运载火箭铝合金球形贮箱由冲压成形的两个半球壳焊接而成[1],为了减轻贮箱质量,需要在冲压半球壳表面进行铣削加工.生产中半球壳采用多道次拉深+中间退火工艺,拉深件贴模精度差导致后续铣削厚度基准确定难,造成半球壳壁厚均匀性差、结构偏重问题出现.通过增加法向压应力调控变形区应力状态是提升半球壳成形精度的重要途径之一.苑世剑等[2⇓-4]通过充液拉深方法调控变形铝合金应力状态,实现了半球壳精确成形,并在直径3 350 mm箱底上应用.除此以外,强力旋压工艺也可以通过施加法向应力提高成形件贴模精度.旋压成形方法具有工艺柔性高、加工载荷低、制造周期短等技术优势[5],已成为国内外箭体箱底整体化制造的一种方式[6].为此,本文针对铝合金半球壳成形精度差问题,开展基于旋压技术的半球壳成形精度提升方法研究.
旋压成形是机床主轴带动金属板坯和芯模一同旋转过程中侧压旋轮按照设定的加载轨迹将板坯逐渐贴靠芯模表面获得回转薄壁件的工艺方法.对于铝合金曲面薄壁构件旋压成形,国内外目前已开展了相关基础性研究.Gao等[7⇓⇓⇓-11]研究了大型薄壁壳体旋压形成机理与不均匀协调机理,从而确定了成形质量与旋压参数的关系,并建立对应的起皱预测模型;夏琴香[12]对铝合金曲面薄壁构件旋压过程中的有限元建模仿真关键技术进行了详细的研究;Zhang等[13]通过实验和有限元模拟手段,揭示了薄壁封头旋压过程中的起皱机理;林波等[14]采用两轮法旋压成形试验实现了半球壳体多道次普通旋压成形;杜陈阳等[15⇓-17]对铝合金曲面薄壁件旋压中的法兰起皱发生规律进行了研究,并提出了起皱预测模型.除了对成形缺陷的研究,针对铝合金曲面薄壁件旋压成形壁厚均匀性的改善也有诸多研究成果.Biplov等[18]采用数值模拟方法研究了流动旋压参数对于半球形件厚度分布的影响;Jia等[19]分析了不同旋压路径对锥筒组合薄壁件成形性能的影响;宋金龙等[20]提出了基于普旋和剪旋规律的变厚度板坯设计方法,以此来改善半球件的壁厚均匀性;Gan等[21]对多道次普通旋压加工中正程和反程轨迹分别进行了参数化设计,并研究了轨迹关键参数对成形件壁厚的影响.
前期研究表明,半球形件普通旋压成形过程在球形底部存在剪切旋压变形特征,导致球形底部厚度遵循近似剪旋正弦律,减薄率在30%以上.为此,大型半球壳整体成形采用剪切旋压和普通旋压的复合成形技术.相对整体加载的拉深成形而言,半球壳旋压成形件减薄量更大,但也具有更好的成形精度.为此,综合考虑拉深和旋压的技术优势,针对中等规格航天铝合金半球壳提出拉深-旋压复合成形工艺.通过利用两种工艺优势,实现构件壁厚均匀性和轮廓精度协同提升,因只有拉深和旋压工序转换需要中间退火,也提高了加工效率.
1 拉深-旋压复合工艺仿真模型
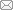
图1
图1
铝合金半球壳拉深-旋压成形示意图
Fig.1
Schematic diagram of deep drawing-spinning forming of aluminum alloy hemispherical shell
1.1 有限元模型建立
拉深-旋压复合成形中,板料拉深处于平面应力状态成形,而强力旋压属于板材体积成形.该半球壳使用圆形坯料为直径1 666 mm、厚度8 mm的铝合金退火材料,其屈服强度和抗拉强度分别为75 MPa和170 MPa.考虑到米级薄板坯料尺寸大,三维实体单元精确计算拉深-多道次旋压耗时冗长,本文基于Abaqus/Explicit平台建立了拉深-旋压复合工艺的二维轴对称有限元模型,兼顾了强力旋压阶段仿真精度与多道次全程加工计算效率.
仿真模型中,铝合金板坯假设为各向同性弹塑性材料,板坯的网格类型为CAX4R,控制沙漏效应的四节点缩减积分双线性轴对称四边形,网格尺寸为4 mm;拉深模具和旋压模具均设置为解析刚体.拉深模具的凹模圆角为50 mm,凸模为500 mm半球面;旋压模具的芯模与拉深凸模同尺寸,旋轮圆角半径为50 mm,尾顶直径根据拉深件贴模区域大小进行设计;假设变形铝合金与凸模(芯模)、凹模、压边圈的接触界面为滑动摩擦,摩擦因数假设为0.15,实际压边力对应载荷为2 MPa;而变形铝合金与旋轮的接触界面为滚动摩擦,因数假设为0.02.
为了更好地模拟多道次成形过程中间退火的影响,在每一道次拉深仿真完成后,提取变形板坯的节点位置,对提交文件中的模具位置和板坯形状进行修改,消除板材应力应变场,并进行下一道次成形过程仿真.
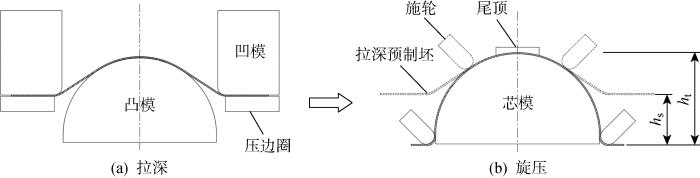
图2
1.2 有限元模型可靠性分析
图3
2 拉深-旋压复合成形工艺分析
为了研究拉深-旋压复合过程旋压占比对铝合金半球壳成形精度的影响,获得合适的旋压占比,尽可能减少现有冲压道次,本研究主要讨论旋压占比与壁厚和贴模度的关系.
2.1 旋压占比对壁厚的影响
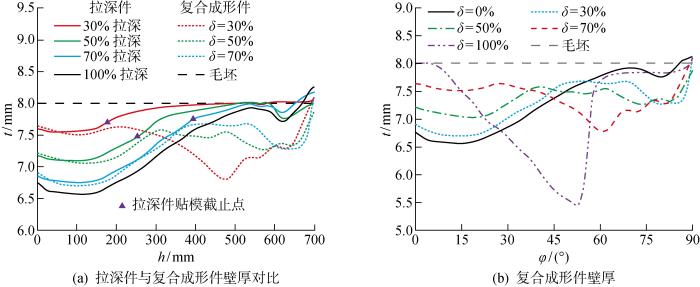
针对全程拉深(δ=0%)和旋压占比δ=30%,50%,70%以及全程旋压(δ=100%)共5种过程,完成多道次成形数值计算并提取拉深件和旋压件的壁厚分布,绘制出铝合金半球壳成形件壁厚分布曲线图,如图4所示.图中:h为成形件上的点对应板坯初始点到板坯中心的距离.
图4
图4
复合成形壁厚数值仿真结果
Fig.4
Numerical simulation results of hybrid process of wall thickness
图4(a)为5种成形条件下拉深阶段成形件壁厚分布,图4(b)为后续旋压件的壁厚分布.需要说明的是:在δ=100%仿真中采用强力旋压+普通旋压的复合工艺路径;图4(a)中初始点水平径向距离600 mm处的板坯在拉深过程中位于凹模圆角位置,受到一定的弯曲作用,进而发生一定程度的减薄;初始点水平径向距离700~833 mm的板坯为法兰.从图4(b)可以看出,对于铝合金半球壳全程拉深件,顶部φ≤30° 范围内壁厚减薄较多,φ>30° 后,越靠近端口则壁厚减薄越小,其壁厚最薄处为6.5 mm.因采用复合旋压方式,全程旋压件强力旋压部分构件壁厚减薄较大.δ=30%,50%,70%的半球壳壁厚变化规律相似,这3种复合成形都在20° 附近出现壁厚最薄的区域,超过该区域成形件壁厚有所增加,且在旋压开始后会出现一定程度的二次减薄.对比图4(a)的拉深贴模段可见:拉深部分的构件厚度分布在旋压前后基本一致,这表明在δ≤70%时,旋压加工对拉深件贴模部分的铝合金壁厚影响不大.因此,相对于全程拉深或旋压而言,拉深和旋压复合的成形方法可以提高半球壳壁厚均匀性分布.
为了更好地选择拉深-旋压复合工艺旋压占比,对复合工艺的构件壁厚分布进一步对比研究.可以得出:在球面件的顶部φ≤45°范围内,δ=30%,50%,70%这3种情况的构件壁厚变化规律基本一致,且随着旋压占比的减小,最小壁厚有减小趋势,其中δ=30%对应的构件最小壁厚为6.7 mm,减薄率为16.25%;其他区域(45°<φ≤90°范围),这3种工艺均在引入旋压后出现二次减薄,且减薄程度随着旋压占比的增加而增加.主要原因是:尽管球顶部分完成拉深贴模,然而,因法兰外缘的刚性约束,普通旋压前期仍存在剪切变形成分,造成半球壳壁厚减薄,旋压占比越大,二次减薄越明显.综合得出:δ=30%的半球壳旋压二次减薄较大,δ=70%的半球壳拉深阶段减薄率较大.因此,旋压占比选择过大或过小均会导致构件减薄率过大的情况发生.
综上所述,δ=50%的构件减薄率相对较小,壁厚均匀性更好;从实际工序来看,δ=50%时,此时是实际全程拉深的第一道序,后续两道拉深工序被一道旋压替代,并减少了一道中间退火,缩短了工艺链长度.因此,选择δ=50%的复合成形策略,可以将成形件的最小壁厚控制在7 mm附近.
2.2 回弹量及贴模度分析
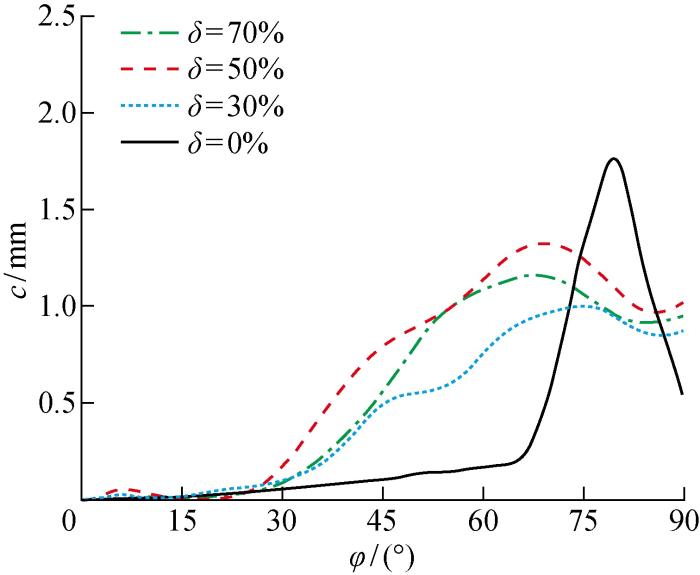
对δ=0%,30%,50%,70%共4种工况的回弹进行仿真计算,并提取回弹后构件内表面坐标与理论型面的距离,得到构件贴模间隙曲线,如图5所示.图中:c为成形件的贴模间隙.由图可见:φ≤30° 范围内回弹均较小;30°<φ≤90° 范围内4种方案的贴模间隙呈先增大后减小的趋势,其中全程拉深件在φ≥70° 时出现较大的回弹量,最大贴模间隙值为1.78 mm,其他3种复合成形(δ=30%,50%,70%)成形件贴模间隙走势大致相同,均在φ=70° 附近出现较大回弹,最大间隙值为1.28 mm,相较于全程拉深有明显下降.在3种复合成形中,δ=50%的贴模间隙值相对较大,δ=70%的间隙值相对较小,但是尺寸偏差仍没有明显改善.
图5
图5
四种方案仿真结果贴模间隙
Fig.5
Simulation results of four schemes for springback clearance
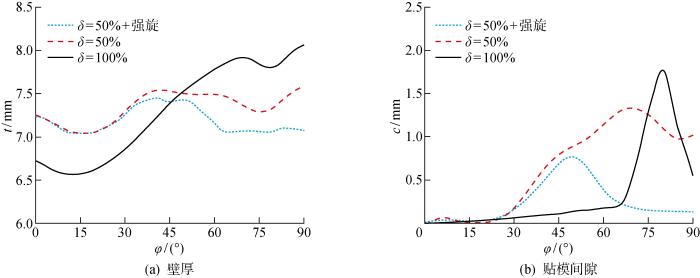
综合考虑壁厚均匀性以及尺寸偏差,选取δ=50%成形方案进行成形件强力旋压,从而提高贴模精度.从上述仿真结果看出:复合工艺在φ≥30°出现较大的贴模间隙.因此.选取强力旋压起始点为 φ=30°,并采取逐渐减薄工艺策略.成形件强力旋压数值仿真结果如图6所示.图6(a)和图6(b)分别为δ=50%成形件强力旋压前后和全程拉深件的壁厚与贴模间隙对比.可以看出:加入强力旋压后,0°≤φ≤30° 的成形件厚度基本没有发生改变,30° <φ≤90°的板坯出现进一步减薄,但是最终稳定在7 mm附近,相比于强力旋压前壁厚更加均匀.成形件在引入强力旋压后构件尺寸偏差更小,贴模间隙控制在0.75 mm以下.相比于全程拉深工艺,复合工艺得到的铝合金半球壳具有更好的厚度均匀性和更小的贴模间隙.
图6
图6
半球壳强旋阶段数值仿真结果
Fig.6
Numerical simulation results of power spinning stage of hemispherical shell
图7
图7
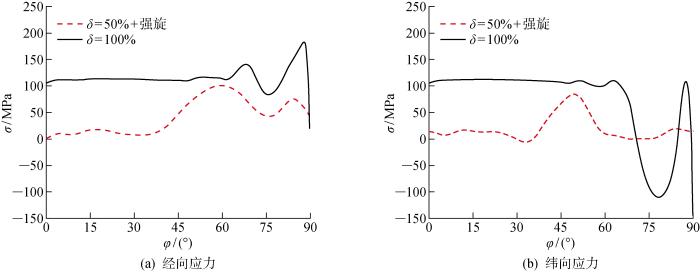
回弹前中间层应力分布
Fig.7
Stress distribution of intermediate layer before springback
综合以上研究结果,相较于原拉深工艺,复合成形构件壁厚更加均匀且贴模精度更高,这主要是由于旋压的加入改变了半球壳的应力状态.
3 拉深-旋压复合成形实验验证
为了验证复合成形方法在1 m级铝合金半球壳上的可靠性,进行了退火态铝合金拉深-旋压复合成形试验.先将铝合金板坯在原有的半球壳生产线上冲压50%的高度,即冲压深度为250 mm,随后将退火态半成品工件安装到双旋轮强力旋压机上进行六道次普旋和强力旋压成形,旋压加工现场如图8所示.
图8
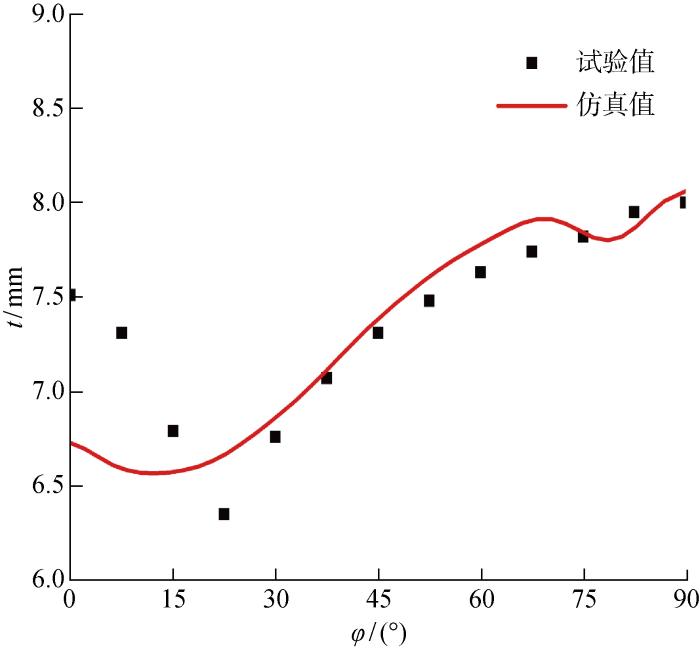
试验所制得的半球样件如图9所示.对其4条母线上分别取13个不同测点进行壁厚测量.经过测量,最小壁厚为6.63 mm,高于6.5 mm,达到厚度标准.最小壁厚低于前面仿真结果的原因是:在实际旋压试验时,为了消除二次装夹带来的定位误差,预先对拉深部分进行强力旋压保证工件和芯模紧密贴合,导致该部分厚度的减薄.按实际旋压工艺路线对半球壳成形进行仿真,得到壁厚仿真结果如图10所示.可以看出:仿真值与试验值的分布规律基本吻合,最大壁厚误差为4.5%,从而验证了上述结论的可靠性.另外,从工程应用角度,采用本文数值仿真方法可以获得可接受的计算精度,为大中型球面形构件兼顾精度与效率的旋压过程数值仿真提高了技术性验证.
图9
图10
随后用圆弧形样板对试验件内表面贴模度进行检验,如图11所示,样板与试验件内表面没有光缝,表明贴合良好,获得了高的轮廓精度.
图11
通过铝合金半球壳拉深-旋压复合成形工艺的实施,实现了该构件厚度均匀性和贴模精度的提高,解决了传统单一拉深工艺的不足.同时,中间退火减少至1次,提高了加工效率.
4 结论
针对铝合金半球壳现有制造质量的现状,提出了拉深-旋压复合工艺成形策略,提高成形件壁厚均匀性和尺寸精度.利用有限元方法研究了其改善厚度和精度的可行性,并开展试验验证,主要得到了以下结论:
(1) 基于Abaqus建立了拉深-旋压复合工艺有限元模型,仿真结果表明:旋压占比δ=50%的复合工艺的综合成形效果最优,能有效改善半球壳的壁厚均匀性.
(2) 多道次普通旋压件经过强力旋压改变了端口位置的应力状态,有效提高了半球壳的贴模精度.
(3) 复合工艺试验结果表明,旋压占比δ=50%复合工艺可以获得壁厚和贴模精度满足制造要求的直径1 m级铝合金半球壳.
参考文献
俄罗斯Fregat上面级
[J].
Russian Fregat upper stage
[J].
大尺度非均质壳体流体压力成形机制与缺陷控制方法
[J].
Mechanism and defects control of fluid pressure forming for large sized inhomogeneous shell
[J].
Fundamentals and processes of fluid pressure forming technology for complex thin-walled components
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.eng.2020.08.014 URL [本文引用: 1]
薄壁曲面整体构件流体压力成形起皱机理与控制
[J].
DOI:10.3901/JME.2018.09.037
[本文引用: 1]

塑性失稳诱发起皱是制约薄壁曲面构件整体成形的瓶颈问题,通过考虑悬空区反胀效果的曲面薄壳流体压力成形力学分析,推导抑制起皱和破裂的非线性流体压力加载曲线,建立临界起皱应力模型为塑性失稳提供理论判据;在此基础上,针对大型贮箱整体箱底构件流体压力成形起皱预测和控制难题,理论计算大型箱底流体压力成形加载路径,分析流体压力加载路径对反胀区形状、失稳行为和应力分布影响规律,揭示曲面薄壳流体压力成形起皱抑制机理;采用我国自主研制的超大型数控流体压力成形装备(成形力1.5万t/高压液体体积5 m<sup>3</sup>),首次试制出直径3 m级运载火箭燃料贮箱整体箱底,解决了大型超薄(厚径比2‰)曲面薄壳失稳难题。
Mechanism and controlling of wrinkles during hydroforming of integral thin-walled curved shell
[J].
DOI:10.3901/JME.2018.09.037
[本文引用: 1]

Wrinkling induced by plastic instability is a critical problem for the forming of integral thin-walled curved shells. Considering the reverse bulging effect in unsupported area, the mechanical characteristics of sheet hydroforming process is analyzed. Loading paths of liquid pressure about wrinkling and rupture are deduced, a model about critical wrinkling stress is built which can be regarded as a criterion for the plastic instability. Focusing on the forming process of storage tanks of rockets, a theoretical loading path is calculated, the influence of loading path on bulging geometry, instability behavior and stress distribution is discussed. The mechanism of wrinkling suppression is revealed. A large numerical control sheet hydroforming equipment with the biggest power in the world was successfully built (forming power 15000 t, volume of high pressure liquid 5 m<sup>3</sup>). An integral storage tank with diameter of 3m is successfully obtained using the proposed method and equipment. The problem on plastic instability of thin-walled shell (ratio of thickness to diameter equals 2‰) is solved.
交叉内筋薄壁筒体错距旋压成形数值仿真
[J].
Numerical simulation of stagger spinning of cylindrical part with cross inner ribs
[J].
超大直径贮箱箱底整体旋压成形技术
[J].
DOI:10.13330/j.issn.1000-3940.2021.03.025
[本文引用: 1]

目前,国内大型贮箱箱底采用瓜瓣顶盖拼焊的方法制造,存在制造可靠性不足、生产效率低等问题。针对大型贮箱箱底制造现状,以某型号运载火箭贮箱箱底作为研究对象,设计了先预成形、后旋压成形的工艺方案,并提出了“一道次剪旋+多道次普旋”的旋压工艺方案,通过有限元仿真分析及工艺试验验证了超大直径贮箱箱底整体旋压成形技术的可行性。结果表明:采用预成形方案能够有效抑制零件边缘起皱,采用剪切旋压与普通旋压相结合的成形工艺能够实现箱底的高精度成形。箱底中心区域采用剪切旋压,构件形状可控性好,模具贴合良好;预成形法兰的边缘区域刚度高,采用多道次普通旋压,既能够达到收边贴模的目的,又能够避免边缘减薄量过大的问题。
Integral spinning forming technology of storage box bottom with super large diameter
[J].
Deformation mode and wall thickness variation in conventional spinning of metal sheets
[J].
A new robust theoretical prediction model for flange wrinkling in conventional spinning
[J].
铝合金大型薄壁异型曲面封头旋压成形研究进展
[J].
DOI:10.3901/JME.2018.09.086
[本文引用: 1]

大型薄壁异型曲面整体构件是航天航空等重要领域迫切需要的高性能轻量化构件。旋压和淬火是实现该类构件整体化制造和性能控制的一种有效途径。然而,大型薄壁异型曲面旋压是多因素耦合作用下的多道次局部加载/卸载复杂过程,成形过程中易出现局部损伤破裂、起皱、隆起、不贴模等缺陷,且旋压后的淬火过程还易造成大的残余应力和淬火变形,并决定着构件的最终使用性能。在建立大型薄壁异型曲面构件旋压和淬火全过程有限元模型的基础上,分析大型薄壁异型曲面构件旋压过程中应力应变分布与变化规律;研究失稳起皱缺陷的形成机理,获得旋压工艺参数对薄壁壳体凸缘周向压应力的影响规律,提出控制凸缘起皱的方法;研究板坯尺寸波动对成形质量的影响;研究获得大型薄壁异型曲面封头旋压件淬火残余应力分布规律和淬火变形规律。
Advances in spinning of aluminum alloy large-sized thin-walled and special-curved surface head
[J].
DOI:10.3901/JME.2018.09.086
[本文引用: 1]

Large-sized thin-walled and special-curved surface heads are the urgent needs of aerospace and aviation industry for its high-performance and lightweight. Spinning-quenching is one effective integral forming process to manufacture these components. However, the spinning of large-sized thin-walled and special-curved surface head is one of the complicated local loading/unloading processes under the action of multi-parameters and their coupled effects. In this process, the heads are very prone to produce forming defects, such as local damage rupture, flange wrinkling, local bulge, and unfitting. Additionally, the quenching treatment after spinning will lead to heavy quenching distortion and residual stress, thus seriously deteriorate the material performance. In this work, a finite element model for the whole process of spinning-quenching are established. Based on the model, the distribution and evolution of stress and strain field of the large-sized thin-walled and special-curved surface heads during spinning process is analyzed. In order to obtain the effect laws of process parameters on flange circumferential compressive stress, the mechanism of flange wrinkling is investigated, and a method of controlling the flange wrinkling is proposed. The effect laws of the thickness variation of slabs on deformation quality are investigated. The quenching residual stress and distortion of the large sized thin-walled and special-curved surface heads are also studied.
铝合金大型复杂薄壁壳体多道次旋压缺陷形成机理
[J].
Forming mechanism of defects in spinning of large complicated thin-wall aluminum alloy shells
[J].
铝合金大型复杂薄壁壳体旋压研究进展
[J].
Advances in spinning of aluminum alloy large-sized complicated thin-walled shells
[J].
Study on spinning process of a thin-walled aluminum alloy vessel head with small ratio of thickness to diameter
[J].
DOI:10.1115/1.4000930
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The thin-walled vessel head with the ratio of thickness to diameter less than 3‰ has long been considered to be difficult to be spun because wrinkling is very likely to occur during the thin-walled vessel head spinning process when the thickness is far smaller than the diameter. Based on process experiments and finite element method, the spinning failure of thin-walled vessel head with a small ratio of thickness to diameter is analyzed in the present research. The mechanism of wrinkling is identified and some effective solutions are discussed to prevent the failure. The results show that the feed ratio, the blank geometry, and the roller trajectory are the main factors influencing the spinning qualities. In the shear spinning, the feasible roller feed ratio is found to be within a very small range because of the thin thickness of blanks. Wrinkling will occur if the feed ratio is slightly outside the operation range. Bending the edge of blank or enlarging the blank size can effectively prevent wrinkling at a larger feed ratio, which would increase the operation range of roller feed ratio. Due to the fact that the conventional spinning is a process of multiple passes, there are many factors affecting the forming quality of thin-walled aluminum alloy vessel head. Wrinkling is likely to happen by the influence of roller trajectory in the first pass due to the fact that the thickness of blank is far smaller than the diameter. The straight-line trajectory is the worst trajectory under which wrinkling is most likely to occur.
超半球壳体多道次拉深旋压工艺研究
[J].针对1060超半球壳体基于板坯多道次拉深旋压进行成形性分析,提出两模法和两轮法的旋压成形试验方案,并设计不同旋压试验方案的芯模和旋轮工装。通过MC2000型数控录返旋压机,分别采用R13、R20和R25、R8不同圆角半径的圆弧式旋轮对1060板坯进行两模法和两轮法的多道次拉深旋压成形试验。两模法旋压毛坯件的凸缘边减薄严重,成形效果差;两轮法旋压采用R25旋轮4道次快速进给,R8旋轮4道次中低速精整旋压的旋压工艺,其旋压件贴模度高,成形效果好。试验结果表明:两轮法旋压工艺能实现板坯经多道次拉深旋压成形为超半球壳体。通过降低芯模转速,调整进给比和降低道次减薄率,可以消除旋压成形过程中出现的反挤、波纹和起皮等缺陷。
Research on process of multi-pass draw-spinning of hyper-hemispherical shell
[J].The formability of aluminum hyper-hemispherical shell deformed from 1060 plates by multi-pass draw-spinning is analyzed. The testing scheme of two-mould and two-roller are proposed, and different mandrels and rollers are designed. Circle-arc rollers of different work-radius test two shaping schemes by MC2000 playback spinning machine. The figuration of two-mould blanks is bad and the thickness of flange is reduced greatly. The figuration of two-roller blanks and inner moulding surface are excellent by the spinning process that the four quick feeding processes of R25 roller and four low feeding processes of R8 roller. The test results show that the figuration of two-roller can shape hyper-hemispherical shell by multi-pass draw-spinning aluminum blanks. Backward extrusion, expansion scab scale and corrugation are controlled by the spinning process of reducing rotational speed of mould, decreasing thinning ratio of pass and adjusting feed rate.
薄壁球面构件普旋法兰起皱预测方法评价
[J].
Evaluation of flange wrinkling prediction methods of conventional spinning for thin-walled spherical components
[J].
Theoretical prediction of flange wrinkling in first-pass conventional spinning of hemispherical part
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.07.031 URL [本文引用: 1]
旋压法兰起皱预测
[J].
Research on prediction of flange wrinkling in conventional spinning
[J].
A study of forming of thin-walled hemispheres by mandrel-free spinning of commercially pure aluminum tubes
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.12.036 URL [本文引用: 1]
Study on die-less spinning of cone-cylinder combined hollow parts
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.04.028
[本文引用: 1]

Die-less spinning can achieve the thin-walled parts with the regular shape of cone and cylinder or even some non-axisymmetric shapes. And it has advantages in forming some difficult demolding shapes. In this study, dieless spinning in a cone-cylinder combined hollow part and its forming mechanism were investigated. A ballcrown-shape roller was used to replace a conventional roller in the spinning process. The roller movement and spindle rotation were controlled by a computer numerical control spinning machine to achieve a planned roller path. The pass sets of tilted and horizontal lines were designed to form the cone and cylinder shape, respectively. Further, two methods were adopted to link the two forming pass sets and spin the cone-cylinder combined shape. One is to connect the cone and cylinder forming lines directly (Schemes A); the other is to connect the cone and cylinder forming lines by transition lines (Schemes B). The effects of two key parameters (roller path and feed ratio f) on the wrinkling and wall thickness distribution were analyzed. The product exhibited wrinkling on the wall using the roller path of Scheme A with f = 0.5 mm/r. f affected the occurrence of wrinkling considerably. Larger f made the flatness of the cylinder wall worse, no matter which roller path (in Scheme A or B) was used. When f was set to 0.25 mm/r (f was lower than L-T1 in this study) with a blank thickness of 2.05 mm, wrinkling could be suppressed in the roller path of Scheme A. The product had an increasing thickness distribution on both the cone and the cylinder. The cylinder wall was even thicker than the disk blank with a blank thickness of 2.05 mm.
铝合金封头旋压成形变厚度毛坯设计方法
[J].
Research on design method of variable thickness blanks for aluminum alloy head spinning forming
[J].
Effects of backward path parameters on formability in conventional spinning of aluminum hemispherical parts
[J].DOI:10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64666-7 URL [本文引用: 1]