陶瓷基复合材料(Ceramic Matrix Composites, CMCs)是20世纪80年代发展起来的一种高温热结构材料,具有耐高温、耐腐蚀、高比强度等优异特性.近些年开始在航空航天等领域得到应用,是高推重比航空发动机飞行器、火箭发动机、核反应堆等重要装备热端部件的理想选材[1].
CMCs的微观损伤机理是分析材料力学性能的基础,传统力学试验对于材料损伤萌生和演化过程的观测局限在材料表面,对于材料内部的损伤无法进行直接原位观测,一般利用材料破坏后的损伤模式进行推断或反演得到,缺乏材料在载荷作用下的原位损伤信息,限制了材料损伤演化的定量研究[2⇓-4].近些年,随着X射线CT无损检测技术的发展,一些学者开展了X射线CT原位加载试验,研究CMCs在载荷作用下的内部损伤模式与演化过程.Bale等[5]利用X射线CT技术,通过原位拉伸试验观测到了常温和高温环境下单向SiCf/SiC纤维束复合材料的基体开裂、纤维断裂、纤维拔出等损伤随拉伸载荷增加的演化过程,展示了X射线CT原位试验对研究材料损伤的强大功能.Wan等[3,6]开展了三维编织Cf/C-SiC的X射线CT原位压缩和三点弯曲试验,观测到加载过程材料内部的变形和原位损伤.Saucedo-Mora等[7]进行了编织SiCf/SiC管的拉伸X射线CT原位试验.Zhang等[8-9]利用X射线CT原位拉伸试验,揭示了平纹SiCf/SiC的拉伸损伤演化和失效机理.虽然X射线CT技术已被大量应用于CMCs的拉伸和弯曲等载荷工况的损伤研究,但对于压缩损伤机理鲜有报道,其压缩损伤模式和演化机理尚不明确.CMCs承受压缩载荷的应用条件较为常见,如机械连接件[10]、飞行器的高温密封弹簧[11]等,因此有必要开展X射线CT原位加载试验,研究其压缩损伤演化机理.
对X射线CT扫描数据进行图像处理时,由于CMCs的初始缺陷及损伤失效模式复杂多样,基于灰度值的阈值分割技术等常规图像分割方法很难准确高效地识别损伤模式.随着深度学习技术的进步,已有学者将其应用于复合材料的组分与损伤表征[12⇓-14],取得了良好的识别效果和效率,节省了大量的时间和人力,一定程度上避免了人工筛选的误差.Forsberg等[15]利用X射线CT扫描图像,结合数字体积相关(Digital Volume Correlation, DVC)技术获得了木材三点弯曲原位加载过程的位移场和应变场.万帆[16]对Cf/C-SiC进行了压缩测试,获得了各级载荷下的位移场及应变场.虽然基于深度学习的图像分割和DVC技术可高效识别材料损伤、有效获得材料全场变形和应变,但尚未见两种方法应用于SiCf/SiC压缩方面的研究.
综上,关于SiCf/SiC陶瓷基复合材料的压缩损伤研究鲜有报道,其压缩损伤机理尚未得到充分认识,因此本文借助高分辨率X射线CT原位加载、基于深度学习的图像分割以及DVC技术等先进试验与分析技术,研究平纹SiCf/SiC的压缩损伤模式、损伤演化及断裂机理.首先开展平纹SiCf/SiC高分辨率X射线CT原位压缩试验,获得材料压缩过程中以及失效后的CT原位图像;然后采用DVC技术计算平纹SiCf/SiC受到压力载荷后的应变场、位移场以及破坏前的变形;最后利用图像处理软件ORS Dragonfly进行基于深度学习的图像分割,获得平纹SiCf/SiC压缩损伤模式和损伤空间分布,以及损伤数量和体积随载荷变化关系等定量数据,揭示平纹SiCf/SiC的压缩损伤演化机理.
1 X射线CT原位压缩试验
1.1 试验材料与试样
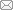
试样采用化学气相渗透(Chemical Vapor Infiltration, CVI)工艺制备的平纹SiCf/SiC,增韧相为第3代SiC纤维,预制体为11层平纹SiC纤维叠层织物.试样由平面激光切割机切割、精研一体机打磨而成,其外观形貌、几何尺寸以及坐标系如图1所示.图中:
图1
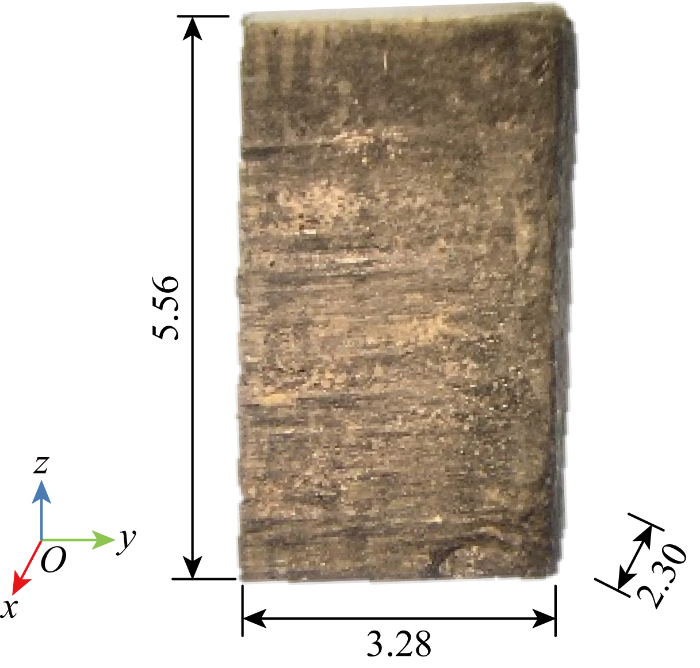
X射线CT扫描平纹SiCf/SiC细观编织结构与孔隙分布如图2 所示.图2(a)中,试样底部有一条缝合纱孔穿过,缝合纱的主要作用是在材料制备过程中保持预制体形状并提高其整体性,缝合密度低且纱线较细,因此对复合材料的力学性能影响较小.CVI制备工艺的特点使得材料内部存在大量的初始孔隙.图2(b)为利用阈值分割法获得的孔隙分布,可以观察到材料的孔隙分布.按照孔隙的位置和大小将其分为两类:一类是分布于纤维束内部的小孔隙(绿色部分),呈颗粒状均匀分布;另一类是分布于纤维束之间的大孔洞(洋红色部分),呈片状分布,主要位于铺层与铺层之间,在厚度方向呈周期状分布.材料的孔隙率约为17.36%,其中小孔隙体积分数约为2.24%,大孔洞体积分数约为15.12%.
图2
图2
X射线CT扫描平纹SiCf/SiC细观编织结构与孔隙分布
Fig.2
Meso-scale architecture and pore distribution of plain weave SiCf/SiC composites obtained by X-ray CT
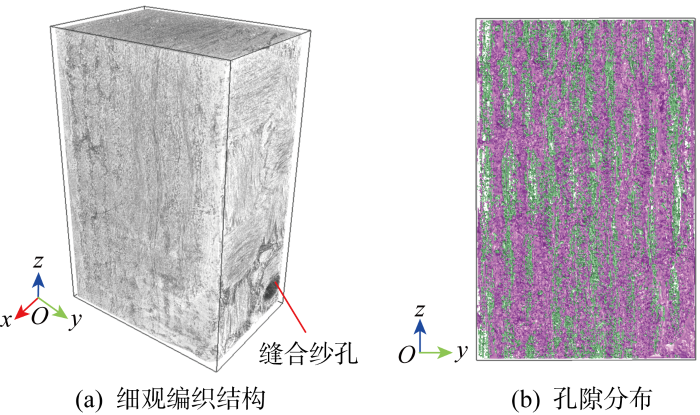
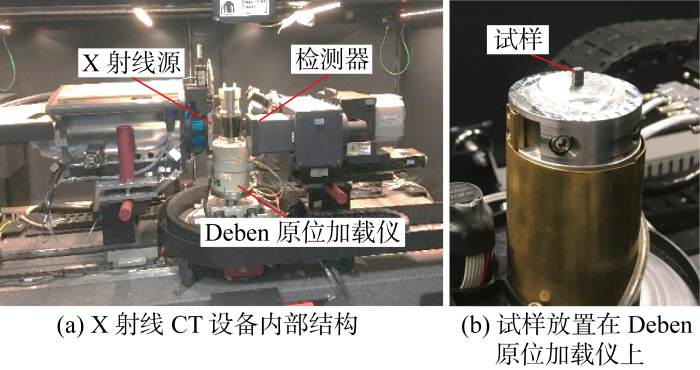
X射线CT 原位压缩加载装置如图3所示.X射线CT设备采用ZEISS Xradia 520 Versa X射线显微镜,如图3(a)所示,压缩仪器采用Deben原位加载仪,如图3(b)所示,最大加载力为5 kN.原位压缩加载采用位移控制,速率0.1 mm/min.将原位加载仪固定在X射线显微镜样品台,设置X射线CT设备扫描参数,开始压缩加载,并在预设的载荷工况附近保持位移不变并进行CT扫描.为获得较高分辨率,X射线CT原位压缩试验采用拼接扫描,即将扫描区域分为上下2部分先后扫描,然后将扫描结果拼接.扫描电压为90 kV,物镜为4倍,曝光时间为9.5 s,体素分辨率为4.402 μm.压缩破坏后,由于试样高度大幅减小,改为常规CT扫描,曝光时间为3.0 s,体素分辨率为5.281 μm.
图3
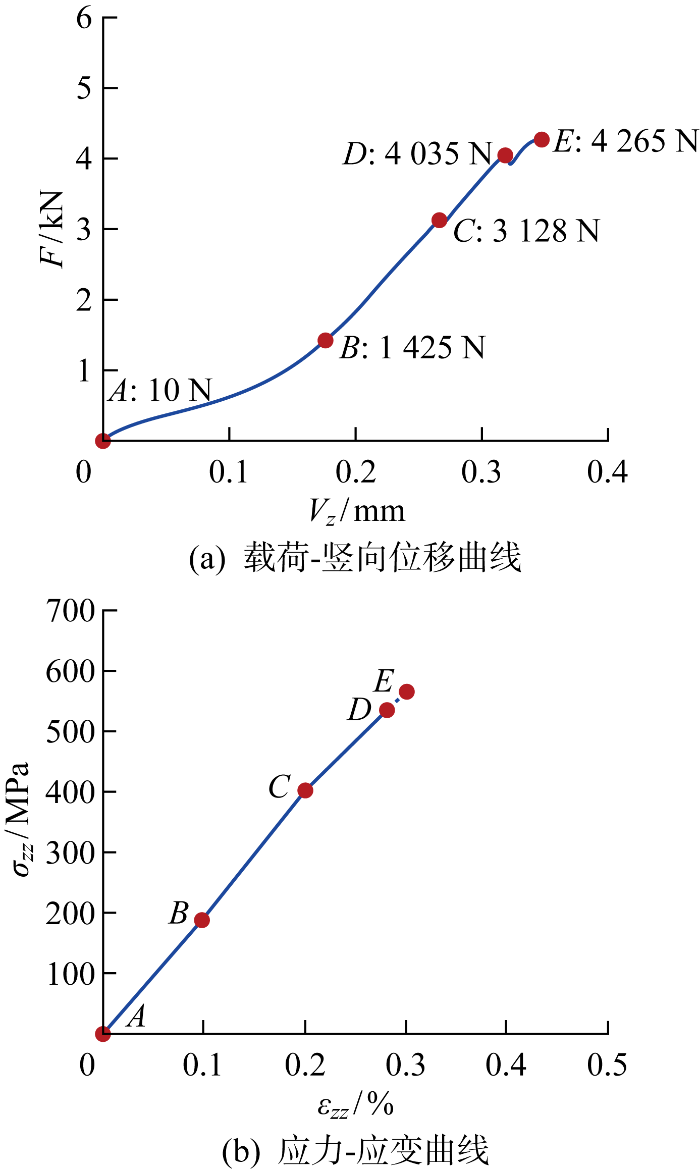
1.2 原位压缩试验曲线
进行原位压缩试验之前,采用相同材料和尺寸开展了3个模拟压缩试验,试验曲线作为原位试验工况设计的参考依据,根据曲线变化特征设计了5级载荷工况:加载初、初次拐点、初次拐点和极限载荷之间、近极限载荷、破坏后,分别用
图4
图4
载荷-竖向位移曲线和应力-应变曲线
Fig.4
Curves of load-vertical displacement and stress-strain
利用DVC技术计算了A~D级载荷下材料的应变,得到平纹SiCf/SiC的单向压缩应力-应变曲线,如图4(b)所示.其中,压应力、压应变均取绝对值.与力-位移曲线相似,在加载前期应力-应变曲线基本呈线性变化,表明压缩过程中材料损伤较小,未对宏观力学性能产生明显影响.在加载后期应力-应变曲线斜率略有降低,表明材料出现损伤.
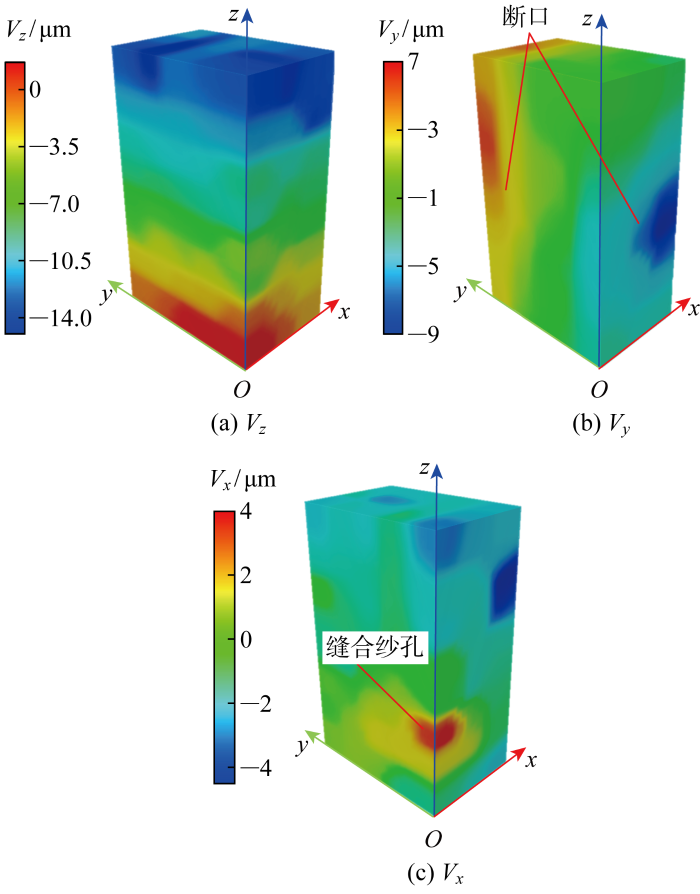
1.3 基于DVC技术的位移场及应变场分析
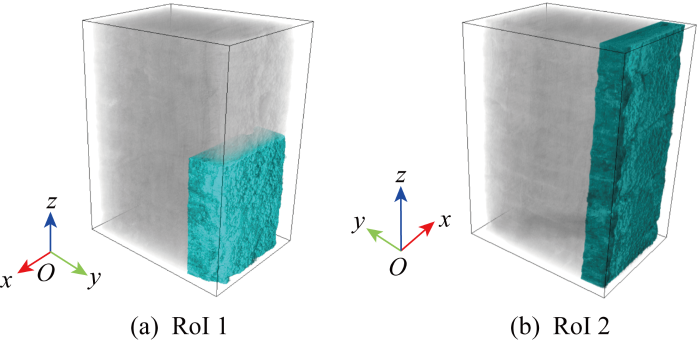
图5
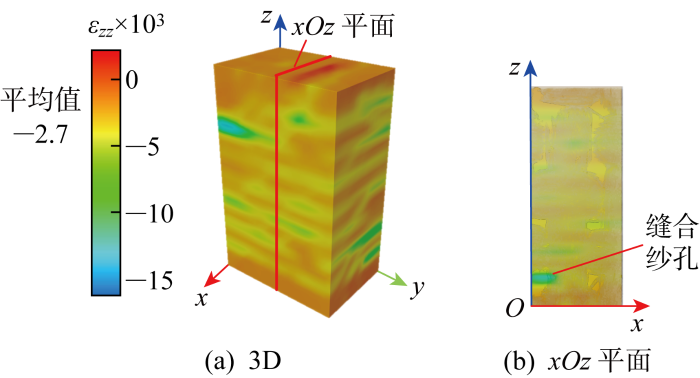
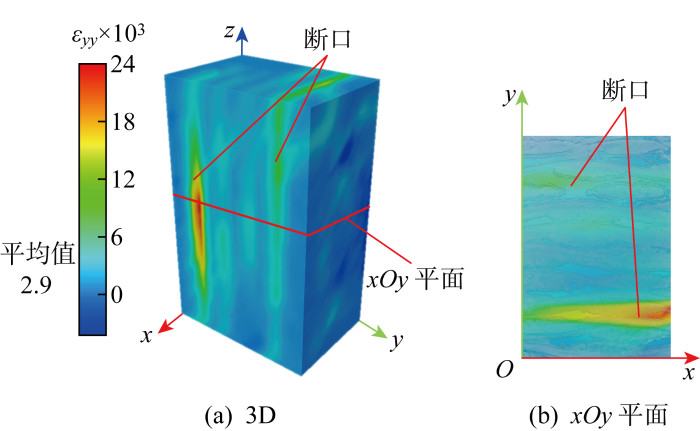
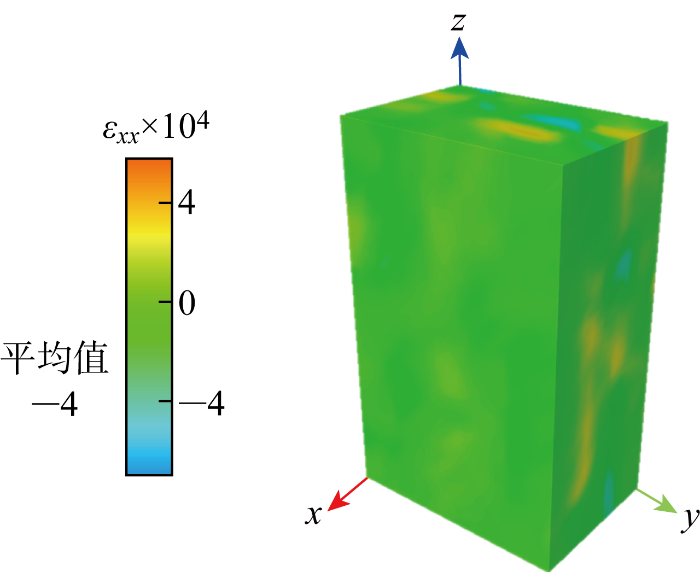
D级载荷下的应变场如图6~8所示.由图6可知,
图6
图7
图8
2 结果分析
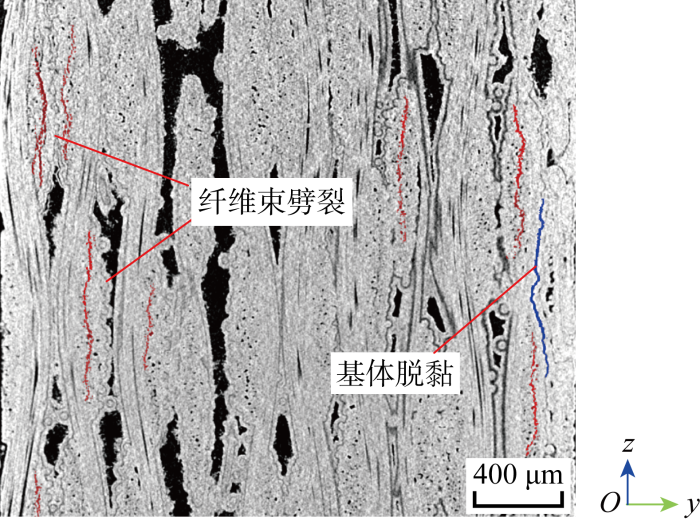
2.1 损伤模式
图9
图10
图11
图12
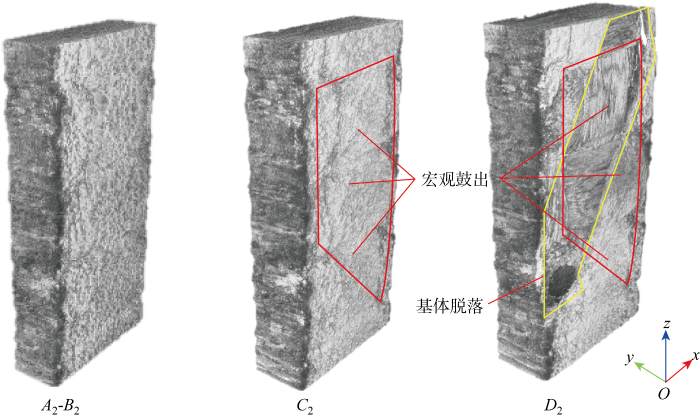
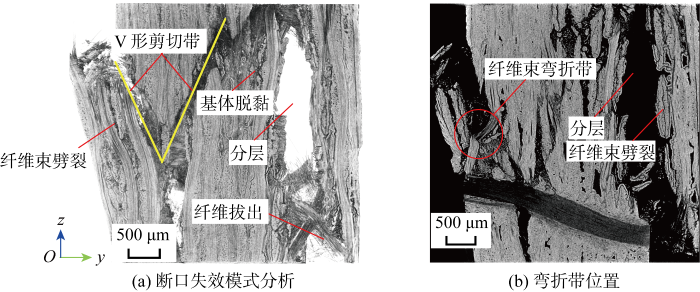
2.2 断口形貌
图13
图13
断口失效模式分析和弯折带位置
Fig.13
Analysis diagram of fracture failure mode and location diagram of kink band
2.3 鼓出变形
图14为
图14
图14
Fig.14
Deformation diagram of
2.4 基于深度学习的损伤识别与分析
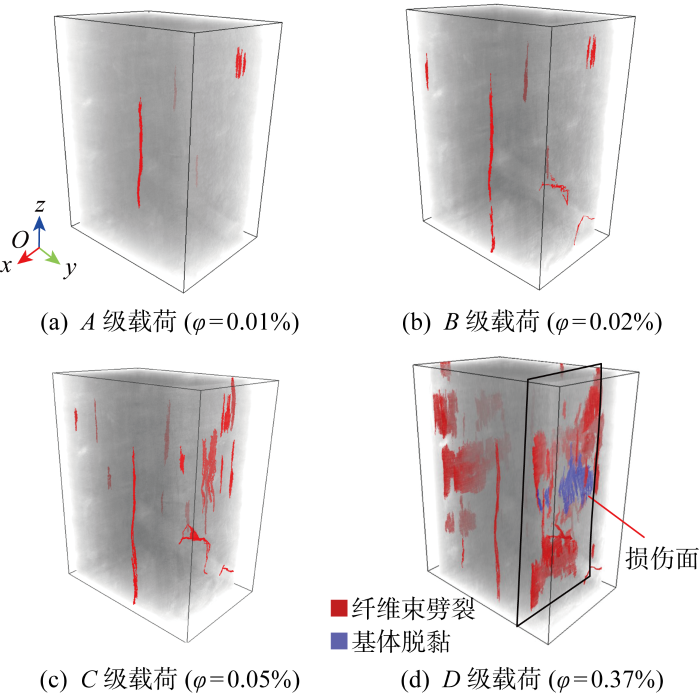
采用基于深度学习的图像分割方法,实现了平纹SiCf/SiC在压缩载荷下损伤的可视化三维表征.图像分割是按照一定的规则(如灰度值范围)将扫描图像划分成不同类别的区域,深度学习是一种对数据特征进行人工智能学习的算法.基于深度学习的图像分割可以准确快速地划分大量灰度值相近但形状特征不同的图像区域,例如将材料损伤与灰度值相近的初始孔隙识别出来.本文利用ORS Dragonfly软件的相关功能进行平纹SiCf/SiC的损伤识别,首先选取
图15
图16
图16
试样损伤演化过程三维空间分布及损伤体积分数
Fig.16
Damage evolution (3D) and fraction volume of damage
基于深度学习的图像分割方法准确有效地获得了平纹SiCf/SiC压缩载荷下的损伤空间分布及数量特征,为损伤演化的定量分析提供了依据.图17为各级载荷下损伤的数量
图17
图17
不同载荷下损伤体积分数及数量变化
Fig.17
Curves of damage proportion and number at different loading levels
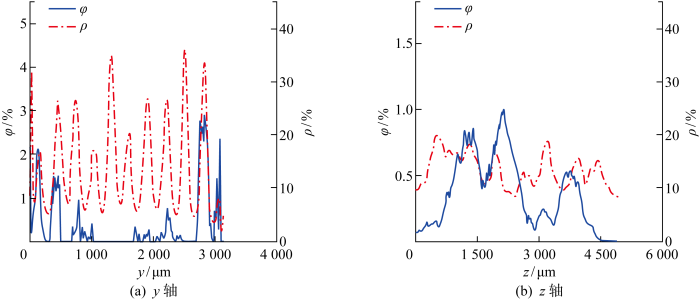
图18
图18
沿y轴和z轴的损伤体积分数与孔隙率分布
Fig.18
Volume fraction of damage and porosity distribution along y and z axes
3 压缩损伤演化与失效机理
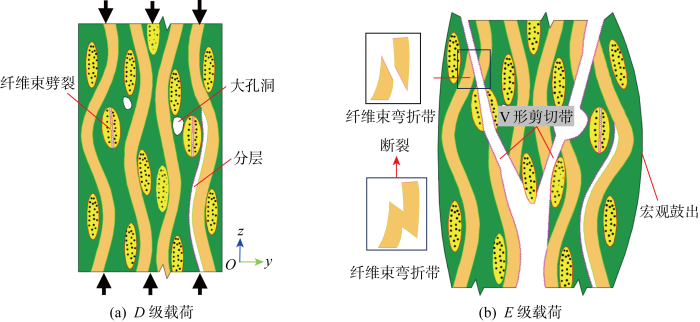
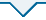
绘制了平纹SiCf/SiC的压缩损伤演化与失效机理示意图,如图19所示,主要包括纤维束劈裂、分层、纤维束弯折带、V形剪切带、厚度方向鼓出变形等损伤失效模式,主要机理分析如下.
图19
图19
压缩损伤演变与失效机理示意图
Fig.19
Schematic diagram of damage progression and failure mechanism
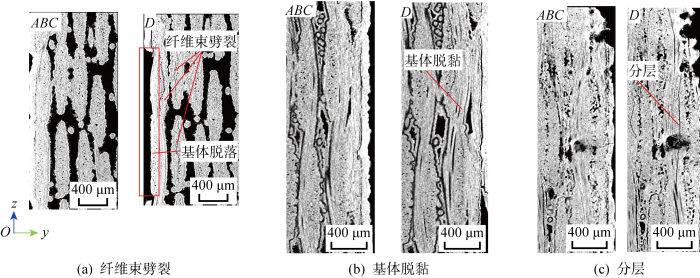
(1) 分层与纤维束劈裂:在压缩载荷作用下,纤维束与基体发生脱黏,并发展成分层;由于缺乏侧向限制,孔洞附近的纤维束容易向两侧外鼓,产生纤维束纵向劈裂.纤维束劈裂与分层多分布于材料表面和孔洞附近,并逐渐相互贯通,形成范围较大的损伤面.
(2) 纤维束弯折断裂与V形剪切带:由于
(3) 厚度方向鼓出变形:在压缩载荷下,试样沿厚度方向容易产生鼓出变形.由于试样上下承压面被约束,试样中间部分鼓出变形大于上下两端,使试样呈现出桶状.中间部位的鼓出变形很大,甚至略大于试样的压缩变形.鼓出变形较大处多伴随纤维束劈裂、分层、纤维束弯折带和V形剪切带,所以厚度方向鼓出变形是产生其他压缩损伤与失效模式的内在原因.
4 结论
通过对平纹SiCf/SiC进行X射线CT原位压缩试验,借助DVC技术分析试样位移场、应变场,利用基于深度学习的图像分割方法识别材料的损伤分布及数量特征,得到以下主要结论:
(1) 高分辨率X射线CT原位压缩试验能够获取平纹SiCf/SiC的内部微观结构、压缩载荷下的损伤萌生与演化特征.平纹SiCf/SiC的压缩应力-应变曲线呈现线性特征.
(2) 对于平纹SiCf/SiC的压缩损伤,载荷较小时易发生表层基体脱黏和脱落,较高载荷时横向纤维束易产生平行于压缩方向的劈裂,且多分布于表层和大孔洞附近.
(3) 平纹SiCf/SiC的压缩断口主要包括纤维束弯折、V形剪切带、厚度方向鼓出、纤维拔出、分层等损伤失效模式,宏观表现为V形剪切带和厚度方向鼓出,压缩鼓出变形驱动其他损伤失效模式的产生.
(4) DVC技术可计算材料压缩载荷下内部的三维位移场和应变场,基于深度学习的图像分割方法可以对平纹SiCf/SiC压缩载荷下的纤维束劈裂、脱黏分层等损伤进行智能识别和三维可视化表征,为研究其压缩损伤演化与失效机理提供了真实可靠的量化数据,为损伤程度的量化评估提供可能性.
参考文献
连续纤维增强陶瓷基复合材料概述
[J].
Review of continuous fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composites
[J].
In situ observation of compression damage in a 3D needled-punched carbon fiber-silicon carbide ceramic matrix composite
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.11.041 URL [本文引用: 1]
In-situ observation of compression damage in a 3D braided carbon fiber reinforced carbon and silicon carbide (C/C-SiC) ceramic composite
[J].
DOI:10.1017/S1431927618000351
URL
[本文引用: 2]

Deformation and mechanical damage in a three-dimensional braided carbon fiber reinforced carbon and silicon carbide ceramic composite, subjected to compressive loading, has been studied in situ by laboratory X-ray computed tomography. Dimensional change was measured and damage visualized by digital volume correlation analysis of tomographs. Cracks nucleated from defects within the fiber bundles and tended to propagate along the fiber bundle/matrix interface. For longitudinal compression, parallel to the fiber bundles, the initial elastic modulus decreased with increasing compressive strain while significant transverse tensile strains developed due to distributed cracking. For transverse compression, perpendicular to the fiber bundles, the compressive elastic modulus was effectively constant; the tensile strains developed along the fiber direction were small, whereas macroscopic fracture between the fiber bundles caused very large bulk tensile strain perpendicular to the loading. The observations suggest that the mechanical strength might be improved through control of pre-existing defects and application of stitch fibers in the transverse direction.
In situ X-ray microtomography characterization of damage in SiCf/SiC minicomposites
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.compscitech.2011.02.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Real-time quantitative imaging of failure events in materials under load at temperatures above 1, 600 ℃
[J].DOI:10.1038/nmat3497 [本文引用: 1]
Damage development during flexural loading of a 5-directional braided C/C-SiC composite, characterized by X-ray tomography and digital volume correlation
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.12.020 URL [本文引用: 1]
In situ observation of mechanical damage within a SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composite
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jnucmat.2016.09.007 URL [本文引用: 1]
Characterisation of damage evolution in plain weave SiC/SiC composites using in situ X-ray micro-computed tomography
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114447 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于X射线CT原位试验的平纹SiC/SiC复合材料拉伸损伤演化
[J].
Tensile damage evolution of plain weave SiC/SiC composites based on in-situ X-ray CT tests
[J].
Automated segmentation of computed tomography images of fiber-reinforced composites by deep learning
[J].DOI:10.1007/s10853-019-03876-z [本文引用: 1]
基于深度学习的平纹Cf/SiC复合材料原位拉伸损伤演化与断裂分析
[J].为揭示平纹C<sub>f</sub>/SiC复合材料的拉伸损伤演化及失效机理,开展了X射线CT原位拉伸试验,获得材料的三维重构图像,利用深度学习的图像分割方法,准确识别出拉伸裂纹并实现其三维可视化。分析了平纹C<sub>f</sub>/SiC复合材料损伤演化与失效机理,基于裂纹的三维可视化结果对材料损伤进行了定量表征。结果表明:平纹C<sub>f</sub>/SiC复合材料的拉伸力学行为呈现非线性,拉伸过程中主要出现基体开裂、界面脱黏、纤维断裂及纤维拔出等损伤;初始缺陷易引起材料损伤,孔隙多的部位裂纹数量也多;纤维束外基体裂纹可扩展至纤维束内部,并发生裂纹偏转。基于深度学习的智能图像分割方法为定量评估陶瓷基复合材料损伤演化与失效机理提供了有效分析手段。
In-situ tensile damage evolution and fracture analysis of plain weave Cf/SiC composites based on deep learning
[J].In order to reveal the tensile damage evolution and failure mechanism of plain weave C<sub>f</sub>/SiC composites, the X-ray CT in-situ tensile test was carried out to obtain the three-dimensional reconstructed image of the material. The deep learning based image segmentation method was used to accurately identify the tensile crack and realize its three-dimensional visualization. The damage evolution and failure mechanism of plain weave C<sub>f</sub>/SiC composites were analyzed, and the damage was quantitatively characterized based on the three-dimensional visualization results. The results show that the tensile mechanical behavior of plain weave C<sub>f</sub>/SiC composites is nonlinear, and damages such as matrix cracking, interface debonding, fiber fracture, and fiber pull-out occur during the tensile process. The initial defects are easy to cause material damage, and the higher the porosity, the more cracks there are. The matrix crack outside the fiber tow can extend to the inside of the fiber tow and the crack deflection occurs. The deep learning based intelligence image segmentation method provides an effective analysis method to quantitatively evaluate the damage evolution and failure mechanism of ceramic matrix composites.
基于深度学习的2.5D陶瓷基复合材料损伤识别与评估
[J].
Deep learning-based damage identification and evaluation of 2.5D ceramic matrix composites
[J].
3D micro-scale deformations of wood in bending: Synchrotron radiation mu CT data analyzed with digital volume correlation
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jsb.2008.08.004 URL [本文引用: 1]