|
|
|
| Textured Perovskite/Silicon Tandem Solar Cells Achieving Over 30% Efficiency Promoted by 4-Fluorobenzylamine Hydroiodide |
Jingjing Liu1,2,3,4,5, Biao Shi1,2,3,4,5(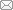 ), Qiaojing Xu1,2,3,4,5, Yucheng Li1,2,3,4,5, Yuxiang Li1,2,3,4,5, Pengfei Liu1,2,3,4,5, Zetong SunLi1,2,3,4,5, Xuejiao Wang1,2,3,4,5, Cong Sun1,2,3,4,5, Wei Han1,2,3,4,5, Diannan Li1,2,3,4,5, Sanlong Wang1,2,3,4,5, Dekun Zhang1,2,3,4,5, Guangwu Li6,7, Xiaona Du1,2,3,4,5, Ying Zhao1,2,3,4,5, Xiaodan Zhang1,2,3,4,5( ), Qiaojing Xu1,2,3,4,5, Yucheng Li1,2,3,4,5, Yuxiang Li1,2,3,4,5, Pengfei Liu1,2,3,4,5, Zetong SunLi1,2,3,4,5, Xuejiao Wang1,2,3,4,5, Cong Sun1,2,3,4,5, Wei Han1,2,3,4,5, Diannan Li1,2,3,4,5, Sanlong Wang1,2,3,4,5, Dekun Zhang1,2,3,4,5, Guangwu Li6,7, Xiaona Du1,2,3,4,5, Ying Zhao1,2,3,4,5, Xiaodan Zhang1,2,3,4,5( ) ) |
1 Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, Solar Energy Conversion Center, Institute of Photoelectronic Thin Film Devices and Technology, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350, People’s Republic of China
2 Key Laboratory of Photoelectronic Thin Film Devices and Technology of Tianjin, Tianjin, 300350, People’s Republic of China
3 Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations, Tianjin, 300192, People’s Republic of China
4 Engineering Research Center of Thin Film Photoelectronic Technology of Ministry of Education, Tianjin, 300350, People’s Republic of China
5 Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072, People’s Republic of China
6 Center of Single-Molecule Sciences, Institute of Modern Optics, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-Scale Optical Information Science and Technology, College of Electronic Information and Optical Engineering, Nankai University, 38 Tongyan Road, Jinnan District, Tianjin, 300350, People’s Republic of China
7 Shenzhen Research Institute of Nankai University, 16Th Floor, Yantian Science and Technology Building, Haishan Street, Yantian District, Shenzhen, 518083, People’s Republic of China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Monolithic textured perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells (TSCs) are expected to achieve maximum light capture at the lowest cost, potentially exhibiting the best power conversion efficiency. However, it is challenging to fabricate high-quality perovskite films and preferred crystal orientation on commercially textured silicon substrates with micrometer-size pyramids. Here, we introduced a bulky organic molecule (4-fluorobenzylamine hydroiodide (F-PMAI)) as a perovskite additive. It is found that F-PMAI can retard the crystallization process of perovskite film through hydrogen bond interaction between F− and FA+ and reduce (111) facet surface energy due to enhanced adsorption energy of F-PMAI on the (111) facet. Besides, the bulky molecular is extruded to the bottom and top of perovskite film after crystal growth, which can passivate interface defects through strong interaction between F-PMA+ and undercoordinated Pb2+/I−. As a result, the additive facilitates the formation of large perovskite grains and (111) preferred orientation with a reduced trap-state density, thereby promoting charge carrier transportation, and enhancing device performance and stability. The perovskite/silicon TSCs achieved a champion efficiency of 30.05% based on a silicon thin film tunneling junction. In addition, the devices exhibit excellent long-term thermal and light stability without encapsulation. This work provides an effective strategy for achieving efficient and stable TSCs.
|
|
Received: 22 January 2024
Published: 02 May 2024
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Biao Shi, Xiaodan Zhang
|
|
|
|

|
|
Fig. 1 Surface chemistry and crystal quality of perovskite films. a XPS spectra of Pb 4f of perovskite films without and with F-PMAI additive. b Local magnification of FTIR spectra of F-PMAI, FAI and FAI/F-PMAI mixture. c Top-view SEM images of final perovskite films without and with F-PMAI. d XRD patterns of final perovskite films without and with F-PMAI. e ToF-SIMS depth profiles show the distribution of respective elements over depth in the samples successively prepared by ITO/Spiro-TTB/perovskite with F-PMAI/C<sub>60</sub>/ALD SnO<sub>2</sub>, each layer corresponds to the feature element In (ITO), Br (perovskite), F (F-PMAI), C (Spiro-TTB, C<sub>60</sub>), Sn (SnO<sub>2</sub>), respectively
|

|
|
Fig. 2 Crystallization and orientational preference studies of perovskite film with F-PMAI. 2D GIWAXS patterns of the perovskite films a without and b with F-PMAI. c Calculated models of F-PMAI adsorbed on (100) and (111) facets of perovskite and the corresponding adsorption energies. Green: Pb, purple: I, black: C, blue: N, white: H, red: F, cyan: Cs. d Schematic illustration of the perovskite crystal growth process without and with F-PMAI additive
|

|
|
Fig. 3 The effect of F-PMAI on defect and carrier dynamic. PL mapping of the perovskite films a without and b with F-PMAI with a structure of ITO/perovskite. c SCLC curves of devices without and with F-PMAI. C-AFM images of perovskite films d without and e with F-PMAI. f Energy-level scheme of perovskite films without and with F-PMAI based on the parameters derived from UPS spectra
|

|
|
Fig. 4 The influence of F-PMAI on PSCs performance. a J-V curves of the champion devices without and with F-PMAI. Rev.: reverse scan; For.: forward scan. b EQE curves of devices without and with F-PMAI. c Stabilized power output of PSCs without and with F-PMAI. d Mott-Schottky plots, e TPV decay curves of PSCs without and with F-PMAI. f Vertical J-V curves of ITO/perovskite without and with F-PMAI/Ag. g Dark J-V curves, h Nyquist curves, i dependence of V<sub>OC</sub> on light intensity of PSCs without and with F-PMAI
|

Table 1 PV parameters of PSCs without and with F-PMAI | Sample | Scan direction | Voc (V) | Jsc (mA cm−2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) | SPO (%) | HI (%) | | w/o | Rev. | 1.10 | 22.65 | 77.43 | 19.38 | 18.6 | 7 | | For. | 1.09 | 22.66 | 72.15 | 17.95 | | w F-PMAI | Rev. | 1.15 | 22.77 | 85.48 | 22.74 | 21.2 | 2 | | For. | 1.14 | 22.82 | 83.00 | 22.07 |
|
|
Table 1 PV parameters of PSCs without and with F-PMAI
|

|
|
Fig. 5 The effect of F-PMAI on TSCs performance and stability. a Schematic structure of monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells. b Top-view SEM of monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells without and with F-PMAI. c J-V curves of the champion devices without and with F-PMAI. d Stabilized power output and e EQE curves of TSCs with F-PMAI. f Thermal stability of TSCs without and with F-PMAI under 85 °C N<sub>2</sub> glove box. T<sub>90</sub> represents the lifetime at which the PCE declines to 90% of its initial value. g Light stability of TSCs without and with F-PMAI under ambient conditions (30%-40% relative humidity (RH), ~ 25 °C). The data are normalized to their initial efficiency
|

Table 2 Champion PV parameters of TSCs without and with F-PMAI | Sample | Scan direction | Voc (V) | Jsc (mA cm−2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) | HI (%) | | w/o | Rev. | 1.77 | 19.32 | 80.11 | 27.61 | 13 | | For. | 1.77 | 19.33 | 69.69 | 24.01 | | w F-PMAI | Rev. | 1.81 | 20.01 | 82.91 | 30.05 | 2 | | For. | 1.82 | 19.91 | 80.63 | 29.32 |
|
|
Table 2 Champion PV parameters of TSCs without and with F-PMAI
|
| 1. | | | 2. | C. Battaglia, A. Cuevas, S. De Wolf, High-efficiency crystalline silicon solar cells: status and perspectives. Energy Environ. Sci. 9, 1552-1576 (2016). | | 3. | M. Jošt, L. Kegelmann, L. Korte, S. Albrecht, Monolithic perovskite tandem solar cells: a review of the present status and advanced characterization methods toward 30% efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 10, 1904102 (2020). | | 4. | R. Wang, T. Huang, J. Xue, J. Tong, K. Zhu et al., Prospects for metal halide perovskite-based tandem solar cells. Nat. Photonics 15, 411-425 (2021). | | 5. | Z. Fang, Q. Zeng, C. Zuo, L. Zhang, H. Xiao et al., Perovskite-based tandem solar cells. Sci. Bull. 66, 621-636 (2021). | | 6. | Y. Zeng, Z. Ding, Z. Liu, W. Liu, M. Liao et al., Efficiency-loss analysis of monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells by identifying the patterns of a dual two-diode model’s current-voltage curves. J. Semicond. 44, 082702 (2023). | | 7. | B. Chen, P. Wang, N. Ren, R. Li, Y. Zhao et al., Tin dioxide buffer layer-assisted efficiency and stability of wide-bandgap inverted perovskite solar cells. J. Semicond. 43, 052201 (2022). | | 8. | A. Al-Ashouri, E. Köhnen, B. Li, A. Magomedov, H. Hempel et al., Monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cell with >29% efficiency by enhanced hole extraction. Science 370, 1300-1309 (2020). | | 9. | J. Xu, C.C. Boyd, Z.J. Yu, A.F. Palmstrom, D.J. Witter et al., Triple-halide wide-band gap perovskites with suppressed phase segregation for efficient tandems. Science 367, 1097-1104 (2020). | | 10. | J. Liu, M. De Bastiani, E. Aydin, G.T. Harrison, Y. Gao et al., Efficient and stable perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells through contact displacement by MgF x. Science 377, 302-306 (2022). | | 11. | R. Santbergen, R. Mishima, T. Meguro, M. Hino, H. Uzu et al., Minimizing optical losses in monolithic perovskite/c-Si tandem solar cells with a flat top cell. Opt. Express 24, A1288-A1299 (2016). | | 12. | M. Jošt, E. Köhnen, A.B. Morales-Vilches, B. Lipovšek, K. Jäger et al., Textured interfaces in monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells: advanced light management for improved efficiency and energy yield. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 3511-3523 (2018). | | 13. | M. Jaysankar, M. Filipič, B. Zielinski, R. Schmager, W. Song et al., Perovskite-silicon tandem solar modules with optimised light harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 1489-1498 (2018). | | 14. | F. Gota, R. Schmager, A. Farag, Paetzold Energy yield modelling of textured perovskite/silicon tandem photovoltaics with thick perovskite top cells. Opt. Express 30, 14172-14188 (2022). | | 15. | Z. Song, C.L. McElvany, A.B. Phillips, I. Celik, P.W. Krantz et al., A technoeconomic analysis of perovskite solar module manufacturing with low-cost materials and techniques. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 1297-1305 (2017). | | 16. | F. Sahli, J. Werner, B.A. Kamino, M. Bräuninger, R. Monnard et al., Fully textured monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells with 25.2% power conversion efficiency. Nat. Mater. 17, 820-826 (2018). | | 17. | Y. Li, B. Shi, Q. Xu, L. Yan, N. Ren et al., Wide bandgap interface layer induced stabilized perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells with stability over ten thousand hours. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2102046 (2021). | | 18. | Q. Xu, B. Shi, Y. Li, L. Yan, W. Duan et al., Conductive passivator for efficient monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cell on commercially textured silicon. Adv. Energy Mater. 12, 2202404 (2022). | | 19. | L. Mao, T. Yang, H. Zhang, J. Shi, Y. Hu et al., Fully textured, production-line compatible monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells approaching 29% efficiency. Adv. Mater. 34, e2206193 (2022). | | 20. | J.-W. Lee, S.-H. Bae, Y.-T. Hsieh, N. De Marco, M. Wang et al., A bifunctional lewis base additive for microscopic homogeneity in perovskite solar cells. Chem 3, 290-302 (2017). | | 21. | T. Bu, J. Li, H. Li, C. Tian, J. Su et al., Lead halide-templated crystallization of methylamine-free perovskite for efficient photovoltaic modules. Science 372, 1327-1332 (2021). | | 22. | X. Luo, H. Luo, H. Li, R. Xia, X. Zheng et al., Efficient perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells on industrially compatible textured silicon. Adv. Mater. 35, e2207883 (2023). | | 23. | F. Zhang, B. Tu, S. Yang, K. Fan, Z. Liu et al., Buried-interface engineering of conformal 2D/3D perovskite heterojunction for efficient perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells on industrially textured silicon. Adv. Mater. 35, e2303139 (2023). | | 24. | X.Y. Chin, D. Turkay, J.A. Steele, S. Tabean, S. Eswara et al., Interface passivation for 31.25%-efficient perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells. Science 381, 59-63 (2023). | | 25. | L. Zhang, Y. Liu, X. Ye, Q. Han, C. Ge et al., Exploring anisotropy on oriented wafers of MAPbBr3 crystals grown by controlled antisolvent diffusion. Cryst. Growth Des. 18, 6652-6660 (2018). | | 26. | C. Ma, M. Grätzel, N.-G. Park, Facet engineering for stable, efficient perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 3120-3128 (2022). | | 27. | C. Ma, M.-C. Kang, S.-H. Lee, S.J. Kwon, H.-W. Cha et al., Photovoltaically top-performing perovskite crystal facets. Joule 6, 2626-2643 (2022). | | 28. | C. Ma, F.T. Eickemeyer, S.H. Lee, D.H. Kang, S.J. Kwon et al., Unveiling facet-dependent degradation and facet engineering for stable perovskite solar cells. Science 379, 173-178 (2023). | | 29. | Y. Wang, S. Ye, Z. Sun, J. Zhu, Y. Liu et al., Multifunctional regioisomeric passivation strategy for fabricating self-driving, high detectivity all-inorganic perovskite photodetectors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 59005-59015 (2023). | | 30. | N. Li, S. Tao, Y. Chen, X. Niu, C.K. Onwudinanti et al., Cation and anion immobilization through chemical bonding enhancement with fluorides for stable halide perovskite solar cells. Nat. Energy 4, 408-415 (2019). | | 31. | Y. Zhu, P. Lv, M. Hu, S.R. Raga, H. Yin et al., Synergetic passivation of metal-halide perovskite with fluorinated phenmethylammonium toward efficient solar cells and modules. Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 2203681 (2023). | | 32. | D. Gao, R. Li, X. Chen, C. Chen, C. Wang et al., Managing interfacial defects and carriers by synergistic modulation of functional groups and spatial conformation for high-performance perovskite photovoltaics based on vacuum flash method. Adv. Mater. 35, e2301028 (2023). | | 33. | Y. Ma, C. Zeng, P. Zeng, Y. Hu, F. Li et al., How do surface polar molecules contribute to high open-circuit voltage in perovskite solar cells? Adv. Sci. 10, e2205072 (2023). | | 34. | Q. Jiang, Y. Zhao, X. Zhang, X. Yang, Y. Chen et al., Surface passivation of perovskite film for efficient solar cells. Nat. Photonics 13, 460-466 (2019). | | 35. | M. Qin, P.F. Chan, X. Lu, A systematic review of metal halide perovskite crystallization and film formation mechanism unveiled by in situ GIWAXS. Adv. Mater. 33, e2105290 (2021). | | 36. | K. Zhang, B. Ding, C. Wang, P. Shi, X. Zhang et al., Highly efficient and stable FAPbI3 perovskite solar cells and modules based on exposure of the (011) facet. Nano-Micro Lett. 15, 138 (2023). | | 37. | X. Wen, S. Huang, S. Chen, X. Deng, F. Huang et al., Optical probe ion and carrier dynamics at the CH3NH3PbI3 interface with electron and hole transport materials. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 3, 1600467 (2016). | | 38. | L. Jing, X. Cheng, Y. Yuan, S. Du, J. Ding et al., Design growth of triangular pyramid MAPbBr3 single crystal and its photoelectric anisotropy between (100) and (111) facetss. J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 10826-10830 (2019). | | 39. | F. Wang, Y. Zhang, M. Yang, D. Han, L. Yang et al., Interface dipole induced field-effect passivation for achieving 21.7% efficiency and stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2008052 (2021). | | 40. | T. Wu, R. Zhao, J. Qiu, S. Wang, X. Zhang et al., Enhancing the hot carrier injection of perovskite solar cells by incorporating a molecular dipole interlayer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2204450 (2022). | | 41. | Y. Lin, Y. Bai, Y. Fang, Q. Wang, Y. Deng et al., Suppressed ion migration in low-dimensional perovskites. ACS Energy Lett. 2, 1571-1572 (2017). | | 42. | Y. Wang, M.I. Dar, L.K. Ono, T. Zhang, M. Kan et al., Thermodynamically stabilized β-CsPbI3-based perovskite solar cells with efficiencies >18%. Science 365, 591-595 (2019). | | 43. | Y. Yang, C. Liu, O.A. Syzgantseva, M.A. Syzgantseva, S. Ma et al., Defect suppression in oriented 2D perovskite solar cells with efficiency over 18% via rerouting crystallization pathway. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2002966 (2021). | | 44. | D. Kim, H.J. Jung, I.J. Park, B.W. Larson, S.P. Dunfield et al., Efficient, stable silicon tandem cells enabled by anion-engineered wide-bandgap perovskites. Science 368, 155-160 (2020). | | 45. | S. Xiong, Z. Hou, S. Zou, X. Lu, J. Yang et al., Direct observation on p- to n-type transformation of perovskite surface region during defect passivation driving high photovoltaic efficiency. Joule 5, 467-480 (2021). | | 46. | Y. Wang, L. Li, Z. Wu, R. Zhang, J. Hong et al., Self-driven prenucleation-induced perovskite crystallization enables efficient perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202302342 (2023). |
|
| [1] |
Juan Zhang, Xiaofei Ji, Xiaoting Wang, Liujiang Zhang, Leyu Bi, Zhenhuang Su, Xingyu Gao, Wenjun Zhang, Lei Shi, Guoqing Guan, Abuliti Abudula, Xiaogang Hao, Liyou Yang, Qiang Fu, Alex K.-Y. Jen, Linfeng Lu. Efficient and Stable Inverted Perovskite Solar Modules Enabled by Solid-Liquid Two-Step Film Formation[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2024, 16(1): 190-. |
| [2] |
Yirong Wang, Yaohui Cheng, Chunchun Yin, Jinming Zhang, Jingxuan You, Jizheng Wang, Jinfeng Wang, Jun Zhang. Manipulating Crystal Growth and Secondary Phase PbI2 to Enable Efficient and Stable Perovskite Solar Cells with Natural Additives[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2024, 16(1): 183-. |
|
|
|
|



