针对天然气掺氢燃烧不稳定性问题,国内外学者利用光学可视化测试技术开展了大量研究.贾亮等[9]通过试验发现高掺氢比会增强火焰的不稳定性.Figura等[10]的研究表明随着氢气浓度的增加,火焰自激振荡的模态和频率发生变化,火焰的振荡特性受到火焰形状和火焰位置的影响.Davis等[11]在相同的进气流速下,通过试验比较了纯甲烷火焰和富氢甲烷火焰的拓扑结构,结果表明,火焰长度越短,富氢火焰的波动越大.Giezendanner等[12]以及Ge等[13]也通过试验发现了火焰的燃烧不稳定与火焰结构变化的强相关性.为了研究掺氢燃烧不稳定的驱动机理,研究人员也开展了受迫振荡研究.Yilmaz等[14]通过简单旋流火焰的受迫振荡试验发现,随着氢气浓度的增加,火焰的热声耦合和压缩显著增加,这种效应会增强非激励频率下的火焰响应,但降低了激励频率下的耦合强度.
虽然针对天然气掺氢燃烧开展了大量研究,但是目前研究工作主要集中在单旋流燃烧上,针对具有实际工业结构的中心分级燃烧器的研究较少.在中心分级燃烧器中,值班级火焰与主燃级火焰存在强烈干涉,火焰间的相互作用非常复杂,在燃烧稳定性方面表现出与单旋流燃烧器完全不同的特性,因此掺氢比对中心分级燃烧的动态响应特性及火焰耦合的影响还需要进一步研究.本文通过试验研究中心分级天然气掺氢火焰的受迫振荡特性,在中心分级燃烧器入口上游施加轴向速度扰动,探究不同掺氢比例下的火焰结构和动态响应特性,从火焰干涉角度分析了分级掺氢火焰的受迫振荡机理.
1 试验装置及研究方法
1.1 试验装置与工况
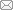
图1
图1
火焰受迫振荡试验平台示意图
Fig.1
Diagram of experimental platform of flame forced oscillation
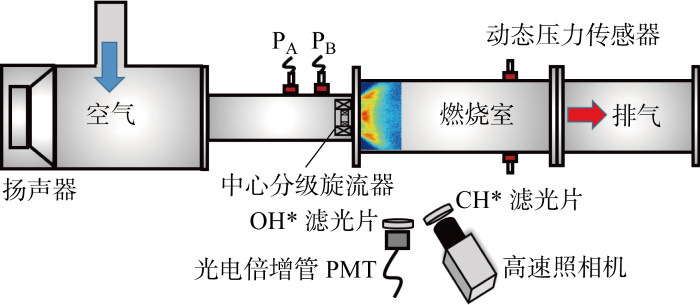
图2
燃烧器入口速度扰动由扬声器提供,扰动幅值采用双传声器法测量[15],将传声器PA与PB测量的压力波动转变为速度脉动,传声器型号为PCB 130F20,灵敏度为12 mV/Pa.燃烧室动态压力采用Kulite XTL-190M动态压力传感器测量.由于OH*的光辐射信号和热释放强度有线性关系[16],全局火焰热释放率通过HAMAMATSU H10723-210光电倍增管(PMT)和波长范围为(307±10) nm的OH*带通滤光片测得.上述参数采样频率均为 5 000 Hz,并基于NI-DAQ 6284同步采集卡和LabView软件实现同步采集.瞬态火焰结构通过VEO 710L互补金属氧化物半导体(CMOS)高速照相机和波长范围为(432±10) nm的CH*带通滤光片拍摄,拍摄频率为 1 000 Hz,拍摄的范围为 70 mm×80 mm,如图2所示.
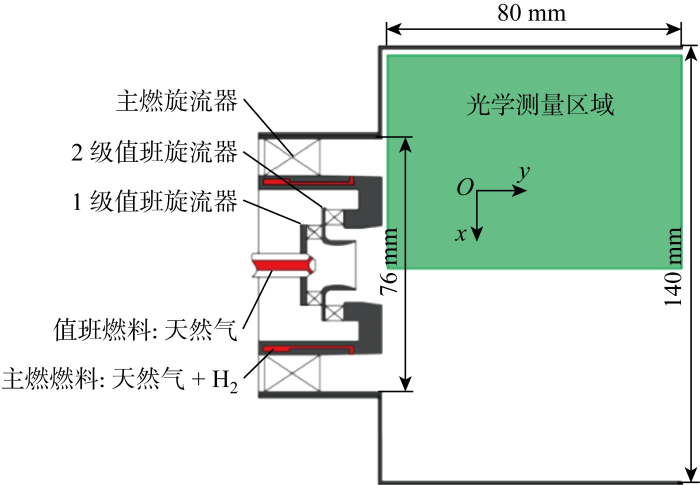
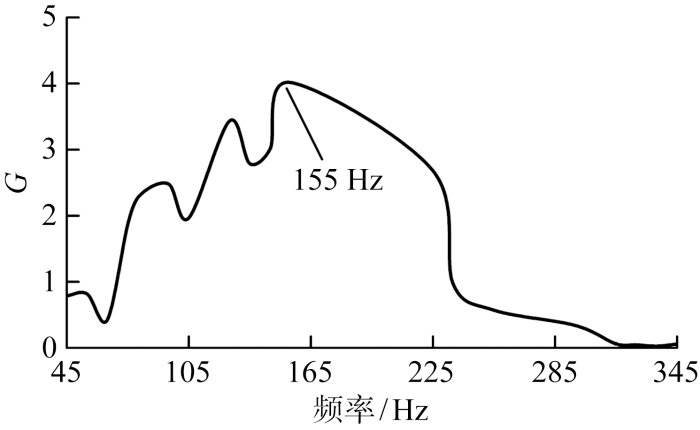
试验中燃烧器入口平均空气流速为10.1 m/s,燃烧室入口雷诺数为 22 500.为避免燃烧室的自激振荡对受迫振荡的影响,控制值班级和主燃级的当量比为1.3和0.6不变,在此当量比下燃烧稳定,无明显自激振荡产生.在此工况下,测量45~345 Hz 内火焰传递函数的幅值G(f)=
图3
图3
不同频率激励下的燃烧室火焰传递函数幅值变化
Fig.3
Amplitude change of combustor FTF at different frequency excitations
为研究掺氢比的影响,改变主燃级燃料的掺氢体积比Rv=0%, 10%, 20%, 30%,试验工况如表1所示.
表1 变Rv试验工况
Tab.1
| 工况编号 | Rv/% | 空气质量 流量/(g·s-1) | 主燃级氢气 质量流量/(g·s-1) | 主燃级天然气 质量流量/(g·s-1) | 值班级天然气 质量流量/(g·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 19.4 | 0.000 0 | 0.550 | 0.142 |
| 2 | 10 | 19.4 | 0.007 2 | 0.519 | 0.142 |
| 3 | 20 | 19.4 | 0.015 2 | 0.486 | 0.142 |
| 4 | 30 | 19.4 | 0.024 0 | 0.449 | 0.142 |
1.2 数据处理方法
利用本征正交分解(POD)方法对试验中高速照相机采集到的CH*荧光图像数据进行分解,提取火焰脉动的主要特征,考察火焰结构的变化.POD法是一种用于提取高频瞬态物理场中主要特征结构的方法,如湍流流场和旋流火焰中的大尺度相干结构[17].使用Classical POD的方法处理瞬态火焰结构.POD方法将时间序列的CH*荧光强度场I(x,t) 分解为特征函数ψi(x)和时间系数ai(t):
POD分解需要建立相关矩阵:
式中:M为时间维度上的采样个数.
对相关矩阵C进行特征值和特征向量分解,其特征向量为时间系数ai=[
式中:Im为瞬时的CH*荧光强度场;
2 结果与分析
2.1 火焰结构变化
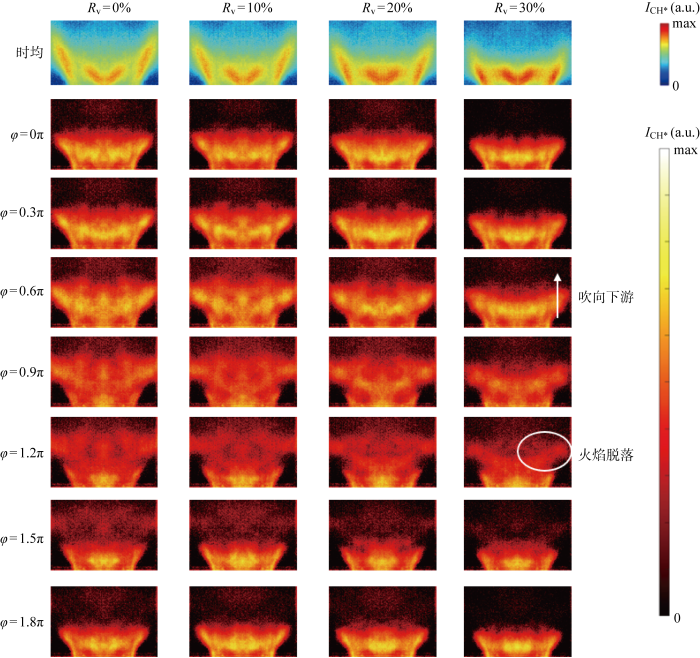
在155 Hz的激励频率下,天然气掺氢火焰呈现强周期性的脉动,为了研究掺氢比对于火焰脉动规律的影响,提取了在上述入口扰动频率下,不同掺氢比火焰的CH*荧光强度
图4
图4
不同掺氢比火焰的CH*荧光强度分布在一个振荡周期内的变化情况及时均火焰结构
Fig.4
Time-averaged flame structure and change of CH* fluorescence intensity distribution of flame with different hydrogen doping ratios in an oscillation period
图5
图6
图7
图8
图8
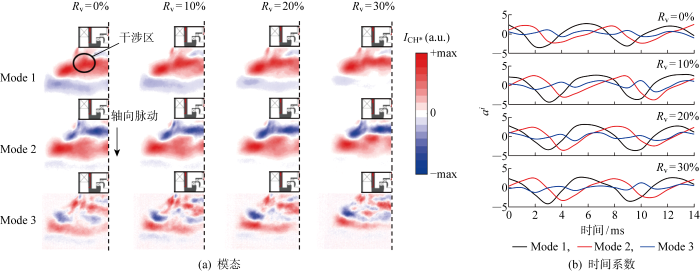
不同掺氢比下的火焰POD模态及对应时间系数
Fig.8
Flame POD modes and time coefficient at different hydrogen doping ratios
图9
图9
火焰POD一阶模态能量占比随Rv的变化
Fig.9
First order mode energy ratio of flame POD versus Rv
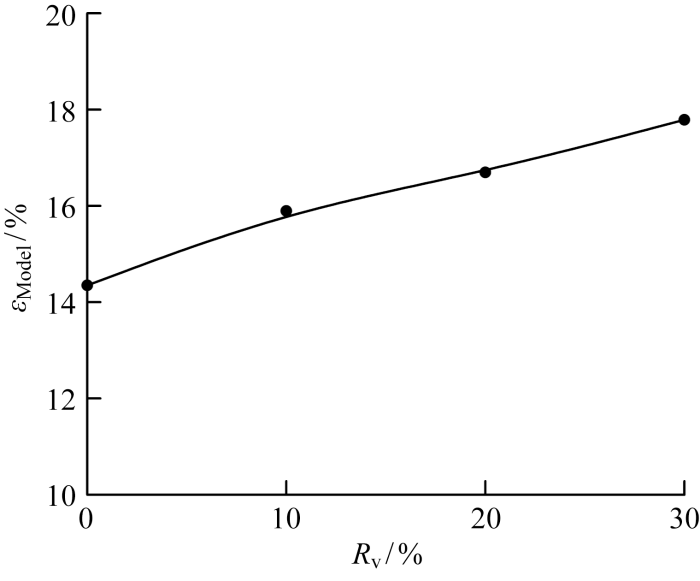
对其模态进行分析,一阶模态的波峰处于主燃级火焰与值班级火焰的干涉区,因此一阶模态由值班级和主燃级火焰间的干涉控制;二阶模态的波峰波谷在两级火焰的非干涉区,表征的是入口空气扰动直接引发的火焰轴向脉动,并且可以发现Rv的变化对于模态本身的波峰波谷分布影响不大.另外,时间系数变化曲线显示,不同掺氢比下的一阶模态和二阶模态的相位差均为0.6π,掺氢比对于火焰脉动相位变化的影响很小.
分析Rv对于能量最高的一阶模态能量占比εModel的影响,可以发现,随着Rv的增大,εModel逐渐增大.这是由于燃料中掺氢使得主燃火焰向燃烧室上游收缩,主燃火焰与值班火焰间的干涉加强,最终导致由火焰干涉主导的脉动模态即εModel增强.
2.2 压力与热释放响应特性
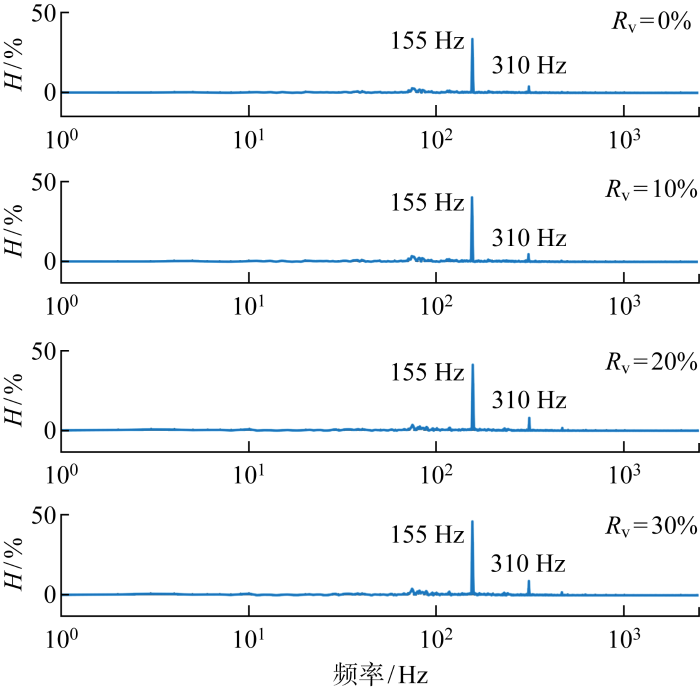
为研究燃烧室内压力对上游速度扰动的响应特性,对不同掺氢比的火焰采集了燃烧室内的压力脉动p,并进行快速傅里叶变换(FFT),结果如图10所示,当Rv>20%时,燃烧室内出现310 Hz的倍频压力脉动,并且随着Rv的增大,倍频压力脉动的幅值逐渐增大.
图10
图10
155 Hz激励下燃烧室内压力脉动FFT结果
Fig.10
FFT result of pressure pulsation in combustor in 155 Hz excitation
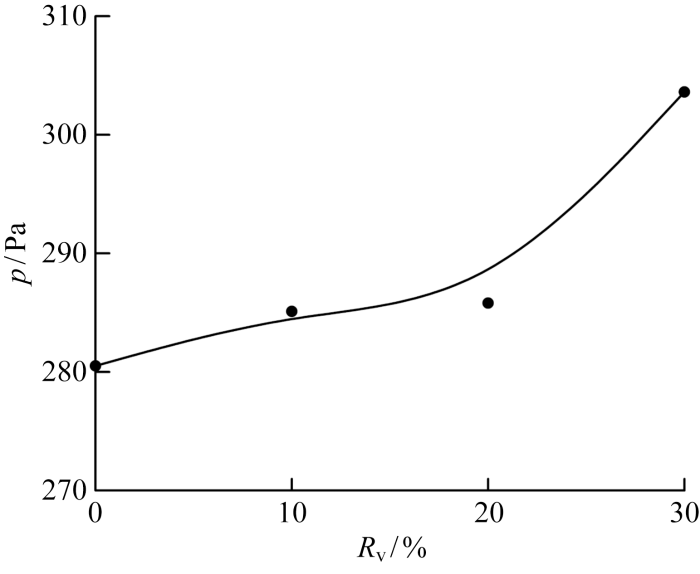
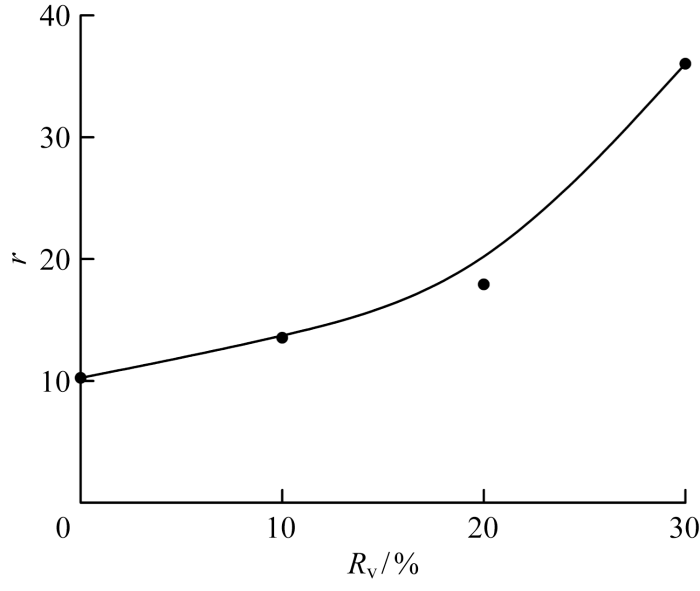
为了比较不同掺氢比下的燃烧室内压力响应大小,提取了激励频率155 Hz下的燃烧室内压力脉动主频幅值,如图11所示.结果显示,随着Rv的增大,燃烧室内压力脉动主频幅值呈现增大趋势;Rv=30%的工况相比不掺氢的工况,压力脉动主频幅值增大了9%.
图11
图11
155 Hz激励下燃烧室内压力脉动主频幅值随Rv的变化
Fig.11
Main frequency amplitude of pressure pulsation in combustor changing with Rv in 155 Hz excitation
同时也与压力信号同步采集了不同掺氢比下的燃烧室内的全局OH*光辐射信号脉动来表征全局热释放脉动H,并进行快速傅里叶变换,结果如图12所示.从图中可以发现,所有工况除受迫频率下的响应外,均存在310 Hz的倍频热释放响应,并且随着Rv的增大其幅值逐渐增大.
图12
图12
155 Hz激励下燃烧室内热释放脉动FFT结果
Fig.12
FFT result of heat release pulsation in combustor in 155 Hz excitation
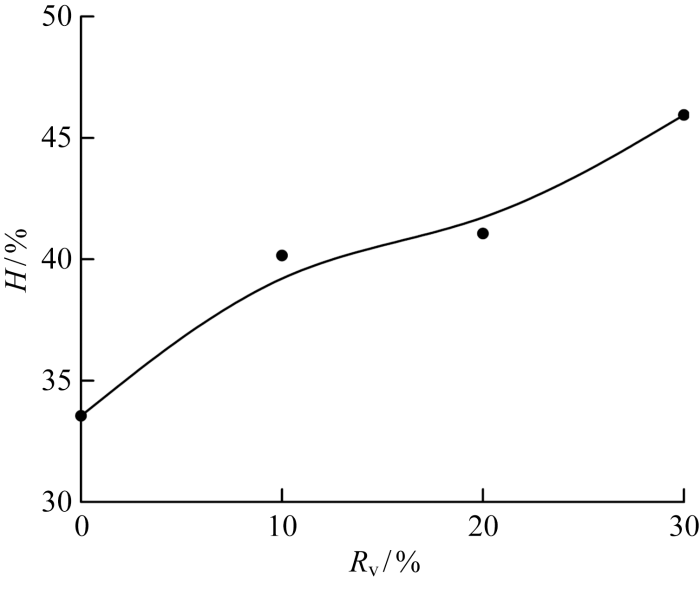
为了比较不同掺氢比下的燃烧室内热释放响应大小,提取了激励频率155 Hz下的燃烧室内热释放脉动主频幅值,如图13所示.结果显示,Rv=30%的工况相比不掺氢的工况,热释放脉动主频幅值增大了37%;且随着Rv的增大,燃烧室内热释放脉动主频幅值变化趋势与压力脉动以及火焰POD一阶模态的能量占比相同,均呈现增大趋势,这也表明燃烧室内的压力受迫响应与火焰热释放及火焰形态响应间存在强相关性.
图13
图13
155 Hz激励下燃烧室内热释放脉动主频幅值随Rv的变化
Fig.13
Main frequency amplitude of heat release pulsation in combustor changing with Rv in 155 Hz excitation
式中:p'为燃烧过程的压力脉动;T为压力脉动周期.瑞利因子的大小表示燃烧过程的压力波动和热释放波动相互耦合叠加的强度,是燃烧过程发生热声振荡的主要驱动原因.结果显示,随着Rv的增大,燃烧室内的全局瑞利因子逐渐增大,说明此时压力与热释放的耦合不断加强,最终导致了受迫振荡幅值的增大.
图14
图14
155 Hz激励下燃烧室全局瑞利因子随Rv的变化
Fig.14
Global Rayleigh index in combustor changing with Rv in 155 Hz excitation
3 结论
本文通过试验研究中心分级天然气掺氢火焰的受迫响应特性,在中心分级燃烧器入口上游施加不同频率的速度扰动,探究不同掺氢比对中心分级天然气掺氢燃烧的火焰结构变化、压力脉动特性及热释放率脉动特性的影响.结论如下:
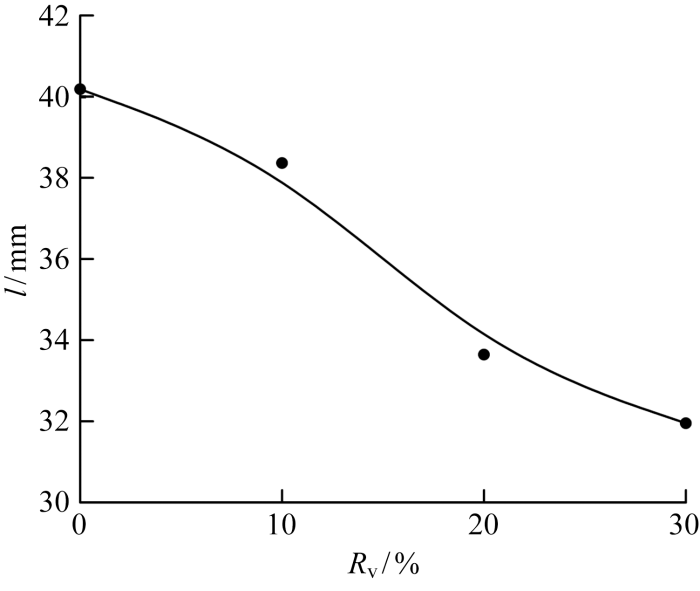
(1) 随着Rv的增大,火焰高度减小,火焰前沿向上游移动,值班级火焰与主燃级火焰质心的距离缩短,导致两级火焰干涉加强.
(2) 随着Rv从0%增大到30%,燃烧室内热释放响应幅值增大了37%,压力响应幅值增大了9%.
(3) 火焰的脉动主要由值班级和主燃级火焰间的干涉主导的火焰脉动和空气扰动直接引发的火焰轴向脉动两者组成,并且Rv的增加,会增强值班级和主燃级火焰间的干涉引发的火焰脉动,加强了压力与热释放的耦合,从而增强了燃烧室内的压力与热释放响应.
参考文献
Experimental analysis of the effects of hydrogen addition on methane combustion
[J].DOI:10.1002/er.v36.5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Measurements of laminar flame speeds of alternative gaseous guel mixtures
[J].
DOI:10.1115/1.4029738
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Global warming and the ever increasing emission levels of combustion engines have forced the engine manufacturers to look for alternative fuels for high engine performance and low emissions. Gaseous fuel mixtures such as biogas, syngas, and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) are new alternative fuels that have great potential to be used with combustion engines. In the present work, laminar flame speeds (SL) of alternative fuel mixtures, mainly LPG (60% butane, 20% isobutane, and 20% propane) and methane have been studies using the tube method at ambient conditions. In addition, the effect of adding other fuels and gases such as hydrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen on SL has also been investigated. The results show that any change in the fuel mixture composition directly affects SL. Measurements of SL of CH4/LPG–air mixtures have found to be about 56 cm/s at ø = 1.1 with 60% LPG in the mixture, which is higher than SL of both pure fuels at the same ø. Moreover, the addition of H2 and O2 to the fuel mixtures increases SL notably, while the addition of CO2/N2 mixture to the fuel mixture, to simulate the EGR effect, decreases SL of CH4/LPG–air mixtures.
Influence of hydrogen addition on flow structure in confined swirling methane flame
[J].DOI:10.2514/1.4235 URL [本文引用: 1]
Effects of H2/CO/CH4 syngas composition variation on the NOx and CO emission characteristics in a partially-premixed gas turbine combustor
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11431-016-0099-x URL [本文引用: 1]
Swirl injector for premixed combustion of hydrogen-methane mixtures
[J].
DOI:10.1115/1.4039267
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In the field of combustion, a special attention was given lately especially to the search for new, greener and more efficient fuels. Among them, hydrogen is intensely studied worldwide as a possible alternative fuel since new ways for producing and transporting it developed lately. Different studies are trying to confirm the possibility of the hydrogen transport using the existing natural gas distribution network, by mixing the two gases. Because the properties of the new mixture influence the combustion parameters, using the existing equipment would face new problems, like the risk of flashback, the effects of higher temperatures, and the modification of the flame front. Hence, new solutions are needed. In this context, this paper presents a newly developed and patented type of injector, designated for the combustion of the premixed hydrogen–methane fuel in various proportions. Based on the characteristics and dimensions of an existing combustion chamber of a gas turbine, different types of injectors were numerically simulated and compared. After the analysis of the results, the preliminary conclusions lead to a first swirl injector made from titanium alloy. The new type of swirled injector was tested on a cheap, simplified low pressure rig, designed to have similar dimensions to the initial combustion chamber, for preliminary validation of the main characteristics and of the stability of the new injector. The experiments indicated good lean blowout characteristics, and the promising results are encouraging for more future tests on a complex experimental setup, for optimizing the final solution.
天然气-氢气-空气混合气火焰传播特性研究
[J].
Flame propagation characteristics of natural gas-hydrogen-air mixtures
[J].
甲烷及掺氢燃气吹熄极限的大涡模拟研究
[J].
DOI:10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2020.329
[本文引用: 1]

利用大涡模拟法计算研究甲烷和掺氢燃气在悉尼非均匀入流射流燃烧器上的吹熄极限.利用GRI 3.0详细反应机理和28步、19步简化反应机理对比计算不同掺氢燃气状态下的层流预混火焰,证明了19步简化反应机理具有良好性能.利用动态增厚火焰燃烧模型结合19步反应机理,计算研究以掺氢燃气(体积比V(H<sub>2</sub>):V(CH<sub>4</sub>):V(CO):V(CO<sub>2</sub>)=0.2:0.2:0.27:0.33)为燃料的悉尼部分预混中心射流火焰.计算得到在FA和FJ布局下,掺氢燃气的火焰吹熄极限速度分别为90 m/s和109 m/s,甲烷的火焰吹熄极限速度分别为74 m/s和128 m/s,分析发现吹熄极限的差异与不同布局下燃气与空气混合不均匀程度相关.研究表明,优化燃气与空气的进气布局和掺混过程可以提升燃烧稳定性.
Large eddy simulation on blow-off limit of methane and hydrogen-mixed gas
[J].
当量比对掺氢天然气预混燃烧特性的影响
[J].
Influence of the equivalent ratio on the premixed combustion characteristics of natural gas mixed and diluted with hydrogen
[J].
The effects of fuel composition on flame structure and combustion dynamics in a lean premixed combustor
[C]//
Effects of hydrogen on the thermo-acoustics coupling mechanisms of low-swirl injector flames in a model gas turbine combustor
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.proci.2012.05.050 URL [本文引用: 1]
Periodic combustion instabilities in a swirl burner studied by phase-locked planar laser-induced fluorescence
[J].DOI:10.1080/00102200302390 URL [本文引用: 1]
Experiment study on the combustion performance of hydrogen-enriched natural gas in a DLE burner
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.03.257 URL [本文引用: 1]
Experimental investigation of thermoacoustic coupling using blended hydrogen-methane fuels in a low swirl burner
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.10.018 URL [本文引用: 1]
不同当量比下氢气体积分数对甲烷-氢混合气预混火焰燃烧不稳定性的影响
[J].
Effect of hydrogen volume fraction on combustion instability of hydrogen/methane premixed flame under different equivalence rates
[J].
Local measurements of the time-dependent heat release rate and equivalence ratio using chemiluminescent emission from a flame
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.combustflame.2004.08.003 URL [本文引用: 1]
Three-dimensional coherent structures in a swirling jet undergoing vortex breakdown: Stability analysis and empirical mode construction
[J].
DOI:10.1017/jfm.2011.141
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The spatio-temporal evolution of a turbulent swirling jet undergoing vortex breakdown has been investigated. Experiments suggest the existence of a self-excited global mode having a single dominant frequency. This oscillatory mode is shown to be absolutely unstable and leads to a rotating counter-winding helical structure that is located at the periphery of the recirculation zone. The resulting time-periodic 3D velocity field is predicted theoretically as being the most unstable mode determined by parabolized stability analysis employing the mean flow data from experiments. The 3D oscillatory flow is constructed from uncorrelated 2D snapshots of particle image velocimetry data, using proper orthogonal decomposition, a phase-averaging technique and an azimuthal symmetry associated with helical structures. Stability-derived modes and empirically derived modes correspond remarkably well, yielding prototypical coherent structures that dominate the investigated flow region. The proposed method of constructing 3D time-periodic velocity fields from uncorrelated 2D data is applicable to a large class of turbulent shear flows.
Combustion dynamics of a low-swirl combustor
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.combustflame.2007.07.017 URL [本文引用: 1]