接触式机械密封失效主要是由于过热和磨损,故而有必要对接触式机械密封的端面温度和端面间的接触摩擦行为开展深入研究.目前,国内外针对机械密封端面温度的预测方法已有不少.Pascovici等[3]和Blasiak[4]分别建立了热流体动力润滑模型,利用解析法求解了机械密封的端面温度分布.文献[5⇓-7]中利用有限差分法迭代求解能量方程和热传导方程,获得了密封环和液膜的温度分布.Meng等[8]提出一种准三维热力学模型,采用Petrov-Galerkin有限元方法得到了机械密封液膜的压力和温度分布.文献[9⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-18]中考虑了密封环的热力变形,基于热弹流润滑模型预测了端面温度分布,并研究变形对密封性能的影响.上述研究均围绕稳定工况下密封端面和液膜的温度计算,而在机械密封瞬态温度场方面,文献[19⇓-21]中进行了探索,通过建立瞬态模型对时间项进行离散,研究了典型启动和停车工况下端面温度、泄漏率等密封性能随时间的变化规律.
综上所述,目前对接触式机械密封端面温升和磨损特性的研究主要集中于稳定工况下,而对于瞬态工况,尤其是交变工况条件下机械密封端面温升及磨损特性的变化规律还鲜有报道.由于在深潜器的航行过程中,其下潜深度和叶轮的工作状态均会对转轴密封的工作条件造成影响,使得推进器机械密封长期服役在工况波动的环境中.在交变工况作用下,密封端面的摩擦接触状态以及热波动特征尚不明确,使得预测和评估深海涉水装备推进器用机械密封的摩擦性能和使用寿命尤为困难.
因此,利用Workbench平台建立带腔内流体的机械密封环二维轴对称模型,重点探究交变工况下其腔内耦合传热特性及密封环端面温升规律.开展机械密封拟实工况试验研究,探究交变工况对机械密封实际工作的影响,监测密封端面温度变化趋势,研究密封端面磨损特性并加以验证分析,掌握密封环磨合过程中端面温升及磨损特性的变化规律,以期为深海涉水装备推进器用机械密封的设计提供指导,对深海涉水装备密封技术的发展和机械密封使用寿命的延长具有实际价值和现实意义.
1 数值模型
1.1 网格划分与边界条件
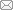
深海涉水装备作业时承受巨大的海水压力,海水深度每增加 100 m,压力增加可达 1 MPa.深海推进器用机械密封常设计压力补偿器,其可根据海水深度自动调整补偿压力,用以减小海水压力变化对动力装置的影响,使机械密封内外侧压差小于 1.5 MPa[33-34].根据某型号深海推进器的结构参数及实际运行工况[35],本文设计的机械密封腔内耦合传热的二维轴对称有限元计算模型及网格划分如图1所示,图中R为半径.采用Workbench自带Mesh单元对模型进行网格划分,对密封环外周及动、静环接触端面进行局部网格加密.S1~S15为各点位边界,密封腔入口速度设为0.2 m/s,出口压力为 400 kPa;入口温度设为 26 ℃,密封腔内壁温度与入口温度相同.采用重整化群(RNG) κ-ε模型进行瞬态计算,动环为浮动环,动静环之间设置接触对,将动环端面WR设为接触面,静环端面WS设为目标面,密封端面摩擦因数设为0.1,产热方程通过用户自定义标量函数(UDF)程序加载到接触面处.动环材料为浸呋喃树脂碳石墨(M106K),静环材料为碳化硅(SSiC),表1为机械密封模型物性参数;表2为尺寸参数,其中rb为动环边界S2半径长度;表3为清水介质26 ℃时的性能参数.为简化计算,在计算过程中作如下基本假设.
图1
图1
密封环几何模型及网格划分(mm)
Fig.1
Geometric model and mesh generation of seal ring (mm)
表1 密封环材料物性参数
Tab.1
| 参数 | 动环(M106K) | 静环(SSiC) |
|---|---|---|
| 密度,ρ/(kg·m-3) | 1 690 | 3 050 |
| 对流换热系数,κ/(W·m-1·K-1) | 70 | 141 |
| 比热容,c/(J·kg-1·K-1) | 783 | 670 |
| 热膨胀系数,αT/K-1 | 4.5×10-6 | 4.3×10-6 |
| 弹性模量,E/GPa | 26.5 | 41.2 |
| 泊松比,ν | 0.15 | 0.12 |
| 摩擦因数,f | 0.1 | 0.1 |
表2 密封环尺寸参数
Tab.2
| 参数 | 取值 | 参数 | 取值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 内径,ri/mm | 40 | 平衡比,B | 0.76 |
| 外径,ro/mm | 50 | rb/mm | 42.6 |
表3 清水介质26 ℃性能参数
Tab.3
| 参数 | 取值 | 参数 | 取值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| κ/(W·m-1·℃-1) | 0.625 | 动力黏度,μ/(mPa·s) | 0.878 0 |
| ρ/(kg·m-3) | 9 981.2 | 黏温系数,ρb/℃-1 | 0.017 5 |
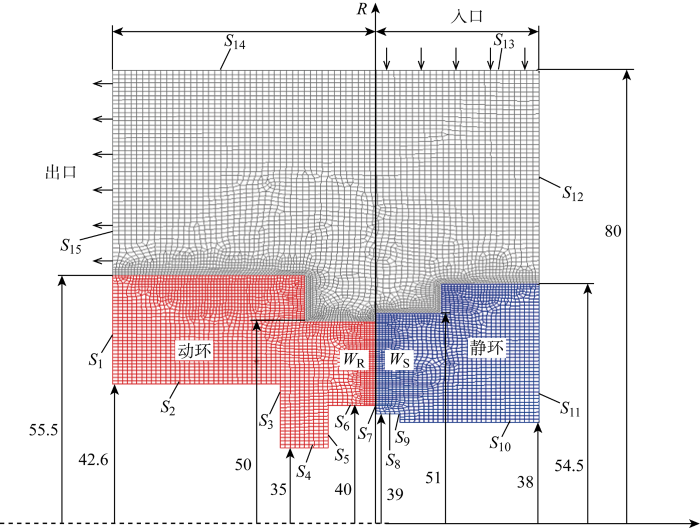
(1) 由于密封端面处的对流换热系数远大于密封环背面,故假设密封环背面S1和S11为绝热面.
(2) 假设流体域边界
(3) 假设密封端面产生的热量均匀分布在WR和WS接触面的每一侧,且由于密封端面间液膜厚度较小,故忽略液膜的对流换热作用.
(4) 由于本案例泄漏量小于机械密封的标准要求,故忽略介质泄漏带走热量的情况.
(5) 忽略热辐射、密封介质物性随温度的变化以及流体的相态变化,此时傅里叶定律可用于密封环和界面处的工作流体.
密封端面传热和受力边界如图2所示.动环底面
图2
式中:h为密封环空气侧的对流换热系数;kf为密封环材料的热传导数;ReD为空气的雷诺数;Pr为空气的普朗特数;D为密封环各边界的直径.
1.2 数学模型
1.2.1 热源计算
在接触式机械密封实际运行过程中,密封端面大多处于混合摩擦或者边界摩擦的状态,采用Luan等[36]的表达式推导计算密封环相对运动端面所产生的热量:
式中:pc为密封端面接触压力;Af为密封接触端面的面积;ω为动环旋转的角速度;f为端面的平均摩擦因数;r为半径.
当机械密封稳定运行时,密封的开启力和闭合力保持平衡,有:
式中:Fo为开启力;Fc为闭合力;Fsp为弹簧力;p1为大气压力;p2为密封流体介质压力;pm为密封端面流体平均膜压.可以推出:
式中:psp为弹簧比压,即密封环接触端面单位面积上所承受的弹性元件作用力.
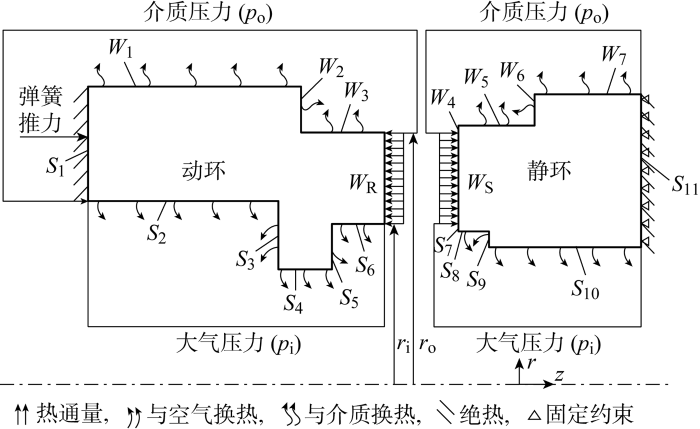
图3
设密封接触端面沿半径方向
式中,r1、r2为半径取值位置.
单位密封面上所承受的开启力(pr+pc)沿半径方向应均匀分布,否则密封端面间将产生倾覆力矩使密封环发生偏转.故半径r处密封端面上的接触压力为
代入式(2),可得半径r处宽度为Δr的环形面积上的产热功率为
单位面积的热功率为
1.2.2 交变工况数学表达式
深潜器在实际下潜与上浮的运行过程中所受工况条件极为复杂,工作介质的压力、密度、主轴转速、支承弹簧力或主轴挠角均可能因下潜深度和叶轮的工作状态而发生改变.pv值是机械密封选型和设计时经常用到的重要参数之一[39],二者的乘积可以衡量机械密封承载能力的高低,故重点关注压力、线速度对深海涉水装备用机械密封性能的影响.其中,p分为两类,一是介质压力pf,二是密封端面比压pc.本文以pf为基础(下文p均指pf),考虑交变工况的具体函数表达,假定交变工况pv值的变化是线性的,分别通过机械密封介质压力或主轴转速的变化,使pv值以一定的幅值和频率上下波动,并比较二者各自的影响作用.
因假定pv值的变化是线性的,所以介质压力与转速的时变函数在每个周期内的极值点左右两侧的斜率不一致,即极值点处的导数不存在.程序设计中,可用循环与分段函数直接表达这种周期性变化,但仿真中模拟设置边界条件以及试验研究中调控工况参数时,需要以单一的数学表达式$f(t) $表示摩擦因数$f$在时域中的变化情况.
根据无穷级数理论,任何周期函数都可用正弦和余弦函数构成的无穷级数表示,称为傅里叶级数.周期为
式中:a0/2为常数项;an、bn分别为第n项时正、余弦分量的系数.
根据傅里叶级数对深海交变工况的形式进行简化设计,假定工况摩擦因数f在初始时刻由平衡位置开始作周期性变化,故为正弦级数.在保证计算精度的前提下,展开至级数前6项,摩擦因数f关于t的表达式如下:
式中:Ap为参数变化过程中的波峰值;Av为参数变化过程中的波谷值.
根据深海推进器实际运行参数,设机械密封稳定运行时主轴转速n'=3 600 r/min,腔内介质压力 p=400 kPa,本文采用控制其中一个参数不变,另一个参数进行有规律的周期性变化模拟深海工况条件.定义无量纲振幅
表4 交变振幅形式
Tab.4
| 变换参数 | 振幅M(Γ=3.2 s) | 压力变化范围/kPa |
|---|---|---|
| 介质压力 | 0.1 | 360~440 |
| 0.2 | 320~480 | |
| 0.3 | 280~520 | |
| 0.4 | 240~560 | |
| 0.5 | 200~600 |
表5 交变周期形式
Tab.5
| 变换参数 | 振幅M (Γ=0.2 s) | 压力交变范围/kPa |
|---|---|---|
| 介质压力 | 1.6 | 320~480 |
| 3.2 | 320~480 | |
| 4.8 | 320~480 | |
| 6.4 | 320~480 | |
| 8.0 | 320~480 |
2 数值模拟与分析
2.1 网格无关性验证
考虑网格数量对计算结果精度的影响,首先进行网格无关性验证,结果如表6所示,以最后一组网格数所得端面平均温度作为对比基准,计算得到不同网格数与基准之间的相对偏差.综合考虑,本文采用的网格单元数为 14 126,节点数为 14 333,其中流体域网格数为 7 428,节点数为 7 635,动环网格数为 4 022,节点数为 4 184,静环网格数为 2 676,节点数为 2 793,流体域近壁面无量纲参数y+值为31.08~66.16.
表6 网格无关性验证
Tab.6
| 网格数 | 端面平均温度/℃ | 偏差/% |
|---|---|---|
| 6 325 | 93.135 2 | 3.30 |
| 8 725 | 91.097 4 | 1.03 |
| 14 126 | 90.288 6 | 0.14 |
| 26 173 | 90.227 0 | 0.11 |
| 36 874 | 90.160 7 |
注:“空白”表示无数值.
2.2 交变工况对密封端面温升的影响
图4为在振幅M=0.5,周期为3.2 s的交变工况下密封环接触端面平均温度(T)-时变曲线.其中,图4(a)为交变介质压力及其工况下端面平均温度的变化情况,图4(b)为交变转速及其工况下端面平均温度的变化情况.从图4可以看出,在交变载荷作用下,端面平均温度分布均表现出明显的瞬态交变特性,接触端面平均温度均随工况参数变化呈现波动上升的趋势,起始端面平均温度迅速上升,随着时间的推移温升速率逐渐减慢,最后达到某一稳定值后趋于动态平衡状态.对比图4(a)和图4(b)可知,当M=0.5时,相比于交变介质压力工况,交变转速工况下密封端面平均温度的交变特性更为明显,其波动幅值更大.结合式(7)可知,这可能是因为介质压力的改变,导致密封端面接触比压不断变化,从而间接影响端面摩擦生热,而摩擦热与转速大小呈正相关.同时可以看出,由于瞬态积分效应的影响,端面平均温度的峰值相比于交变介质压力和交变转速均表现出一定的滞后性.
图4
图4
M=0.5交变工况下密封端面平均温度时变曲线
Fig.4
Time-varying curve of average temperature of seal face under an alternating condition of M=0.5
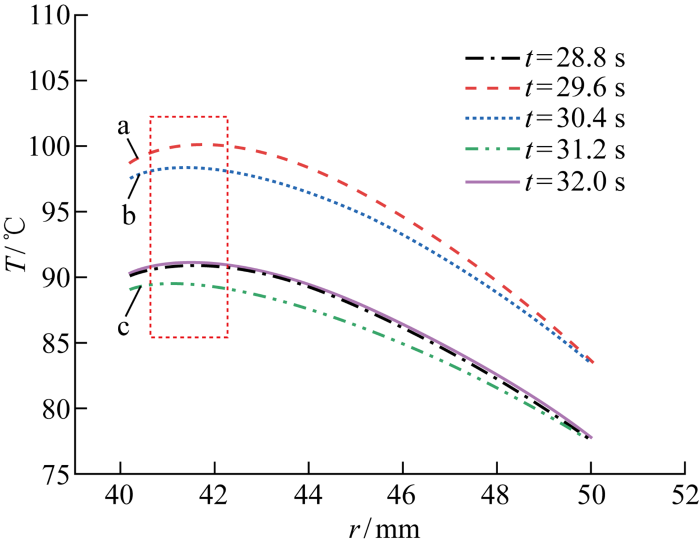
对比不同工况下密封环瞬时温度场云图可知,密封端面最高温度均靠近密封端面内径处.选取图4(b)中交变转速工况最后一个交变周期不同时刻密封环端面温度沿径向分布曲线,如图5所示;并取转速由峰值到平衡值再到谷值,即如图4(b)中a、b、c处3个时刻对应密封环的瞬时温度场分布云图.从图5和6中可以看出,在运行过程中密封端面最高温度区域位于动、静环接触端面靠近内径处,温度沿径向逐渐降低,这是因为密封环的外周与冲洗介质接触,散热条件较好,而密封环内径侧与大气接触,散热性较差.密封环内温度成抛物线型沿着轴向外径扩散,靠近密封端面的区域温度梯度大,远端较小,这是由于受密封环自身热传导及其边界对流换热的双重作用的影响.M106K动环的对流换热较强,平均温度较低,且SSiC静环的导热系数较高,故静环的温度梯度小,温度分布较为均匀.
图5
图5
M=0.5交变转速工况下的密封沿径向的端面温度
Fig.5
Radial temperature of seal face at an alternating speed of M=0.5
图6
图6
M=0.5交变转速工况下的密封环温度场分布云图
Fig.6
Contour map of temperature field of seal ring at an alternating speed of M=0.5
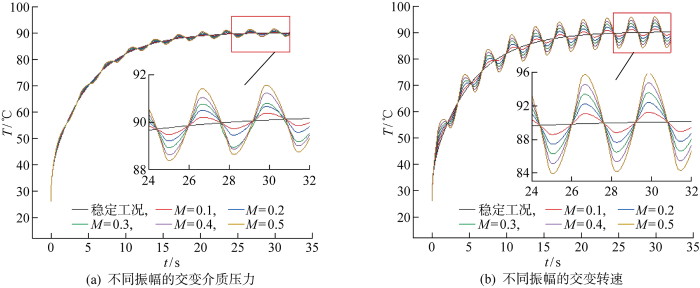
稳定工况和不同振幅交变介质压力以及转速工况下端面平均温度时变曲线如图7所示.其中,图7(a)是交变介质压力工况下的端面平均温度变化曲线,图7(b)为交变转速工况下的端面平均温度变化曲线,交变工况周期均为3.2 s.由图7可见,稳定工况下(n'=3 600 r/min,p=400 kPa),密封端面平均温度随时间的变化可表示为一条光滑上升的曲线;初始阶段,端面平均温度迅速上升,随着时间的增加,端面温升速率减小并趋于稳定.对于交变工况,随着交变参数振幅的增大,端面摩擦热增加,平均温度波动的幅值也随之增加,相较于稳定工况,交变转速工况下端面平均温度最大偏移为16.06%,交变介质压力工况下端面平均温度最大偏移为3.93%,交变转速工况下端面平均温度随振幅增加其波动程度更为显著.
图7
图7
不同振幅的交变工况下密封端面平均温度时变曲线
Fig.7
Time-varying curve of average temperature of seal face under alternating condition at different amplitudes
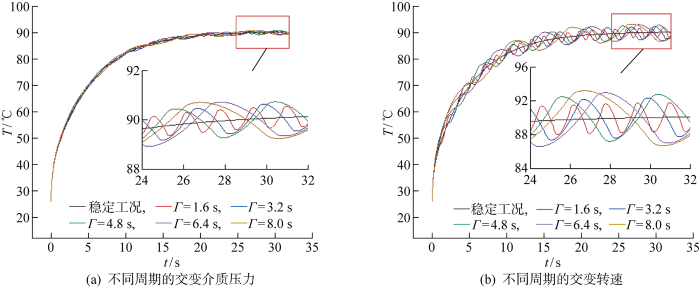
稳定工况和不同周期交变介质压力和转速工况下密封端面平均温度时变曲线如图8所示.其中,图8(a)为交变介质压力工况下密封端面平均温度曲线,图8(b)为交变转速工况下密封端面平均温度变化曲线,交变振幅M均为0.2.由图8可见,在转速相同的情况下(n'=3 600 r/min),密封端面平均温度呈波动上升的趋势,波动趋势与交变周期有关,周期越短,端面平均温度上下波动的频率越快,反之则越慢.密封端面的温度在不同交变周期工况下,其上下波动的幅值并未出现明显的差异,相较于稳定工况,交变转速工况下端面平均温度最大偏移为7.76%,交变介质压力工况下端面平均温度最大偏移为1.91%,再次验证转速交变相较于介质压力交变更容易影响密封端面温度波动.由此可知,转速的瞬时变化对深海推进器机械密封的密封性能和使用寿命具有极大考验.
图8
图8
不同周期的交变工况下密封端面平均温度时变曲线
Fig.8
Time-varying curve of average temperature of seal face under alternating condition in different periods
3 试验研究
3.1 交变工况机械密封试验装置
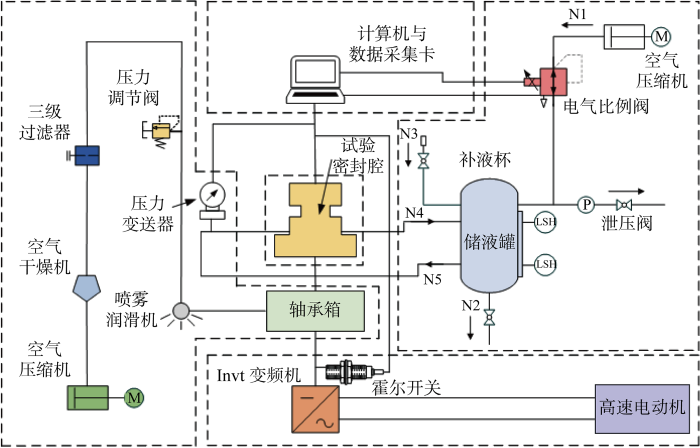
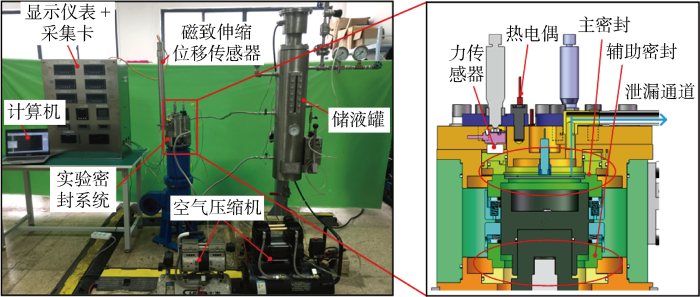
围绕深海涉水装备在恶劣交变工况下运行时的密封性能开展了深海推进器机械密封拟实试验,实时监测密封端面温度变化及泄漏情况,观察并测量试验后端面形貌及磨损程度.本试验装置系统主要由试验密封腔、轴承辅助系统、供液调压系统、动力控制与传动系统以及数据采集与控制系统组成,如图9所示.图中,N1~N5为流向顺序.
图9
图9
交变工况机械密封试验装置系统示意图
Fig.9
System diagram of mechanical seal test rig under alternating conditions
试验密封腔实物装置如图10所示,该装置为背靠背双端面密封,两道密封结构相同,每道结构主要包括动环、静环、动环座、静环座、O形圈和弹簧等.密封腔内上端密封为主密封,试验所需相关数据从该道密封中获得,下端辅助密封的主要作用是防止密封腔内密封介质污染轴承.轴承辅助系统的作用是给轴承提供润滑,以及监控轴承在高速运转过程中的稳定性和可靠性.供液调压系统主要通过基于LabVIEW自主开发的压力检测与控制程序,给密封腔体提供一定压力的恒温密封介质,通过比例阀,根据数据采集卡输出的电信号连续地对空气压缩机的供气压力进行控制,进而可改变储液罐内液体的实时工作压力.动力传动系统的主要作用是调控和监测电动机转轴的转速.数据采集与控制系统主要测试试验过程中的工况参数和密封性能参数信号.
图10
3.2 试验测试
试验中动环材料选用M106K,静环材料选用SSiC,密封环尺寸及物理参数详见表1和表2.密封介质的初始温度均为26℃.在给定工况下(见表7~9),每组试验测试时间均为2 h,表中
图11
表8 第2组试验
Tab.8
| 编号 | 工况条件 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M(p) | 交变范围/ kPa | 交变周期/s | 转速/ (r·min-1) | |
| 2# | 0.1 | 360~440 | 32 | 3 600 |
| 3# | 0.2 | 320~480 | 32 | 3 600 |
| 4# | 0.3 | 280~520 | 32 | 3 600 |
| 5# | 0.2 | 320~480 | 16 | 3 600 |
| 6# | 0.2 | 320~480 | 48 | 3 600 |
表9 第3组试验
Tab.9
| 编号 | 工况条件 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M(n') | 交变范围/ (r·min-1) | 交变周期/s | 介质压力/ kPa | |
| 7# | 0.1 | 3 240~3 960 | 32 | 400 |
| 8# | 0.2 | 2 880~4 320 | 32 | 400 |
| 9# | 0.3 | 2 520~4 680 | 32 | 400 |
| 10# | 0.2 | 2 880~4 320 | 16 | 400 |
| 11# | 0.2 | 2 880~4 320 | 48 | 400 |
3.3 试验结果与讨论
3.3.1 交变工况对端面温升的影响
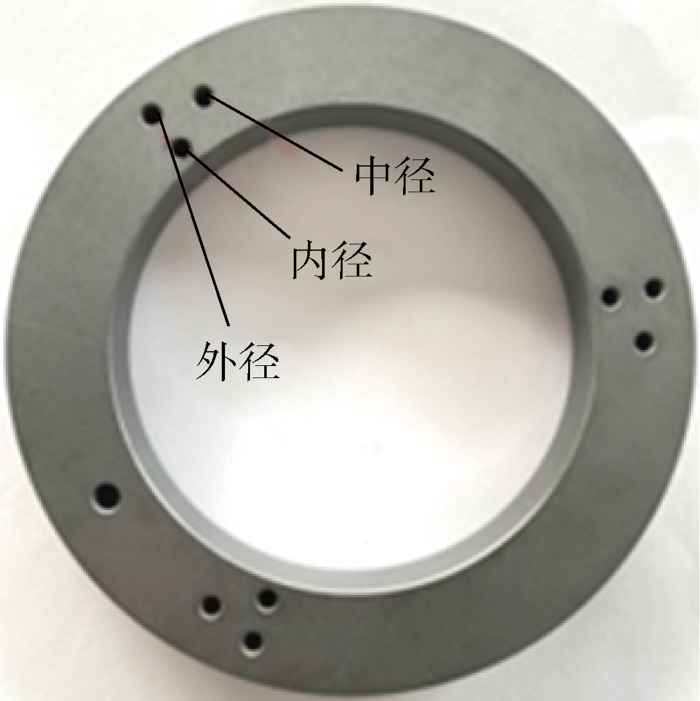
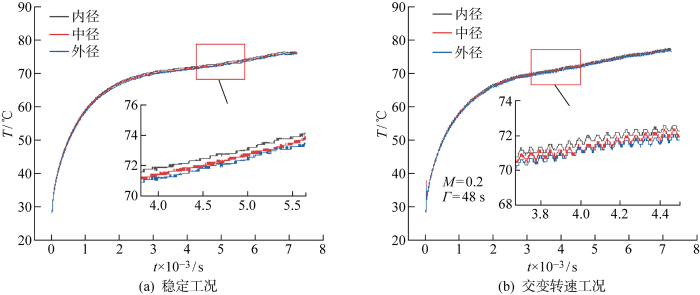
图12为试验过程中静环端面沿径向取内径、中径和外径3处不同位置平均温度的时变曲线图.其中, 图12(a)为稳态工况下静环端面沿径向的温度时变曲线图,即表6中的1#试验结果;图12(b)为交变转速工况下静环端面沿径向的温度时变曲线图,即表8中的11#试验结果.由图12可知,在不同工况下静环端面温度均呈现先快速上升、后趋于平缓的趋势,这是因为初始时密封环温度与环境温度相同,开机启动后,动环高速旋转产生摩擦热,密封端面温度快速上升,机械密封在运行初期存在明显的磨合阶段[41],随着不断磨合,石墨逐渐脱落并转移至碳化硅表面形成自润滑层,造成端面间的摩擦因数一定程度上降低,同时密封端面微凸体弹性接触比例增大,而塑性接触比例下降,意味着机械密封端面间的弹塑性接触压力下降,也降低了端面发生严重黏着磨损的可能性.由于密封端面摩擦因数与接触压力的降低,端面间的产热功率也随之降低,故端面温度呈现出随时间减速上升的变化规律.当产热功率与冲洗介质的散热效率相等时,端面温度将趋于稳定.此外,还可以看出,在稳态和交变工况下,静环端面温度均为内径处最高、外径处最低,这是因为外径处与冲洗介质接触,散热条件较好,但因密封环接触端面较窄,仅为1 mm,所以内、外径温差较小,均保持在约1 ℃.
图12
图12
稳定和交变工况下密封端面沿径向的温度曲线
Fig.12
Temperature along radial direction of seal face under stable and alternating conditions
根据以上试验结果,将静环端面内径、中径和外径3处位置的温度取平均值进行进一步分析.如图13所示,图13(a)为稳定工况与振幅M=0.3、交变周期Γ=32 s时,交变介质压力和交变转速工况下静环端面平均温度时变曲线,即1#、4#和9#试验结果;图13(b)为稳定工况与转速振幅M=0.2、介质压力为400 kPa时,在不同交变周期工况下的静环端面平均温度时变曲线,即1#、8#、10#和11#试验结果.由图13(a)可知,相较于稳定工况,交变工况下静环端面平均温度均呈波动上升的趋势,波动形式与交变工况波动的周期基本吻合.同时,交变振幅相同时,交变转速工况下端面温度曲线波动的幅度较大,其对端面平均温度的影响尤为显著,这是因为转速的变化会直接作用于配对摩擦副使得产热功率增加,而压力的变化除了改变闭合力外也同时影响端面开启力.因端面温升密封环可能会发生沿泄漏方向的收敛变形,增加介质压力同时也使进入密封间隙的流体增多,减少了固体接触承载的比例,一定程度上改善了润滑条件.由于压力的双向影响,振幅相同时,相对交变压力工况,交变转速工况对端面温度曲线波动的影响更大.
图13
图13
密封端面平均温度时变曲线
Fig.13
Time-varying curve of average temperature of seal face
图13(b)中结果表明,交变转速工况下端面平均温度时变曲线与稳定工况下的时变曲线整体趋势基本相同.交变转速工况下端面温度波动的频率与交变周期有关,工况的交变周期越小,端面温度上下波动的频率越快,反之则端面温度上下波动的频率越慢.此外,通过分析交变压力工况下静环端面温度时变数据可得上述相同结论,且振幅和周期相同的条件下,交变压力温度波动的幅值均小于对应条件下交变转速工况端面温度波动的幅值.综上所述,试验所得密封端面温度情况与模拟计算所得到的密封端面温度变化特性结论一致,在一定程度上验证了数值模拟的准确性.
3.3.2 交变工况对密封环表面形貌的影响
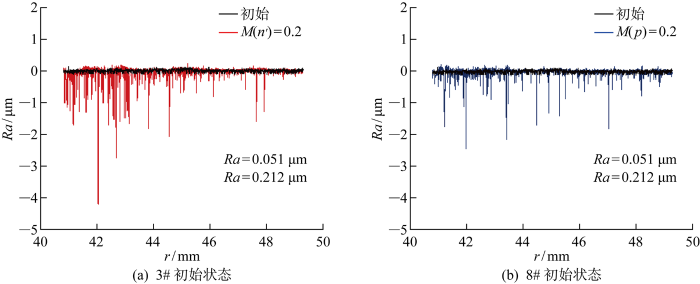
为了进一步揭示交变工况对机械密封性能影响,开展了密封端面表面形貌的试验测试研究.通过对比不同工况条件试验前后动环表面形貌发现,不同交变工况试验后M106K动环端面内径处均出现不同程度的磨损,如图14所示为交变工况试验前后动环端面沿径向的粗糙度(Ra)对比.其中,图14(a)为3#试验前后动环端面沿径向的粗糙度测试结果,图14(b)为8#试验前后动环端面沿径向的粗糙度测试结果,图中黑色线均表示试验前动环端面的粗糙度测试结果.由图可见,试验前动环端面初始状态平面度较好;试验后,动环端面粗糙度显著增大,靠内径处磨损较为严重.当交变振幅和周期均相同时,相对于交变压力试验工况,交变转速试验工况下的动环端面粗糙度明显较大.
图14
图14
试验前后动环端面沿径向粗糙度对比
Fig.14
Comparison of radial roughness of end face of rotating ring before and after test
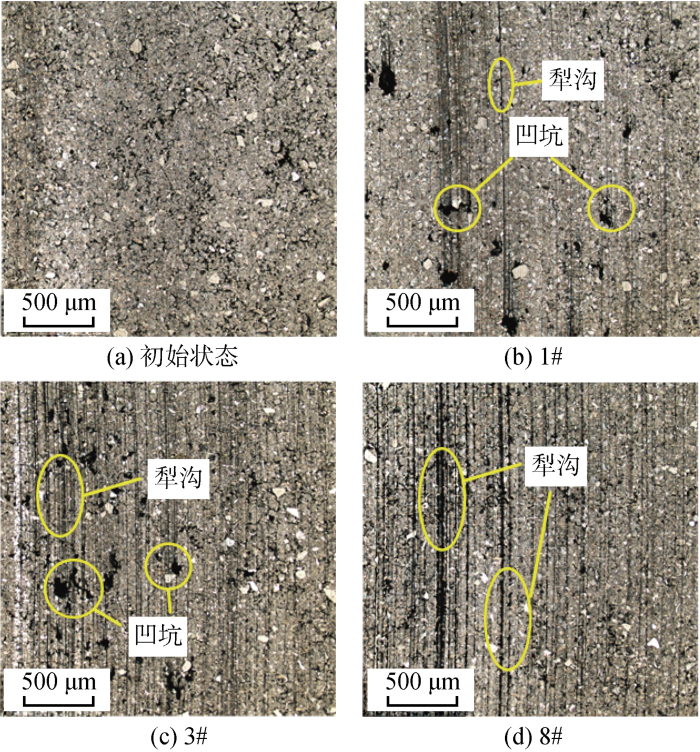
图15所示为使用激光显微镜放大5倍得到的不同工况试验后M106K动环端面形貌照片.由石墨和呋喃树脂的属性可知,图15(a)中颜色较浅部分为石墨基体,颜色较深部分为呋喃树脂填充物或未被填充的孔隙.对比图15(a)~(d)可知:试验前动环端面石墨基体较为密实,未见单独的石墨颗粒,试验后基体略显疏松. 1#试验后端面磨损较轻,出现较浅的犁沟和凹坑;3#试验后端面犁沟和凹坑的数量及深度均略有增加;8#试验后动环端面磨损程度较为严重,出现密集且较深的犁沟.这是因为浸呋喃树脂是一种含有热固树脂的材料,在摩擦副运转过程中,较高的端面温度会致使M106K中的树脂析出和结块而形成游离磨粒,对动环端面造成局部磨粒磨损,当振幅和周期相同时,交变转速工况下密封端面的摩擦热影响尤为显著,端面温度波动的幅度更大,端面磨损现象更为显著.
图15
图15
不同工况试验后M106K动环表面激光显微照片
Fig.15
Laser micrograph of end face of rotating ring(M106K)after test under different conditions
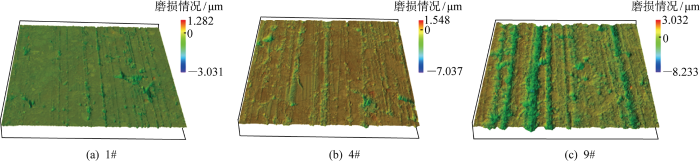
为进一步分析动环端面的形貌变化及其特征,在激光显微镜下将试验后动环端面靠近内径处形貌放大50倍,如图16所示,以端面初始状态为基准0,磨损情况中正值表示磨损后端面变形量,负值表示磨损深度.可见动环端面粗糙峰基本被磨平,端面沿周向呈现出明显的磨痕.在稳定工况下,端面磨损程度较轻,出现较浅的犁沟和凹坑,在交变介质压力工况下,端面磨损加剧,呈现出深浅不一的犁沟,凹坑的数量也相应有所增加.在交变转速工况下,摩擦热影响尤为显著,动环端面磨损程度最为严重,这可能是因为工况的瞬时交变下SSiC-M106K摩擦副接触状态随之不断发生变化,浸渍石墨部分受高温碳化形成游离磨粒并存储在摩擦副表面,磨屑聚集,在密封端面造成三体磨粒磨损[42];交变工况加剧后,犁沟数量显著增加,且转速对端面接触状态的影响较介质压力的影响更大,交变周期相同时,随着转速振幅的增加,动环端面的磨损程度显著增加.此外,试验后部分静环表面出现多道环形黑色印记,这可能是因为石墨部分碳化脱落形成的游离微粒,在较高的端面比压作用下转移到碳化硅静环表面,形成黑色环带.由此可知,交变工况对深潜器用机械密封端面的磨损影响不可忽视.
图16
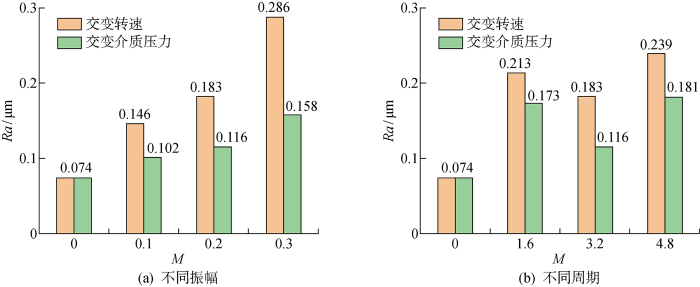
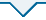
由于在不同工况下动环内径处磨损较为明显,故取动环端面靠近内径处3 mm宽度测定其在不同工况试验后的粗糙度数据,如图17所示.其中,图17(a)为不同振幅的交变介质压力和交变转速工况下动环端面内径处粗糙度,图17(b)为不同周期的交变介质压力和交变转速工况下动环端面内径处粗糙度.结合上述动环端面内径处形貌图分析可知:交变介质压力和交变转速工况试验后动环端面内径处磨损程度与交变参数的振幅呈正相关.振幅增大,磨损加剧,导致试验后石墨环端面粗糙度增大.相较于稳定工况下动环端面粗糙度,振幅为0.1、0.2、0.3时,交变介质压力工况下动环端面粗糙度分别增加37.8%、56.8%、113.5%,交变转速工况下动环端面粗糙度分别增加97.3%、147.3%、286.5%,不同交变周期对端面磨损程度的影响未见明显差异.振幅相同,交变周期为16、32和48 s时,交变介质压力工况下动环端面粗糙度最高增加147.3%,交变转速工况下动环端面粗糙度最高增加223.0%.由此可知,深海推进器在工况复杂多变条件下运行时,密封端面易发生过度磨损,大大缩短了机械密封的使用寿命,且转速的瞬时变化更易加剧密封端面的磨损程度.
图17
图17
动环端面内径处粗糙度
Fig.17
Roughness at inner diameter of end face of rotating ring
综上所述,交变工况使得摩擦副接触状态不断变化及端面温度不断波动,浸呋喃树脂石墨在摩擦过程中易发生颗粒掉落或孔隙边缘刮擦,导致动环端面产生犁沟和凹坑而发生破坏,且摩擦副间存在的磨屑不利于润滑液膜的形成.当工况条件恶劣时,在周期性交变工况的作用下密封端面磨损程度加剧,极大降低了机械密封的密封性能,因此,应密切关注深海环境下复杂恶劣工况对机械密封产生的不良影响.
4 结论
通过对交变工况下深海涉水装备用机械密封进行端面温升和磨损特性的研究,可以得出以下结论:
(1) 对于稳定工况和交变工况,密封端面温度上升的整体趋势相同, 最高温度区域发生在密封端面靠近内径处;交变工况下密封端面温度随工况参数的变化呈波动上升趋势,表现出明显的交变瞬态特性;端面温度波动的幅值与工况参数的振幅呈正相关关系,相较于稳定工况,数值计算中交变转速工况下端面平均温度最大偏移16.06%,远高于交变介质压力工况下端面平均温度最大偏移量.在振幅相同、周期不同的交变工况下,交变周期越小,密封环端面温度波动的频率越快,交变转速工况下端面平均温度最大偏移7.76%,亦高于交变介质压力工况下端面平均温度最大偏移量.数值模拟和试验结果均表明转速的瞬时变化易对深海推进器机械密封的端面摩擦状态产生较大影响.
(2) 在稳定工况下,M106K动环端面磨损程度较轻;在交变工况下,动环端面出现大量凹坑和深浅不一且密集分布的犁沟,端面内径区域粗糙度变大,磨损程度较为严重,相较于稳定工况,交变转速工况下端面粗糙度最高增大286.5%,交变介质压力工况下端面粗糙度最高增大147.3%.交变工况下深海推进器机械密封更易发生不可修复的损伤,设计时需根据深海复杂多变的工况对机械密封进行合理结构优化(如表面涂层技术)以避免密封端面过早失效.
参考文献
深海潜水器研究现状与展望
[J].
Research status and prospect of deep-sea underwater vehicle
[J].
机械密封热力耦合有限元模型与密封性能分析
[J].
Thermal-mechanical coupled finite element model and seal performance analysis of mechanical seals
[J].
A thermo-hydrodynamic analysis of a mechanical face seal
[J].
DOI:10.1115/1.2920930
URL
[本文引用: 1]

A thermo-hydrodynamic analysis is performed for a face-to-face double seal configuration. Temperature and viscosity variations both across and along the sealing gap are considered and realistic boundary conditions are considered. The energy equation is solved analytically and the radial temperature variation is presented by an implicit equation. This approach enables analytical parametric investigation and gives better understanding of the effects of various parameters on the seal’s thermal behavior.
An analytical approach to heat transfer and thermal distortions in non-contacting face seals
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.10.011 URL [本文引用: 1]
Three-dimensional modeling of THD lubrication in face seals
[J].
DOI:10.1115/1.1327584
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In this study, the seal is supposed to operate in laminar flow, under steady-state conditions and without phase changing in the lubricant film. The model tackles the three-dimensional general case of misaligned faces and wavy rotor face in stable dynamic tracking regime. The general equations of the THD lubrication and the equations of heat transfer through the rings are established. Different types of heat exchange on the external frontiers of the ring are considered. The equations are numerically solved by using the finite difference method in an iterative procedure which ensure the heat transfer conditions on the boundaries of the fluid film and of the solid rings. Complete and approximated solutions are compared and the validity of the approximations is discussed. A parametric study is carried out in the three-dimensional cases corresponding with misaligned, wavy, and notched faces. The results show the influence of the interface geometry, the nature of the lubricant, the fluid flow, the ring materials, and the different heat transfer conditions on the ring surfaces.
A numerical analysis of the grooved surface effects on the thermal behavior of a non-contacting face seal
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.proeng.2012.07.037 URL [本文引用: 1]
Analysis of stability of two-phase flow mechanical seal with spiral groove under high speeds
[J].DOI:10.1007/s40430-020-02713-8 [本文引用: 2]
Thermohydrodynamic analysis on herringbone-grooved mechanical face seals with a quasi-3D model
[J].
A simple and easy-to-use TEHD model for non-contacting liquid face seals
[J].DOI:10.1080/10402000308982615 URL [本文引用: 1]
A simple approach to the thermos elasto hydrodynamic behavior of mechanical face seals
[J].DOI:10.1080/10402000802441587 URL [本文引用: 1]
An analytical approach of the thermoelasto hydrodynamic behaviour of mechanical face seals operating in mixed lubrication
[J].
A mixed thermoelasto hydrodynamic lubrication analysis of mechanical face seals by a multiscale approach
[J].DOI:10.1080/10402004.2015.1023407 URL [本文引用: 1]
Experimental and numerical study of the lubrication regimes of a liquid mechanical seal
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.triboint.2015.05.022 URL [本文引用: 1]
The effect of surface roughness on thermal-elasto-hydrodynamic model of contact mechanical seals
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11433-013-5266-3 URL [本文引用: 1]
Mechanism of a wavy-tilt-dam mechanical seal under different working conditions
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.triboint.2015.03.020 URL [本文引用: 1]
热弹变形对核主泵用流体静压型机械密封性能的影响
[J].针对核主泵用流体静压型机械密封在高压和高速条件下,其密封性能易受端面热弹变形影响的特点,通过建立收敛台阶端面流体静压型机械密封的稳态传热模型,并考虑流体粘度随压力、温度的变化,建立端面流体膜压力和密封环温度的控制方程,采用有限差分法求解各控制方程,采用有限元法求解密封环热、弹变形,对密封进行流、固、热耦合分析,研究热弹变形对密封性能的影响;同时改变操作参数,研究端面温度、热弹变形、端面流体膜平衡间隙等随之产生的变化规律。结果表明,端面的弹性变形大于热变形;热弹变形的综合影响使端面由外径向内径形成收敛间隙,导致开启力、泄漏率和液膜刚度增加;动环角速度越高,流体温升越大,端面热变形越明显,泄漏率越大;流体注入温度越低,温粘效应越显著;流体注入压力越高,热弹变形量越大,密封端面平衡间隙亦越大。
Effects analysis of thermo-elastic deformation on the performance of hydrostatic mechanical seals in reactor coolant pumps
[J].The thermo-elastic deformation of a hydrostatic mechanical seal used in reactor coolant pumps plays an important role in sealing performance because of the operations at high-pressure, high-speed and in a wide temperature range. A steady heat transfer model is established for such a hydrostatic face seal with convergence gap. Considering the variation of dynamic viscosity along with that of fluid pressure and temperature, the governing equations of fluid film pressure and seal ring temperature are set up and solved by using finite difference method. The thermo-elastic deformation is solved by using finite element method. The thermal-fluid-solid coupled analyses are carried out. The effects of thermo-elastic deformation on sealing performance are studied. The variations of face temperature, thermal-elastic deformation, and fluid film thickness with operating conditions are presented. It is found that the amount of elastic deformation is greater than that of thermal deformation under the considered conditions. A convergence gap between two sealing faces from the outer radius to inner radius is formed by thermo-elastic deformation, which results in the increases of opening force, leakage rate and liquid film stiffness. The higher the angular speed of rotating ring is, the greater the fluid temperature rise, the more obvious the face thermal deformation, and the greater the leakage rate will be. A lower temperature of the inlet fluid will lead to a greater effect of temperature on viscosity. A higher pressure of the inlet fluid will result in the increases of thermo-elastic deformation and the balancing film thickness.
核主泵用双锥度端面流体静压机械密封热弹流效应研究
[J].
Thermo-elasto-hydrostatic effect analysis of a double tapered hydrostatic mechanical seal in reactor coolant pumps
[J].
Thermo-elasto-hydrodynamic analysis of triangular textured mechanical face seals
[J].
Analysis of mechanical seal behavior during transient operation
[J].
DOI:10.1115/1.2834409
URL
[本文引用: 1]

A mathematical model that predicts the transient behavior of gas or liquid lubricated hydrostatic mechanical seals has been developed. The analysis includes an evaluation of the fluid, contact, and deformation mechanics of a mechanical seal subject to constant or varying rotational speed and sealed pressure. Squeeze film effects are included. For gas seals, slip at the walls is also taken into account. Results include predictions of film thickness distributions, contact forces, leakage rates, pressure distributions, heat generation rates, thermal deformation, and mechanical deformation.
A transient dynamic analysis of mechanical seals including asperity contact and face deformation
[J].DOI:10.1080/10402000208982551 URL [本文引用: 1]
瞬态启停机械密封轴对称动力学模型与密封行为分析
[J].
Axisymmetric dynamic model and seal behavior analysis of mechanical seals during startup and shutdown operation
[J].
Friction and wear behavior of different seal materials under water-lubricated conditions
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s40544-020-0364-5
[本文引用: 1]

The shaft mechanical face seal in a high-speed turbopump of a liquid rocket engine often operates under extremely harsh conditions. For example, a low-temperature and low-viscosity fluid (such as liquid oxygen or liquid hydrogen) is used as a lubricant. The performance of the seal rings, especially the friction and wear behavior, directly determines whether the seal functions normal. In this study, the friction and wear behavior of several ring materials are tested using a pin-on-disk tribo-tester, and the wear morphology of the ring is investigated. The friction coefficients (COFs) and mass-wear rates under dry-friction and water-lubricated conditions, which are used to simulate low-viscosity conditions, are obtained. The results show that at a pressure-velocity (PV) value of 2.4 MPa·(m/s), the COF between the copper graphite (stator) and copper-chrome alloy disk (rotor) is low (with a value of 0.18) under the dry-friction conditions, and the 5-min wear mass of the copper graphite is approximately 2 mg. Under the water-lubricated conditions, compared with other materials (such as copper-chrome alloy, S07 steel, alumina ceramic coating, and nickel-based calcium fluoride), the S07 steel with a diamond-like carbon film is preferred for use in a high-speed turbopump under extreme conditions. The results of this study can provide theoretical and experimental guidance in the design of mechanical face seals in liquid rocket engines.
Face rub-impact monitoring of a dry gas seal using acoustic emission
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11249-013-0210-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Analysis of the dynamic friction of a gas face seal based on acoustic emissions
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11249-017-0954-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Mechanism of bi-Gaussian surface topographies on generating acoustic emissions under a sliding friction
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.triboint.2018.10.015 URL [本文引用: 1]
Bi-fractal feature of bi-Gaussian stratified surfaces
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.triboint.2019.02.022
[本文引用: 1]

Surface serves as the fingerprint of a component. Researchers have observed the bi-fractal feature of a surface roughness. The increasing number of researchers attempting to model the roughness from a bi-Gaussian stratified perspective provides the possibility of understanding the bi-fractal mechanism. Engineering (two-process and worn surfaces) and simulated surfaces are selected to establish a database of bi-Gaussian stratified surfaces. The bi-fractal feature of these bi-Gaussian stratified surfaces is analyzed, finding that the upper Gaussian component of a bi-Gaussian stratified feature reduces the power spectral density (PSD) and partially diverges the slope of the logarithmic PSD to render a bi-fractal behavior. The proportion of the components plays a greater role than the ratio of the component root-mean-square values.
Characterization and simulation of bi-Gaussian surfaces induced by material transfer and additive processes
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.triboint.2019.03.032 URL [本文引用: 1]
Frictional characteristics of impregnated graphite with different graphitization degree versus chromium stainless steel under varying PV values
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.triboint.2019.106063 URL [本文引用: 1]
浸酚醛树脂石墨/SiC密封材料摩擦学特性研究
[J].
Study on tribological properties of phenolic resin impregnated graphite/SiC ceramic sealing materials
[J].
浸酚醛树脂石墨与9Cr18不锈钢配副的摩擦磨损正交试验研究
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-0329.2019.04.001
[本文引用: 1]

机械密封是航空航天涡轮泵系统的核心基础元件,其密封性、可靠性和耐磨性不仅取决于密封的结构设计,而且取决于密封端面摩擦副材料的配对。为最大程度地实现密封摩擦副材料的国产化,开展国产典型石墨密封环的摩擦磨损特性研究具有重要意义。通过选取国内三大石墨生产商出品的空天领域常用典型石墨(编号分别为1<sup>#</sup>、2<sup>#</sup>和3<sup>#</sup>)与9Cr18钢配副进行干磨条件下的试验测试,基于正交试验方法,通过改变线速度、端面比压和硬环表面粗糙度,使用UMT-Ⅲ摩擦磨损试验机对比分析了配对摩擦副的摩擦磨损特性。结果表明,该配对副适用于大PV值的工况条件,摩擦线速度是影响配对副综合摩擦学特性的主要因素。当材料选用1<sup>#</sup>石墨,转速为750 r/min、端面比压为1.77 MPa、钢盘表面粗糙度Ra=0.2 μm时,配对副的综合摩擦学特性最佳。
Orthogonal experimental study on tribological behavior of phenolic resin impregnated graphite-9Cr18 stainless steel friction pairs in a mechanical seal
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-0329.2019.04.001
[本文引用: 1]

Mechanical seal is the core component of aeronautical turbopump system. Its sealability,reliability and wear resistance not only depend on the structural design of the seal,but also on matching of the material of the friction pair for the seal end faces. In order to maximize the localization of materials of the sealing friction pair,it is important to study the friction and wear characteristics of typical graphite seal rings. The friction and wear characteristics of typical domestic graphite used in aerospace field(numbered 1<sup>#</sup>,2<sup>#</sup> and 3<sup>#</sup>) from three major graphite manufacturers in match with 9Cr18 steel pair were compared under dry running condition by UMT-3 universal friction and wear tester based on orthogonal experiment and by changing the linear velocity,face specific pressure and surface roughness of hard ring. The results show that the pair is suitable for working conditions with large PV value and the linear velocity of friction is the main factor affecting the comprehensive tribological properties of the pair.When the material is 1<sup>#</sup> graphite,the rotation speed is 750 r/min,the face specific pressure is 1.77 MPa and the surface roughness of the steel plate is 0.2 μm,the comprehensive tribological properties of the friction pair are the best.
Dry friction and wear characteristics of impregnated graphite in a corrosive environment
[J].DOI:10.3901/CJME.2014.0616.111 URL [本文引用: 1]
N2O4环境下液体火箭发动机涡轮泵机械密封浸渍石墨的磨损机理研究
[J].
DOI:10.3901/JME.2019.07.119
[本文引用: 1]

针对液体火箭发动机涡轮泵机械密封浸渍石墨在N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>环境下磨损量较大的现象,以宏观试验与微观检测相结合的方法探索其产生的机理。对机械密封石墨的磨损表面进行了电镜观测,根据磨损形貌对正常磨损区与异常磨损区进行了区分,并对异常磨损的诱因进行了假设。提出了石墨表面的树脂腐蚀模型与孔隙气蚀模型,设置了包含静态腐蚀及动态磨损的试验流程以验证树脂腐蚀和孔隙气蚀的作用结果,分别在水及N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>环境下进行试验,并通过扫描电镜及红外光谱分析等手段观测了试验前后石墨表面的微观组织变化,介质试验后气孔平均直径为33 μm,为试验前的2倍。研究结果表明: N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>环境并不会造成石墨浸渍物酚醛树脂的腐蚀,造成石墨磨损量较大的诱因是气相N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>在石墨表面孔隙内部破裂导致的气蚀,气蚀后石墨的磨损可达数十微米量级。针对减少浸渍石墨的气蚀,给出了3项制备工艺的改进措施。本文的研究成果也可为其他高速旋转机械的机械密封石墨磨损研究及选材提供参考。
Wear mechanism of liquid rocket engine turbopump mechanical seal graphite surface in the N2O4 environment
[J].
DOI:10.3901/JME.2019.07.119
[本文引用: 1]

In view of the phenomenon that the mechanical seal impregnated graphite has a large amount of wear in N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> environment, the mechanism by combining the macroscopic test and microscopic examination is explored. The wear surface of graphite in mechanical seal is observed by electron microscope. The normal wear zone and abnormal wear zone are distinguished according to wear morphology, and the cause of abnormal wear is assumed. The resin corrosion model and pore cavitation model of graphite surface are proposed. The test process of static corrosion and dynamic wear is set up to verify the effect of resin corrosion and pore cavitation. The experiments are carried out in water and N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> environment, and the microstructure changes of graphite surface are observed by scanning electron microscope and infrared spectrum analysis. The average pore diameter after the medium test is 33 μm, which is twice that before the test. The results show that the N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> environment does not cause the corrosion of graphite impregnated phenolic resin, and the cause of larger wear of graphite is cavitation caused by gas phase N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> rupture inside the graphite surface pores. The wear of graphite after cavitation can reach the order of tens of microns. In order to reduce cavitation erosion of impregnated graphite, the improvement measures of three preparation processes are given. The research results can also provide reference for graphite wear research and material selection of mechanical seals of other high-speed rotating machinery.
深海液压系统压力补偿器研究
[J].
Research on pressure compensator used for deep-sea hydraulic system
[J].
深海装备压力补偿器及测试系统的设计
[J].
Design of pressure compensator for deep-sea equipment
[J].
Heat transfer correlations for laminar flows within a mechanical seal chamber
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.triboint.2008.10.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
接触式机械密封端面平均温度耦合计算方法
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2014.09.035
[本文引用: 1]

研究接触式机械密封端面平均温度与端面摩擦因数相耦合的计算方法问题。将机械密封环简化为等截面当量筒体,推导出了接触式机械密封端面平均温度的计算式,给出了密封环简化为当量筒体的具体方法;基于分形理论,建立了接触式机械密封端面摩擦因数计算模型。考虑端面平均温度与端面摩擦因数的相互耦合关系,提出了端面平均温度的具体计算方法。通过模拟计算,对B104a-70型机械密封端面平均温度的影响因素进行了分析。结果表明,端面平均温度随着弹簧比压或密封流体压力的增大,线性地增大;随着转速的增大,近似线性地增大,且端面越光滑,线性越好,增大的幅度也越大;随着端面分形维数的增大或特征尺度系数的减小,非线性地增大,当端面较粗糙时,端面平均温度的变化较小;当端面较光滑时,随着端面分形维数的增大或特征尺度系数的减小,端面平均温度迅速增大。
Average temperature coupling calculation method for end faces of contact mechanical seals
[J].
机械密封动环外周表面织构换热机理及结构优化
[J].
Heat transfer mechanism and optimization of circumferential texture of mechanical seal
[J].
机械密封磨合过程端面接触特性
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.10.028
[本文引用: 1]

为研究和掌握机械密封磨合过程端面接触特性的变化规律,考虑机械密封端面微凸体实际微接触面积与微接触截面积之间的区别,对微凸体临界弹性变形微接触面积和临界塑性变形微接触面积的表达式进行修正;推导得出机械密封端面弹性接触面积比、弹塑性接触面积比和塑性接触面积比的表达式。对B104a-70型机械密封进行磨合试验,试验介质为20℃清水,压力为0.5 MPa,弹簧比压为0.15 MPa,转速为2900 r·min<sup>-1</sup>。研究结果表明,随着磨合过程的进行,软质环端面迅速趋于光滑,磨损率迅速减小;磨合使密封端面间的接触特性发生了较大的变化,量纲1真实接触面积由0.00348增大到0.00567,弹性接触面积比由0.716增大到0.822,弹塑性接触面积比由0.231降低到0.128,塑性接触面积比由0.053降低到0.050。
Contact characterizations of end faces in mechanical seals running-in
[J].