


收稿日期: 2023-03-25
修回日期: 2023-05-21
录用日期: 2023-05-31
网络出版日期: 2023-06-16
Application and Prospect of Two-Part Tariff Mechanism in Context of Transmission and Distribution Price Reform
Received date: 2023-03-25
Revised date: 2023-05-21
Accepted date: 2023-05-31
Online published: 2023-06-16
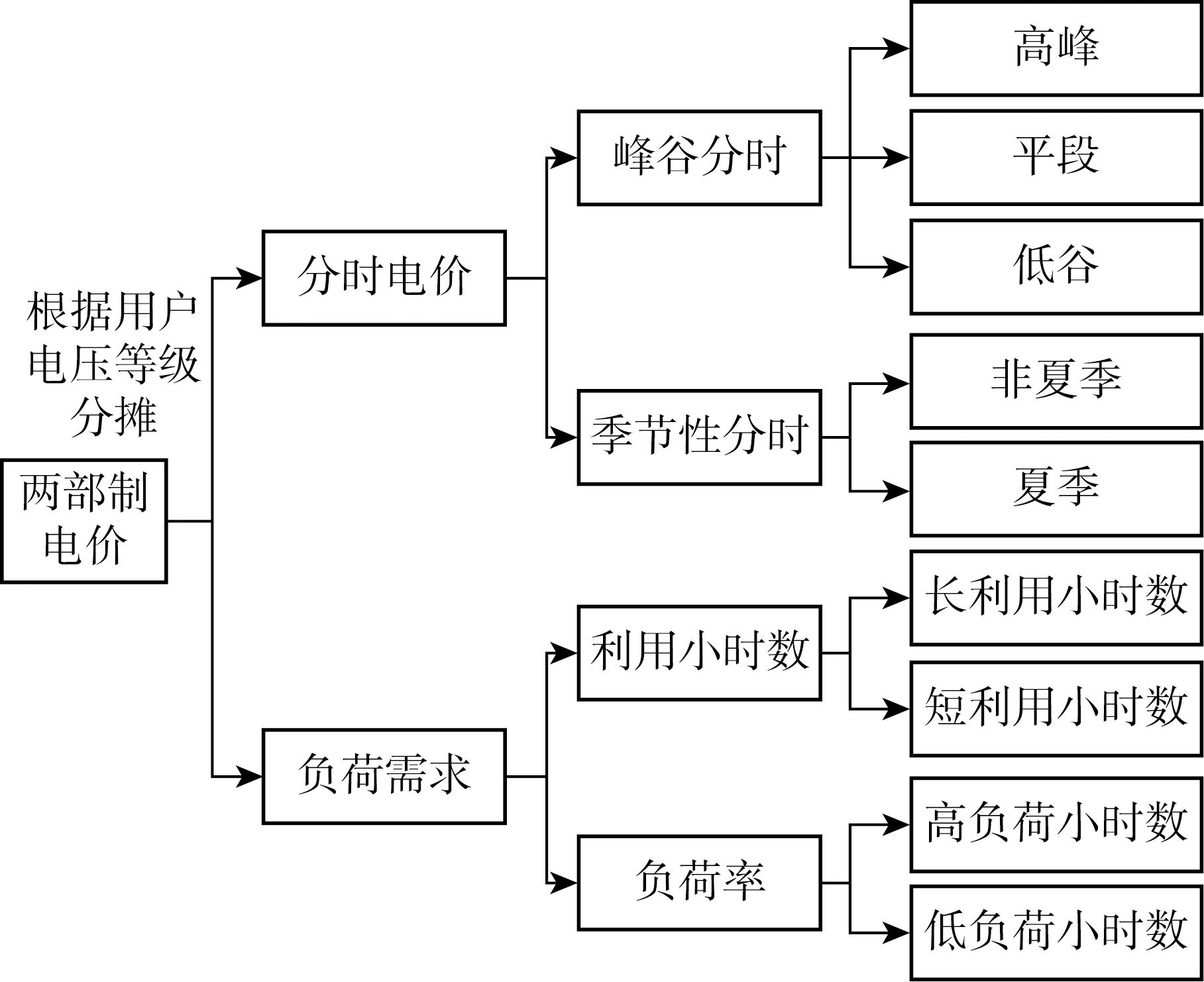
在输配电价机制改革的背景下,现有两部制电价无法合理反映电力用户真实用电成本的弊端逐渐显露.两部制电价机制承担着分配电力发电、输送、配电、出售电价空间和调节电力系统的资源等重要功能,亟需对现有两部制电价做出改进与完善.本文围绕两部制电价机制展开分析和讨论.首先,介绍两部制电价的基本理论和计费比例,研究基于不同负荷率和电压等级分摊输配电成本的方法.然后,针对两部制电价的收取方式,分别对负荷率套餐、分时电价等电量电价机制以及电费和负荷调整、改进计价比例等基本电价机制进行总结归纳.在此基础上,结合美国、法国、日本等国外两部制实践经验,分析两部制电价机制理论的执行方式.最后,提出我国两部制电价机制的未来发展方向和建议.
任曦骏 , 宋竹萌 , 王宝 , 叶钰童 , 潘思佳 , 王梦圆 , 徐潇源 . 输配电价改革背景下两部制电价的应用现状与发展前景[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2024 , 58(10) : 1479 -1488 . DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.102
In the context of the reform of transmission and distribution tariff mechanism, the drawbacks of the existing two-part tariff system which cannot reasonably reflect the real cost of electricity consumption by power users have gradually emerged. The two-part tariff mechanism is responsible for allocating the space for electricity generation, transmission, distribution and sale tariffs, and regulating the resources of the power system. Therefore, it is urgent to improve the existing two-part tariff mechanism. This paper, focusing on the two-part tariff mechanism, first, introduces the basic theory and billing ratio of the two-part tariff, and studies the method of apportioning transmission and distribution costs based on different load rates and voltage levels. Then, it summarizes the electricity tariff mechanisms such as load rate packages and time-of-use tariffs and the basic tariff mechanisms such as tariff, load adjustments, and improved billing ratios respectively for the collection methods of two-part tariffs. Afterwards, it analyzes the implementation mode of two-part tariff mechanism theory by combining the practical experience of two-part system in the United States, France, Japan, and other foreign countries. Finally, it proposes the future development direction and suggestions of China’s two-part tariff mechanism.

| [1] | 莫志宏, 蔡文翔. 我国电力市场化改革理论研究进展及前景展望[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2020(5): 110-112. |
| MO Zhihong, CAI Wenxiang. Current status and development of research on power market reform theory in China[J]. Price: Theory & Practice, 2020(5): 110-112. | |
| [2] | 郑世林. 中国电力体制改革与电网企业生产率[J]. 产业经济评论, 2021(3): 5-18. |
| ZHENG Shilin. The effect of China’ s unbundling reform in electricity on the productivity of power supply enterprises[J]. Review of Industrial Economics, 2021(3): 5-18. | |
| [3] | 林卫斌, 李妙华, 陈昌明. 新一轮电力体制改革的逻辑与进展[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2016(9): 8-13. |
| LIN Weibin, LI Miaohua, CHEN Changming. Logic and progress of the new round of power system reform[J]. Price: Theory & Practice, 2016(9): 8-13. | |
| [4] | 董晋喜, 谭忠富, 王佳伟, 等. 电力体制改革背景下输配电价关键问题综述[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2020, 32(3): 113-122. |
| DONG Jinxi, TAN Zhongfu, WANG Jiawei, et al. Review on key issues in transmission and distribution electricity price under background of power system reform[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2020, 32(3): 113-122. | |
| [5] | 肖艳利, 刘小敏, 万晔, 等. 输配电价监管下电网投资策略优化研究: 基于输配电价、电网投资与社会经济效益关系的视角[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2022(11): 88-92. |
| XIAO Yanli, LIU Xiaomin, WAN Ye, et al. Research on the optimization of power grid investment strategy under the supervision of transmission and distribution price: Based on the relationship between transmission and distribution price, power grid investment and socioeconomic benefits[J]. Price: Theory & Practice, 2022(11): 88-92. | |
| [6] | 程曦, 吴霜, 王静怡, 等. 输配电价改革背景下电网项目多阶段投资优化决策研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(15): 116-123. |
| CHENG Xi, WU Shuang, WANG Jingyi, et al. Research on multi-stage investment optimization of power grid projects under transmission and distribution price reform[J]. Power System Protection & Control, 2021, 49(15): 116-123. | |
| [7] | 朱刘柱, 金文, 叶彬, 等. 输配电价改革背景下电网投资策略情景模拟及优化研究[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2021(5): 101-105. |
| ZHU Liuzhu, JIN Wen, YE Bin, et al. Research on scenario simulation and optimization of grid investment strategy under the situation of transmission and distribution price reform[J]. Price: Theory & Practice, 2021(5): 101-105. | |
| [8] | 徐熙林, 赵琳, 张娜, 等. 我国省级电网输配电价定价流程优化及激励性调整方案探讨[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2022(1): 160-164. |
| XU Xilin, ZHAO Lin, ZHANG Na, et al. Discussion on pricing process optimization and incentive adjustment scheme of electricity transmission and distribution in provincial power grid of China[J]. Price: Theory & Practice, 2022(1): 160-164. | |
| [9] | 田廓. 基于电网投资视角的省级电网输配电价定价办法解析及投资优化策略[J]. 智慧电力, 2020, 48(5): 7-13. |
| TIAN Kuo. Provincial power grid enterprise transmission and distribution price method analysis & investment optimization policy based on perspective of grid investment[J]. Smart Power, 2020, 48(5): 7-13. | |
| [10] | 杨丽彬, 赵霞, 叶泽, 等. 区域电网两部制输电价格的科学设计与合理应用: 基于两部制定价“产量扩大效应”的理论诠释[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2022(12): 8-12. |
| YANG Libin, ZHAO Xia, YE Ze, et al. Scientific design and reasonable application of two-part transmission price in regional power grid: Theoretical interpretation of “output expansion effect” based on two-part pricing[J]. Price: Theory & Practice, 2022(12): 8-12. | |
| [11] | STEELE SANTOS P E, CORADI LEME R, GALV?O L. On the electrical two-part tariff—The Brazilian perspective[J]. Energy Policy, 2012, 40: 123-130. |
| [12] | 张晗, 韩冬, 刘坦, 等. 碳中和背景下分布式光伏渗透与售电市场耦合机制分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57(4): 464-472. |
| ZHANG Han, HAN Dong, LIU Tan, et al. Analysis of market coupling mechanism between distributed photovoltaic penetration and electricity market under background of carbon neutrality[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57(4): 464-472. | |
| [13] | 刘飞, 车琰瑛, 田旭, 等. 新型电力系统下的抽水蓄能电站成本疏导机制: 综述与展望[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57(7): 757-768. |
| LIU Fei, CHE Yanying, TIAN Xu, et al. Cost sharing mechanisms of pumped storage stations under the new-type power system: Review and envisioning[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57(7): 757-768. | |
| [14] | 翟海燕, 樊伟, 张予燮, 等. 抽水蓄能电站两部制电价机制研究: 基于电量电价盈利与容量电价定价测算模型构建的分析[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2022(9): 178-182. |
| ZHAI Haiyan, FAN Wei, ZHANG Yuxie, et al. Study on two-part electricity price mechanism of pumped storage power station: Analysis of calculation model construction based on electricity price profitability and capacity price pricing[J]. Price: Theory & Practice, 2022(9): 178-182. | |
| [15] | 姚军, 吴永飞, 王亚莉, 等. 两部制电价政策执行方式对市场资源配置效率的影响[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56(3): 154-161. |
| YAO Jun, WU Yongfei, WANG Yali, et al. Impact analysis of two-part tariff policy executive mode on market resource allocation efficiency[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56(3): 154-161. | |
| [16] | COSTELLO K W, HEMPHILL R C. It’s high time to transition away from volumetric distribution rates: Why not a 3-part tariff?[J]. The Electricity Journal, 2022, 35(9): 107205. |
| [17] | KOPSAKANGAS-SAVOLAINEN M. The welfare effects of different pricing schemes for electricity distribution in Finland[J]. Energy Policy, 2004, 32(12): 1429-1435. |
| [18] | MUKHERJEE A, TSAI Y. Does two-part tariff licensing agreement enhance both welfare and profit?[J]. Journal of Economics, 2015, 116(1): 63-76. |
| [19] | 中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会. 关于第三监管周期省级电网输配电价及有关事项的通知[EB/OL]. (2023-05-09)[2023-05-19]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/tzgg/202305/t20230515_1355748.html. |
| National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Notice on transmission and distribution tariffs for provincial power grids and related matters for the third regulatory cycle[EB/OL]. (2023-05-09)[2023-05-19]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/tzgg/202305/t20230515_1355748.html. | |
| [20] | 高峰, 刘军, 叶泽. 基于负荷率和分时因素的两部制输配电价定价模型及其应用研究[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2022(6): 125-129. |
| GAO Feng, LIU Jun, YE Ze. Research on pricing model of two-part transmission and distribution system based on load rate and time-of-use factors and its application[J]. Price: Theory & Practice, 2022(6): 125-129. | |
| [21] | 张粒子, 张伊美, 叶红豆, 等. 可选择两部制电价定价模型及其方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2016, 40(3): 59-65. |
| ZHANG Lizi, ZHANG Yimei, YE Hongdou, et al. An optional two-part tariff pricing model based on the customers load characteristics[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(3): 59-65. | |
| [22] | 吴磊, 韩冬, 毛贵江, 等. 适应分布式发电市场化交易的过网费计算方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57(7): 887-898. |
| WU Lei, HAN Dong, MAO Guijiang, et al. Calculation method of network usage charge for market-oriented trading in distributed generation market[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57(7): 887-898. | |
| [23] | GRANDJEAN A, ADNOT J, BINET G. A review and an analysis of the residential electric load curve models[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2012, 16(9): 6539-6565. |
| [24] | WANG Z K, CRAWLEY J, LI F G N, et al. Sizing of district heating systems based on smart meter data: Quantifying the aggregated domestic energy demand and demand diversity in the UK[J]. Energy, 2020, 193: 116780. |
| [25] | BARY C. Coincidence-factor relationships of electric-service-load characteristics[J]. Electrical Engineering, 1945, 64(9): 623-628. |
| [26] | 黄海涛, 高畅, 吴洁晶, 等. 负荷率电价的选择性证明及实用化选项设计方法[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2017, 33(5): 74-78. |
| HUANG Haitao, GAO Chang, WU Jiejing, et al. Selective proof and practical option design method for load factor price[J]. Power System & Clean Energy, 2017, 33(5): 74-78. | |
| [27] | MAHONY C S, BAARTMAN J M. Tariff developments for electricity-intensive industry in South Africa[J]. Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining & Metallurgy, 2018, 118(6): 569-574. |
| [28] | FARUQUI A, BOURBONNAIS C. The tariffs of tomorrow: Innovations in rate designs[J]. IEEE Power & Energy Magazine, 2020, 18(3): 18-25. |
| [29] | Xcel Energy. Colorado commercial and industrial—Gas and electric rate schedule summaries[EB/OL]. (2017-01-17)[2023-07-01]. https://www.xcelenergy.com/staticfiles/xe-responsive/Company/Rates%20&%20Regulations/July%202023%20CO%20Business%20Rates%20Brochure.pdf. |
| [30] | MORELL DAMETO N, CHAVES-áVILA J P, GóMEZ SAN ROMáN T. Revisiting electricity network tariffs in a context of decarbonization, digitalization, and decentralization[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(12): 3111. |
| [31] | CHEN Y B, ZHANG L X, XU P, et al. Electricity demand response schemes in China: Pilot study and future outlook[J]. Energy, 2021, 224: 120042. |
| [32] | PENG X, TAO X M. Cooperative game of electricity retailers in China’s spot electricity market[J]. Energy, 2018, 145: 152-170. |
| [33] | ZAPF M, WEINDL C, PENGG H, et al. Specific grid charges for controllable loads in smart grids—A proposal for a reform of the grid charges in Germany[C]// NEIS 2018-Conference on Sustainable Energy Supply and Energy Storage Systems. Hamburg, Germany: IEEE, 2018: 237-242. |
| [34] | 深圳之窗. 2021深圳电费收费标准[EB/OL]. (2021-02-26)[2023-02-27]. https://chat.shenchuang.com/xwrd/20210226/1578816.shtml. |
| Shenzhen Window. 2021 Shenzhen electricity tariffs[EB/OL]. (2021-02-26)[2023-02-27]. https://chat.shenchuang.com/xwrd/20210226/1578816.shtml. | |
| [35] | 黄海涛, 吴洁晶, 顾丹珍, 等. 计及负荷率分档的峰谷分时电价定价模型[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2016, 44(14): 122-129. |
| HUANG Haitao, WU Jiejing, GU Danzhen, et al. Pricing model of time-of-use electricity tariff considering customers classified by load factor[J]. Power System Protection & Control, 2016, 44(14): 122-129. | |
| [36] | YANG P, TANG G G, NEHORAI A. A game-theoretic approach for optimal time-of-use electricity pricing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28(2): 884-892. |
| [37] | YANG S X, NIE T Q, LI C C. Research on the contribution of regional energy Internet emission reduction considering time-of-use tariff[J]. Energy, 2022, 239: 122170. |
| [38] | 刘子旭, 米阳, 卢长坤, 等. 计及需求响应和风电消纳的电-热系统低碳优化调度[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57(7): 835-844. |
| LIU Zixu, MI Yang, LU Changkun, et al. Low-carbon optimal dispatch of electric-thermal system considering demand response and wind power consumption[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57(7): 835-844. | |
| [39] | 朱月尧, 祁佟, 吴星辰, 等. 计及实时碳减排的产消群价格型需求响应机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57(4): 452-463. |
| ZHU Yueyao, QI Tong, WU Xingchen, et al. Price-based demand response mechanism of prosumer groups considering real-time carbon emission reduction[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57(4): 452-463. | |
| [40] | 范帅, 危怡涵, 何光宇, 等. 面向新型电力系统的需求响应机制探讨[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46(7): 1-12. |
| FAN Shuai, WEI Yihan, HE Guangyu, et al. Discussion on demand response mechanism for new power systems[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46(7): 1-12. | |
| [41] | ANDRUSZKIEWICZ J, LORENC J, WEYCHAN A. Seasonal variability of price elasticity of demand of households using zonal tariffs and its impact on hourly load of the power system[J]. Energy, 2020, 196: 117175. |
| [42] | HU Y, LI Y Z, CHEN L J. Multi-objective optimization of time-of-use price for tertiary industry based on generalized seasonal multi-model structure[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 89234-89244. |
| [43] | WEN M, CHEN Y, AN L L, et al. Optional two-part electricity price based on user load rate[C]// 2019 IEEE 3rd Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration. Changsha, China: IEEE, 2019: 2161-2165. |
| [44] | AL-SOUFI K Y, MEMON A M, MARAABA L S, et al. Interactive power factor management with incentives toward reduction in fuel consumption and carbon emission[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 168283-168291. |
| [45] | AHMAD A, KASHIF S A R, SAQIB M A, et al. Tariff for reactive energy consumption in household appliances[J]. Energy, 2019, 186: 115818. |
| [46] | KOMATSU H, KIMURA O. Peak demand alert system based on electricity demand forecasting for smart meter data[J]. Energy & Buildings, 2020, 225: 110307. |
| [47] | MBURAMATARE D, GBONEY W K, DE DIEU HAKIZIMANA J. Electricity tariff design “theoretical concepts vs practices”: Review of tariff design approaches in East Africa-case studies of Rwanda, Kenya, Uganda and Tanzania[J]. International Journal of Energy Economics & Policy, 2022, 12(5): 260-273. |
| [48] | TSAO Y C, THANH V V, LU J C. Efficiency of resilient three-part tariff pricing schemes in residential power markets[J]. Energy, 2022, 239: 122329. |
| [49] | FINK S, PORTER K, MUDD C, et al. A survey of transmission cost allocation methodologies for regional transmission organizations[EB/OL]. (2011-02-01)[2023-02-27]. https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy11osti/49880.pdf. |
| [50] | YE Y Z, YANG B, CHONGFUANGPRINYA P, et al. Evaluation of impact of regulation signal on energy storage operation in PJM regulation market[C]// 2019 IEEE Milan PowerTech. Milan, Italy: IEEE, 2019: 1-6. |
| [51] | ZHANG L, LIAO J, WEN M, et al. Thermal power capacity price seletction mechanism[C]// 2021 11th International Conference on Power and Energy Systems. Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2021: 638-642. |
| [52] | ASANO H, TSUKAMOTO Y. Transmission pricing in Japan[J]. Utilities Policy, 1997, 6(3): 203-210. |
| [53] | WANG C, ZHOU K L, YANG S L. A review of residential tiered electricity pricing in China[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 79: 533-543. |
| [54] | AKAGI S, YOSHIZAWA S, ITO M, et al. Multipurpose control and planning method for battery energy storage systems in distribution network with photovoltaic plant[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2020, 116: 105485. |
| [55] | LESCOEUR B, GALLAND J B. Tariffs and load management: The French experience[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 1987, 2(2): 458-464. |
| [56] | BOIVIN J Y. Demand side management—The role of the power utility[J]. Pattern Recognition, 1995, 28(10): 1493-1497. |
| [57] | EDF particulier. Tarif Bleu[EB/OL]. (2023-01-01)[2023-02-27]. https://particulier.edf.fr/content/dam/2-Actifs/Documents/Offres/Grille_prix_Tarif_Bleu.pdf. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |