZHU Yanfei, et al. Mechanism of dewatering-induced ground subsidence in deep subway station pit and calculation method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(5): 1010-1019. |
| [1] | 李登, 庄欠伟, 黄昕, 周东荣, 朱小东, 张弛, 魏良孟. 竖向小曲率半径曲线顶管掘进管节-土体相互作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57(S1): 69-79. |
| [2] | 刘婧, 陈锦剑, 王建华. 上海世博500 kV地下变基坑降水流固耦合分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2010, 44(06): 721-725. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 976
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 614
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||