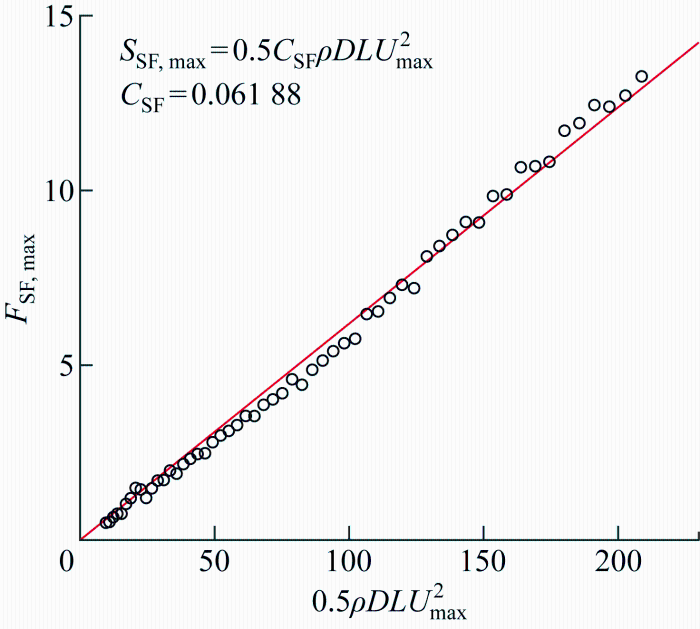在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性.
当前针对双向剪切流场下的柔性立管阻力特性研究仍为空白,严重影响了南海油田的相关立管设计工作.本文设计了双向剪切流实验室模拟平台,开展了双向剪切流作用涡激振动状态时柔性立管阻力特性,基于光纤光栅应变传感器测得柔性立管模型顺流向应变时历,采用张力作用下梁弯曲理论计算柔性立管模型的平均阻力,并根据莫里森公式计算实验模型在不同流速工况下的阻力系数,研究了不同雷诺数下阻力系数的分布特性以及涡激振动状态对阻力系数的影响.实验中首次发现了双向剪切流流场诱发的剪力极值现象,对该现象进行了分析,总结提出了双向剪切流场下特有的立管模型剪力系数.这将为南海立管设计提供重要的参考依据.
1 实验装置、实验模型和实验方案
中海油研究总院于南海北部流花海域开展了全剖面海流、温度、盐度数据检测,流速场测量结果[14 ] 如图1 所示.图中: H 代表深度,箭头代表流速矢量;U max 为双向剪切流边缘最大流速.图1(a) 显示南海海域存在一种由内孤立波诱发的呈现双向剪切分布的海流流场.为了研究该流场下的柔性立管平均阻力特性,将该流场简化为流速大小对称、方向相反的双向剪切流,如图1 (b) 所示.
图1
图1
双向剪切流场示意图
Fig.1
Schematic diagram of bidirectionally sheared flow
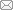
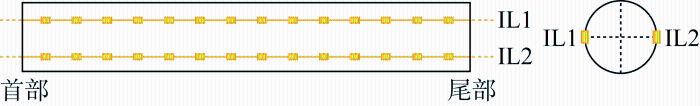
实验于上海交通大学海洋工程国家重点实验室深水实验池中进行.实验装置示意图如图2 所示,实验立管模型安装在从动轮两端,端部安装张紧器以提供初始张力,实验时通过旋转从动轮以形成双向剪切流场.实验坐标系建立在立管模型的端点处,X 轴代表立管模型的顺流向,Y 轴代表立管模型的横流向[15 ] .
图2
图2
实验装置示意图
Fig.2
Schematic diagram of the experimental setup
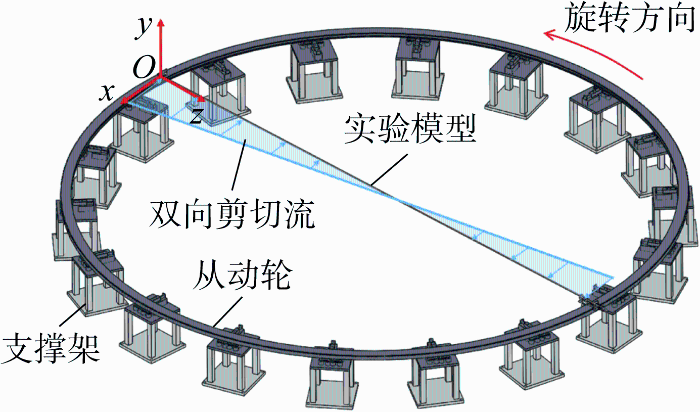
实验立管模型的主要物理参数如表1 所示.实验立管模型由铜质电缆、橡胶套以及三丙聚丙烯管(PPR管)制作而成,截面示意图如图3 所示.
图3
图3
实验立管模型截面示意图
Fig.3
Cross section of the model of experimental riser
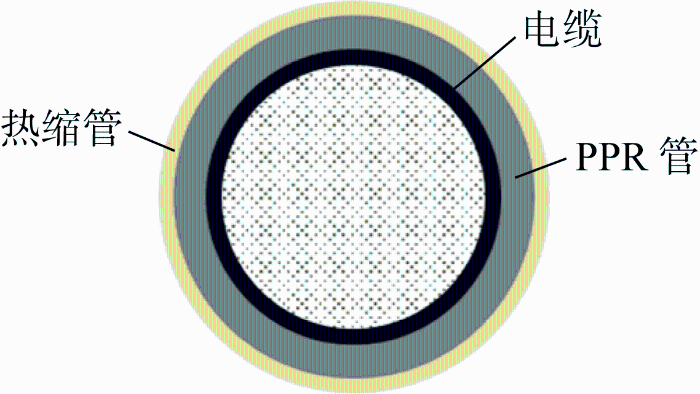
为了测量立管模型的顺流向涡激振动应变响应,在实验模型的两个方向布置4组光纤应变片,于顺流向分别布置14个应变测点,如图4 所示.实验立管应变数据采样频率为250 Hz.
图4
图4
光纤测点分布示意图
Fig.4
Distribution of gauge points along the pipe
v r =U m a x f 1 D
式中:f 1 为实验测得立管一阶固有频率.实验流速工况以边缘最大流速定义,实验流速工况由0.30~1.39 m/s共58个工况,对应的约化速度范围为6.59~30.79.
2 涡激振动数据处理方法
2.1 应变信号预处理
涡激振动状态下柔性立管顺流向应变信号通常可以分解为
(1) ε I L 1 ( z , t ) = ε C F - T ( z , t ) + ε v i v - I L ( z , t ) + ε m b ( z ) ε I L 2 ( z , t ) = ε C F - T ( z , t ) - ε v i v - I L ( z , t ) - ε m b ( z )
式中:ε CF-T (z , t )是张力导致的拉伸应变;ε mb (z )是顺流向的初始弯曲应变;ε viv-IL (z , t )为顺流向的涡激振动应变.涡激振动以及初始弯曲应变有如下关系:
(2) ε - v i v ( z , t ) = 0 ε - m b ( z ) = ε m b ( z )
2.2 模态分析法
以顺流向为例,对模态分析原理进行说明.模态分析法基于线性模态叠加,可以将模型表面测得的应变信号结合结构的模态振型计算得到测点的位移.一般地,模型表面的位移可以表示为
(3) $w(t, z)=\sum_{i=1}^{n} p_{i}(t) \varphi_{i}(z), \quad z \in[0, L]$
式中:pi (t )表示第i 阶模态的位移权重;φi (z )表示模型的第i 阶位移振型.
根据位移与曲率的关系,可以得到曲率κ (z ,t )的表达式为
(4) $\begin{array}{c}\kappa(z, t)=\frac{\partial^{2} w(z, t)}{\partial z^{2}}=\sum_{i=1}^{n} p_{i}(t) \varphi_{i}^{\prime \prime}(z), \\z \in[0, L]\end{array}$
本实验中立管模型两端边界条件为简支端,其第i 阶位移振型可以用正弦三角函数表示为
(5) $\varphi_{i}(z)=\sin \frac{i \pi z}{L}, \quad i=1,2, \cdots$
(6) $\begin{array}{c}\varepsilon(z, t)=-R \sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(\frac{i \pi}{L}\right)^{2} p_{i}(t) \varphi_{i}(z), \\z \in[0, L]\end{array}$
通过上述方程就能建立起应变ε (z ,t )与位移w (z ,t )的关系[16 -17 ] .
2.3 平均阻力逆向识别方法
根据直梁横向弯曲振动理论,带张力的梁弯曲的运动控制方程为
(7) $\begin{array}{l}E I \frac{\partial^{4} w(z, t)}{\partial z^{4}}-T \frac{\partial^{2} w(z, t)}{\partial z^{2}}+ \\c \frac{\partial w(z, t)}{\partial t}+\bar{m} \frac{\partial^{2} w(z, t)}{\partial t^{2}}=f(z, t)\end{array}$
式中:w (z , t )为模型中和轴上的位移;T 为顶端瞬时张力;c 为阻尼系数;f (z , t )为模型所受到的水动力分布载荷.
基于模态分析法,可以获得位移模态权重pi (t ),利用模态函数φi (x )可以得到位移对空间变量z 的各阶导数:
(8) ∂ 4 w ( z , t ) ∂ z 4 = ∑ i = 1 n p i ( t ) φ i ( 4 ) ( z ) ∂ 2 w ( z , t ) ∂ z 2 = ∑ i = 1 n p i ( t ) φ ″ i ( z )
进一步应用中心差分法,可获得模型各节点处的速度和加速度:
(9) ∂ w ( z , t ) ∂ t = ∑ i = 1 n p · i ( t ) φ i ( z ) ∂ 2 w ( z , t ) ∂ t 2 = ∑ i = 1 n p ¨ i ( t ) φ i ( z )
代入式(7)即可得到沿立管模型轴线方向上的水动力载荷分布.实验立管模型在顺流向所受平均拖曳力[18 ] 为
(10) $f_{\mathrm{md}}(z)=E I \frac{\partial^{4} \bar{w}(z)}{\partial z^{4}}-T \frac{\partial^{2} \bar{w}(z)}{\partial z^{2}}$
对于本实验,水动力外径为D 的柔性立管模型,其在背景流作用下沿管长所受拖曳力可表示为
(11) $f_{\mathrm{md}}(z)=\frac{1}{2} \rho D C_{D, \mathrm{~m}}(z) U|U|$
式中:CD ,m (z )为节点z 处的平均阻力系数;ρ 为流体密度;U 为节点背景流速.节点处的平均阻力系数可以表示为
(12) $C_{D, \mathrm{~m}}(z)=\frac{2 f_{\mathrm{md}}(z)}{\rho D U|U|}$
3 结果分析
3.1 顺流向初始位移
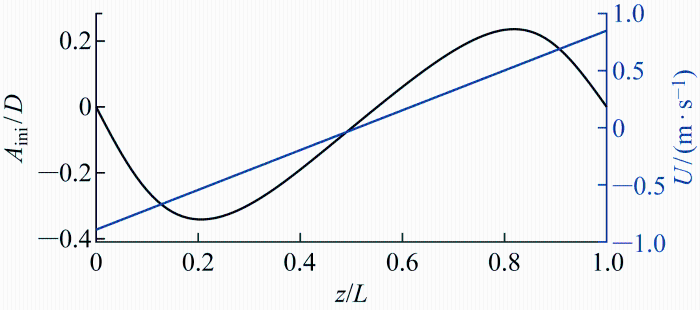
图5 ~7 为不同边缘流速下的顺流向平均无量纲拖曳位移以及流速沿管长分布情况.图中黑色线代表平均无量纲拖曳位移,蓝色代表流速沿管长分布情况;A ini /D 表示顺流向由平均阻力导致的无量纲初始位移;z/L 表示沿管长无量纲坐标.可以看出,不同于均匀流和剪切流等单向分布流场,双向剪切流下柔性立管拖曳位移呈现出反对称分布的特征,这与流速分布特征一致.初始位移在两端铰接点与接近中点处为0,在约1/4和3/4管长位置到达拖曳位移极值.
图5
图5
0.52 m/s流速工况下初始位移和背景流速沿管长分布情况
Fig.5
Distribution of initial displacement and flow velocity at U max = 0.52 m/s
图6
图6
0.90 m/s流速工况下初始位移和背景流速沿管长分布情况
Fig.6
Distribution of initial displacement and flow velocity at U max = 0.90 m/s
图7
图7
1.09 m/s流速工况下初始位移和背景流速沿管长分布情况
Fig.7
Distribution of initial displacement and flow velocity at U max = 1.09 m/s
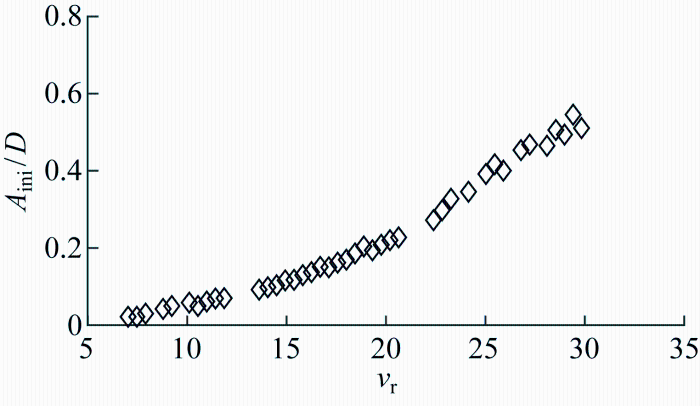
图8 展示了不同流速工况下沿管长最大拖曳无量纲位移.可以看出最大拖曳无量纲位移随着约化速度增加而增加,实验工况下最大拖曳位移达到了0.55D .
图8
图8
最大初始位移随约化速度变化情况
Fig.8
Maximum initial displacement versus reduced velocity
3.2 平均阻力系数特性
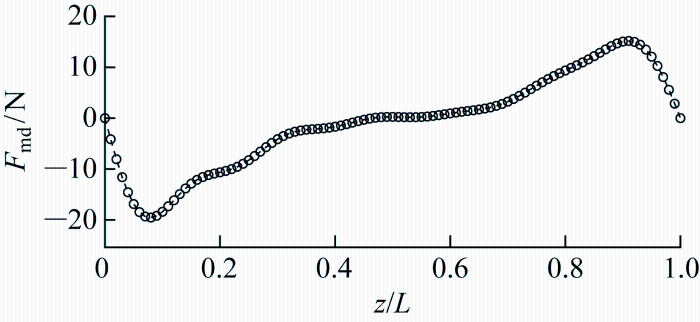
图9 和图10 展示了0.52 m/s流速工况下平均阻力以及平均阻力系数沿管长分布情况.图中:F md 表示平均阻力;C D, m z/L =0.4~0.6部分.可以看出,双向剪切流下平均阻力同样也与流场速度一样呈现反对称分布,相较于初始位移平均阻力极值出现的位置更偏向端部.平均阻力系数则是接近于对称分布,在两端阻力系数为0.
图9
图9
0.52 m/s流速工况下平均阻力沿管长分布情况
Fig.9
Distribution of mean drag at U max =0.52 m/s
图10
图10
0.52 m/s流速工况下平均阻力系数沿管长分布情况
Fig.10
Distribution of mean drag coefficient at U max = 0.52 m/s
图11 和图12 展示了1.09 m/s流速工况下平均阻力以及平均阻力系数沿管长分布情况.平均阻力沿着管长同样呈现反对称分布,阻力极值出现的位置同样没有发生偏移,但背景流速的提高使得平均阻力极值增加.但相较于随着流速增加而增加的平均阻力,平均阻力系数基本维持在1~2的范围内.
图11
图11
1.09 m/s流速工况下平均阻力沿管长分布情况
Fig.11
Distribution of mean drag at U max =1.09 m/s
图12
图12
1.09 m/s流速工况下平均阻力系数沿管长分布情况
Fig.12
Distribution of mean drag coefficient at U max = 1.09 m/s
图13 展示了平均阻力系数随着雷诺数变化的趋势.图中:C D, m , a z/L <0.6).实验雷诺数定义为
(13) $R e=\frac{U_{\max }}{\nu D}$
式中:ν 为运动黏度系数,取1.00×10-6 m2 /s.可以看出,随着雷诺数的上升,平均阻力系数均值基本维持不变,值为1.47.确证了在双向剪切流场下的涡激振动状态柔性立管同样发生了阻力放大现象.在先前的阶梯流诱导涡激振动阻力特性研究中,涡激振动平均阻力系数能够放大到1.6~2.7范围[19 ] ;剪切流诱导涡激振动平均阻力系数范围为1.3~1.9[20 ] .可以发现双向剪切流的阻力放大程度与剪切流相当,这是由剪切流和双向剪切流接近的流速分布导致的.
图13
图13
平均阻力系数随雷诺数变化情况
Fig.13
Mean drag coefficient versus Reynolds number
3.3 剪力分布特性
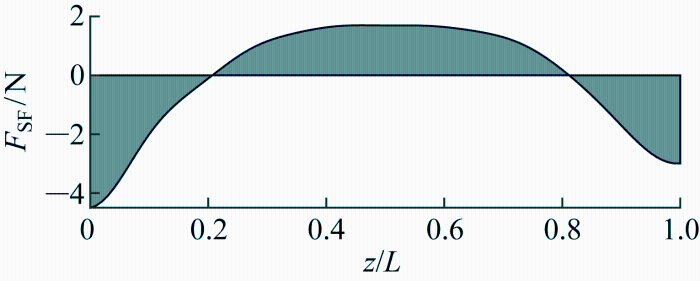
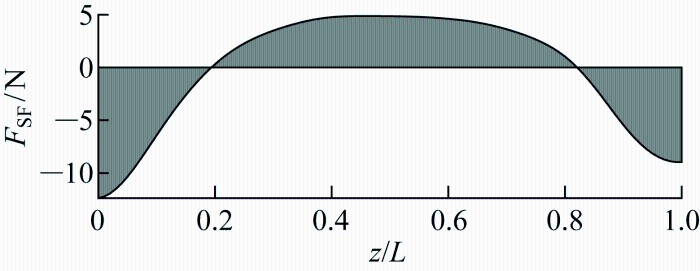
如上节内容所述,双向剪切流将诱导柔性立管呈现反对称的分布的平均阻力,这种反对称平均阻力将会产生一种特殊的剪力分布.图14 ~16 展示了不同流速工况下剪力沿管长的分布情况.图中:F SF 表示平均阻力导致的剪力分布.可以看出剪力除了在两端达到极值外在立管中部同样会产生一个剪力极值.在有关内波作用的文献中,通常形容内波为“犹如剪刀一般,破坏力极大”[21 -22 ] ,该中部剪力极值的存在即反映了内波流的剪切效应.
图14
图14
0.52 m/s流速工况下剪力沿管长分布情况
Fig.14
Distribution of shear force at U max =0.52 m/s
图15
图15
0.90 m/s流速工况下剪力沿管长分布情况
Fig.15
Distribution of shear force at U max =0.90 m/s
图16
图16
1.09 m/s流速工况下剪力沿管长分布情况
Fig.16
Distribution of shear force at U max =1.09 m/s
为了定量分析该剪力极值,本文引入剪力系数C SF 衡量双向剪切流诱导中部剪力极值的幅值,剪力系数与中部剪力极值的关系为
(14) $F_{\mathrm{SF}, \max }=0.5 C_{\mathrm{SF}} \rho D L U_{\max }^{2}$
图17 展示了剪力系数的拟合结果.采用最小二乘法进行系数拟合,得到剪力系数值为0.061 88.最终获得双向剪切流下中部剪力极值经验公式为
(15) $F_{\mathrm{SF}, \max }=0.5 C_{\mathrm{SF}} \rho D L U_{\max }^{2}, \quad C_{\mathrm{SF}}=0.06188$
该剪力系数将为南海立管结构强度设计提供外载荷参数输入.
图17
图17
剪力系数拟合结果
Fig.17
Fitting result of shear force coefficient
4 结论
针对南海独有的双向剪切流场,本文开展了双向剪切流下柔性立管模型平均阻力特性实验研究,对双向剪切流下立管模型的初始位移、平均阻力、平均阻力系数以及剪力分布特性进行了研究,主要结论有:
(1) 不同于以往的均匀流以及剪切流等流场,双向剪切流下柔性立管会产生反对称的初始位移以及平均阻力分布.平均阻力极值点相较于初始位移极值点更偏向立管端部.
(2) 确证了双向剪切流下涡激振动状态柔性立管仍会产生阻力放大效应,实验结果表明平均阻力系数将会放大至1.47.这与剪切流下涡激振动柔性立管阻力放大效应相当.
(3) 首次发现了双向剪切流致使的柔性立管中部剪力极值现象,引入了剪力系数C SF 并提出了中部剪力极值的经验公式F SF,max =0.5C SF ρDL U m a x 2 C SF =0.061 88,该公式将为南海立管设计提供强度校核载荷输入.
参考文献
View Option
[1]
WILLIAMSON C H K GOVARDHAN R Vortex-induced vibrations
[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics 2004 , 36 : 413 -455 .
[本文引用: 1]
[2]
SARPKAYA T A critical review of the intrinsic nature of vortex-induced vibrations
[J]. Journal of Fuids and Structures 2004 , 19 (4 ): 389 -447 .
[本文引用: 1]
[3]
顾继俊 , 马天麒 , 陈磊磊 , 等 . 内输高温高压流体海底悬跨管道的非线性涡激振动响应分析
[J]. 石油科学通报 2022 , 7 (1 ): 116 -126 .
[本文引用: 1]
GU Jijun MA Tianqi CHEN Leilei et al Nonlinear dynamic response of suspended span pipe conveying high temperature and high pressure flow
[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin 2022 , 7 (1 ): 116 -126 .
[本文引用: 1]
[4]
YIN D PASSANO E JIANG F et al State-of-the-art review of vortex-induced motions of floating offshore wind turbine structures
[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2022 , 10 (8 ): 1021.
[本文引用: 1]
[5]
高云 , 郑文龙 , 熊友明 , 等 . 不同表面粗糙度下圆柱体涡激振动响应特性数值研究
[J]. 上海交通大学学报 , 2018 , 52 (4 ): 419 -428 .
DOI:10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2018.04.006
[本文引用: 1]
使用数值模拟方法,研究了不同粗糙度下圆柱体的涡激振动响应特性,对圆柱体的涡激振动位移响应幅值、响应频率、涡激力、漩涡泄放模式以及涡激振动位移响应与涡激力之间的相位角等参数进行了分析.结果表明,圆柱体涡激振动响应幅值随着粗糙度的上升呈下降趋势.当圆柱体表面光滑或表面粗糙度较小时,涡激振动响应可分为初始分支、上分支以及低分支.在初始分支以及上分支区间,圆柱体尾部漩涡泄放模式呈2S模式;在低分支区间,圆柱体尾部漩涡泄放模式呈2P模式.当圆柱体表面粗糙度较大时,涡激振动响应仅存在初始分支和低分支.初始分支区间,尾部漩涡泄放模式呈2S模式;低分支区间,尾部漩涡泄放模式呈2P模式.
GAO Yun ZHENG Wenlong XIONG Youming et al Numerical study of the vortex induced vibrations of a circular cylinder with different degrees of surface roughness
[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University 2018 , 52 (4 ): 419 -428 .
[本文引用: 1]
[6]
ASSI G R S CRESPI T GHARIB M Novel geometries of serrated helical strakes to suppress vortex-induced vibrations and reduce drag
[J]. Applied Ocean Research 2022 , 120 : 103034 .
[本文引用: 1]
[7]
FENG Y L CHEN D Y LI S W et al Vortex-induced vibrations of flexible cylinders predicted by wake oscillator model with random components of mean drag coefficient and lift coefficient
[J]. Ocean Engineering 2022 , 251 : 110960 .
[本文引用: 1]
[8]
ZHAO B ZHANG M FU S et al Drag coefficients of double unequal-diameter flexible cylinders in tandem undergoing vortex/wake-induced vibrations
[J]. Ocean Engineering 2023 , 270 : 113642 .
[本文引用: 1]
[9]
TOGNARELLI M A SLOCUM S T FRANK W R et al VIV response of a long flexible cylinder in uniform and linearly sheared currents
[C]//Offshore Technology Conference . Houston , USA : One Petro , 2004 : OTC-16338-MS.
[本文引用: 1]
[10]
TRIM A D BRAATEN H LIE H et al Experimental investigation of vortex-induced vibration of long marine risers
[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures 2005 , 21 (3 ): 335 -361 .
[本文引用: 1]
[11]
SONG L FU S CAO J et al An investigation into the hydrodynamics of a flexible riser undergoing vortex-induced vibration
[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures 2016 , 63 : 325 -350 .
[本文引用: 1]
[12]
SONG L FU S DAI S et al Distribution of drag force coefficient along a flexible riser undergoing VIV in sheared flow
[J]. Ocean Engineering 2016 , 126 : 1 -11 .
[本文引用: 1]
[13]
ZHANG M FU S SONG L et al Hydrodynamics of flexible pipe with staggered buoyancy elements undergoing vortex-induced vibrations
[J]. Journal of Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering 2018 , 140 (6 ): 061805.
[本文引用: 1]
[14]
谢波涛 , 雷方辉 . 南海流花海域内孤立波特征分析
[J]. 中国造船 2013 , 54 (Sup. 2): 2 ): 210 -218 .
[本文引用: 1]
XIE Botao LEI Fanghui Characteristics of internal solitons at Liuhua Area in the South China Sea
[J]. Shipbuliding of China 2013 , 54 (Sup. 2): 210 -218 .
[本文引用: 1]
[15]
FU X FU S REN H et al Experimental investigation of vortex-induced vibration of a flexible pipe in bidirectionally sheared flow
[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures 2022 , 114 : 103722 .
[本文引用: 1]
[16]
LIE H BRAATEN H JHINGRAN V G et al Comprehensive riser VIV model tests in uniform and sheared flow
[C]//International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering . Rio de Janeiro , Brazil : American Society of Mechanical Engineers , 2012 , 44922 : 923 -930 .
[本文引用: 1]
[17]
LIE H KAASEN K E Modal analysis of measurements from a large-scale VIV model test of a riser in linearly sheared flow
[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures 2006 , 22 (4 ): 557 -575 .
[本文引用: 1]
[18]
SONG L FU S ZENG Y et al Hydrodynamic forces and coefficients on flexible risers undergoing vortex-induced vibrations in uniform flow
[J]. Journal of Waterway , Port , Coastal , and Ocean Engineering 2016 , 142 (4 ): 04016001.
[本文引用: 1]
[19]
CHAPLIN J R BEARMAN P W HUARTE F J H et al Laboratory measurements of vortex-induced vibrations of a vertical tension riser in a stepped current
[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures 2005 , 21 (1 ): 3 -24 .
[本文引用: 1]
[20]
宋磊建 , 付世晓 , 于大鹏 , 等 . 剪切流下发生涡激振动的柔性立管阻力特性研究
[J]. 力学学报 2016 , 48 (2 ): 300 -306 .
DOI:10.6052/0459-1879-15-309
[本文引用: 1]
利用缩尺模型试验的方法研究了线性剪切流下涡激振动发生时柔性立管的阻力特性.文中基于光纤光栅应变传感器测得的模型应变信息,采用梁复杂弯曲理论计算了立管的平均阻力,继而分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,并提出了用于估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式.结果表明:涡激振动对阻力系数有放大效应,使得立管局部阻力系数高达3.2;平均阻力系数在1.0×10<sup>4</sup>到1.2×10<sup>5</sup>的雷诺数区间内的值为1.3~2.0,并随雷诺数的增大而减小.本文提出的经验公式可准确估算高雷诺数下涡激振动发生时柔性立管的阻力系数,此经验公式考虑了流速、涡激振动主导模态以及主导频率对阻力系数的影响.
SONG Leijian FU Shixiao YU Dapeng et al Investigation of drag forces for flexible risers undergoing vortex-induced vibration in sheared flow
[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 2016 , 48 (2 ): 300 -306 .
DOI:10.6052/0459-1879-15-309
[本文引用: 1]
<p>The drag forces of a flexible riser undergoing vortex-induced vibration(VIV) in sheared flow were investigated using a scale model test.The mean drag forces were determined based on beam theory using the strains measured by the fiber bragg grating strain sensors of the riser.The distributions of the drag coefficients along the riser and Reynolds numbers(<em>Re</em>), and the VIV amplification of the drag coefficient, were studied, and a new empirical model to estimate the drag coefficient on a flexible riser undergoing VIV was proposed.The results show that VIV can amplify the drag coefficient, resulting in the local drag coefficient of the riser up to 3.2.For <em>Re</em> values from 1.0×10<sup>4</sup>~1.2×10<sup>5</sup>, the mean drag coefficient value was between 1.3 and 2.0, and decreased as <em>Re</em> increased.Furthermore, the proposed empirical prediction model, which accounts for the effects of current, the VIV dominant modal number and the frequency in the cross-flow direction, can predict riser drag coefficients under VIV accurately at high <em>Re</em> values.</p>
[21]
胡伟杰 , 刘正礼 , 陈彬 . 南海内波流对深水钻井的影响及对策
[J]. 石油钻采工艺 , 2015 , 37 (1 ): 160 -162 .
[本文引用: 1]
HU Weijie LIU Zhengli CHEN Bin Impacts of internal waves in the South China Sea on deepwater drilling safety and corresponding countermeasures
[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology 2015 , 37 (1 ): 160 -162 .
[本文引用: 1]
[22]
宋玲安 . 海洋内波流对深水钻井影响技术分析
[J]. 石化技术 2021 , 28 (7 ): 67 -68 .
[本文引用: 1]
SONG Ling’an Analysis on the influence of ocean wave flow on deepwater drilling
[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology 2021 , 28 (7 ): 67 -68 .
[本文引用: 1]
Vortex-induced vibrations
1
2004
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
A critical review of the intrinsic nature of vortex-induced vibrations
1
2004
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
内输高温高压流体海底悬跨管道的非线性涡激振动响应分析
1
2022
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
Nonlinear dynamic response of suspended span pipe conveying high temperature and high pressure flow
1
2022
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
State-of-the-art review of vortex-induced motions of floating offshore wind turbine structures
1
2022
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
不同表面粗糙度下圆柱体涡激振动响应特性数值研究
1
2018
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
Numerical study of the vortex induced vibrations of a circular cylinder with different degrees of surface roughness
1
2018
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
Novel geometries of serrated helical strakes to suppress vortex-induced vibrations and reduce drag
1
2022
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
Vortex-induced vibrations of flexible cylinders predicted by wake oscillator model with random components of mean drag coefficient and lift coefficient
1
2022
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
Drag coefficients of double unequal-diameter flexible cylinders in tandem undergoing vortex/wake-induced vibrations
1
2023
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
VIV response of a long flexible cylinder in uniform and linearly sheared currents
1
2004
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
Experimental investigation of vortex-induced vibration of long marine risers
1
2005
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
An investigation into the hydrodynamics of a flexible riser undergoing vortex-induced vibration
1
2016
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
Distribution of drag force coefficient along a flexible riser undergoing VIV in sheared flow
1
2016
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
Hydrodynamics of flexible pipe with staggered buoyancy elements undergoing vortex-induced vibrations
1
2018
... 在背景洋流作用下,柔性立管会在顺流向(in-line,IL)以及横流向(cross flow,CF)发生涡激振动现象(vortex-induced vibration, VIV)[1 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -5 ] .对于横流向,立管所受水动力通常分解为均值为定值的平均阻力以及均值为零的脉动阻力.顺流向的涡激振动位移由平均阻力导致的初始位移以及脉动阻力导致的振动位移耦合组成.在立管设计中,平均阻力通常基于莫里森公式计算,其中最主要的参数为阻力系数.不同于刚性圆柱绕流时所受平均阻力,涡激振动状态下柔性立管通常伴随着明显的阻力放大系数[6 -7 ] ,因此确定柔性立管涡激振动状态下的阻力系数是开展柔性立管的强度设计与校核工作的关键基础[8 ] .许多研究学者已经针对不同流场下的柔性立管涡激振动特性开展了研究.Tognarelli等[9 ] 开展了均匀流及剪切流下的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验,获取了不同雷诺数工况下顺流和横流向的涡激振动响应特征.Trim等[10 ] 基于挪威深水计划开展了长细比达1 400的柔性立管涡激振动响应特性实验.针对柔性立管的阻力特性研究,Song等[11 ] 开展了剪切流下柔性立管涡激振动响应特性试验,分析了阻力系数沿管长方向和雷诺数的分布特性以及涡激振动对阻力系数的放大效应,同时提出了当估算柔性立管发生涡激振动时阻力系数的经验公式[12 -13 ] .然而,在我国南海存在一种由内孤立波诱发的双向剪切流场,这种特殊的流场以流速分离点(O )为界呈现流速方向相反、幅值相等的流速分布特性. ...
南海流花海域内孤立波特征分析
1
2013
... 中海油研究总院于南海北部流花海域开展了全剖面海流、温度、盐度数据检测,流速场测量结果[14 ] 如图1 所示.图中: H 代表深度,箭头代表流速矢量;U max 为双向剪切流边缘最大流速.图1(a) 显示南海海域存在一种由内孤立波诱发的呈现双向剪切分布的海流流场.为了研究该流场下的柔性立管平均阻力特性,将该流场简化为流速大小对称、方向相反的双向剪切流,如图1 (b) 所示. ...
Characteristics of internal solitons at Liuhua Area in the South China Sea
1
2013
... 中海油研究总院于南海北部流花海域开展了全剖面海流、温度、盐度数据检测,流速场测量结果[14 ] 如图1 所示.图中: H 代表深度,箭头代表流速矢量;U max 为双向剪切流边缘最大流速.图1(a) 显示南海海域存在一种由内孤立波诱发的呈现双向剪切分布的海流流场.为了研究该流场下的柔性立管平均阻力特性,将该流场简化为流速大小对称、方向相反的双向剪切流,如图1 (b) 所示. ...
Experimental investigation of vortex-induced vibration of a flexible pipe in bidirectionally sheared flow
1
2022
... 实验于上海交通大学海洋工程国家重点实验室深水实验池中进行.实验装置示意图如图2 所示,实验立管模型安装在从动轮两端,端部安装张紧器以提供初始张力,实验时通过旋转从动轮以形成双向剪切流场.实验坐标系建立在立管模型的端点处,X 轴代表立管模型的顺流向,Y 轴代表立管模型的横流向[15 ] . ...
Comprehensive riser VIV model tests in uniform and sheared flow
1
2012
... 通过上述方程就能建立起应变ε (z ,t )与位移w (z ,t )的关系[16 -17 ] . ...
Modal analysis of measurements from a large-scale VIV model test of a riser in linearly sheared flow
1
2006
... 通过上述方程就能建立起应变ε (z ,t )与位移w (z ,t )的关系[16 -17 ] . ...
Hydrodynamic forces and coefficients on flexible risers undergoing vortex-induced vibrations in uniform flow
1
2016
... 代入式(7)即可得到沿立管模型轴线方向上的水动力载荷分布.实验立管模型在顺流向所受平均拖曳力[18 ] 为 ...
Laboratory measurements of vortex-induced vibrations of a vertical tension riser in a stepped current
1
2005
... 式中:ν 为运动黏度系数,取1.00×10-6 m2 /s.可以看出,随着雷诺数的上升,平均阻力系数均值基本维持不变,值为1.47.确证了在双向剪切流场下的涡激振动状态柔性立管同样发生了阻力放大现象.在先前的阶梯流诱导涡激振动阻力特性研究中,涡激振动平均阻力系数能够放大到1.6~2.7范围[19 ] ;剪切流诱导涡激振动平均阻力系数范围为1.3~1.9[20 ] .可以发现双向剪切流的阻力放大程度与剪切流相当,这是由剪切流和双向剪切流接近的流速分布导致的. ...
剪切流下发生涡激振动的柔性立管阻力特性研究
1
2016
... 式中:ν 为运动黏度系数,取1.00×10-6 m2 /s.可以看出,随着雷诺数的上升,平均阻力系数均值基本维持不变,值为1.47.确证了在双向剪切流场下的涡激振动状态柔性立管同样发生了阻力放大现象.在先前的阶梯流诱导涡激振动阻力特性研究中,涡激振动平均阻力系数能够放大到1.6~2.7范围[19 ] ;剪切流诱导涡激振动平均阻力系数范围为1.3~1.9[20 ] .可以发现双向剪切流的阻力放大程度与剪切流相当,这是由剪切流和双向剪切流接近的流速分布导致的. ...
Investigation of drag forces for flexible risers undergoing vortex-induced vibration in sheared flow
1
2016
... 式中:ν 为运动黏度系数,取1.00×10-6 m2 /s.可以看出,随着雷诺数的上升,平均阻力系数均值基本维持不变,值为1.47.确证了在双向剪切流场下的涡激振动状态柔性立管同样发生了阻力放大现象.在先前的阶梯流诱导涡激振动阻力特性研究中,涡激振动平均阻力系数能够放大到1.6~2.7范围[19 ] ;剪切流诱导涡激振动平均阻力系数范围为1.3~1.9[20 ] .可以发现双向剪切流的阻力放大程度与剪切流相当,这是由剪切流和双向剪切流接近的流速分布导致的. ...
南海内波流对深水钻井的影响及对策
1
2015
... 如上节内容所述,双向剪切流将诱导柔性立管呈现反对称的分布的平均阻力,这种反对称平均阻力将会产生一种特殊的剪力分布.图14 ~16 展示了不同流速工况下剪力沿管长的分布情况.图中:F SF 表示平均阻力导致的剪力分布.可以看出剪力除了在两端达到极值外在立管中部同样会产生一个剪力极值.在有关内波作用的文献中,通常形容内波为“犹如剪刀一般,破坏力极大”[21 -22 ] ,该中部剪力极值的存在即反映了内波流的剪切效应. ...
Impacts of internal waves in the South China Sea on deepwater drilling safety and corresponding countermeasures
1
2015
... 如上节内容所述,双向剪切流将诱导柔性立管呈现反对称的分布的平均阻力,这种反对称平均阻力将会产生一种特殊的剪力分布.图14 ~16 展示了不同流速工况下剪力沿管长的分布情况.图中:F SF 表示平均阻力导致的剪力分布.可以看出剪力除了在两端达到极值外在立管中部同样会产生一个剪力极值.在有关内波作用的文献中,通常形容内波为“犹如剪刀一般,破坏力极大”[21 -22 ] ,该中部剪力极值的存在即反映了内波流的剪切效应. ...
海洋内波流对深水钻井影响技术分析
1
2021
... 如上节内容所述,双向剪切流将诱导柔性立管呈现反对称的分布的平均阻力,这种反对称平均阻力将会产生一种特殊的剪力分布.图14 ~16 展示了不同流速工况下剪力沿管长的分布情况.图中:F SF 表示平均阻力导致的剪力分布.可以看出剪力除了在两端达到极值外在立管中部同样会产生一个剪力极值.在有关内波作用的文献中,通常形容内波为“犹如剪刀一般,破坏力极大”[21 -22 ] ,该中部剪力极值的存在即反映了内波流的剪切效应. ...
Analysis on the influence of ocean wave flow on deepwater drilling
1
2021
... 如上节内容所述,双向剪切流将诱导柔性立管呈现反对称的分布的平均阻力,这种反对称平均阻力将会产生一种特殊的剪力分布.图14 ~16 展示了不同流速工况下剪力沿管长的分布情况.图中:F SF 表示平均阻力导致的剪力分布.可以看出剪力除了在两端达到极值外在立管中部同样会产生一个剪力极值.在有关内波作用的文献中,通常形容内波为“犹如剪刀一般,破坏力极大”[21 -22 ] ,该中部剪力极值的存在即反映了内波流的剪切效应. ...