随着传感器技术的巨大改进和进步,结合传感技术的智能轮胎为轮胎动态信息的感知获取提供了新思路,利用传感器测量实际的轮胎动态数据,再通过算法分析进行轮胎状态和参数的估计.近些年来,一些学者对轮胎垂向力的估计算法进行了相关研究.赵健等[10]设计了三轴加速度测试微机电系统(MEMS),通过对加速度信号特征的分析提取,利用反向传播(BP)神经网络建立了垂向力估计算法.王国林等[11]利用环模型分析了接触角与垂向力的关系,结合内衬层加速度数据对垂向力进行估计.梁冠群等[12]等利用加速度信号估计接地长度,并通过多项式拟合研究垂向力和接地长度及胎压的关系来估测轮胎垂向力.加速度传感器轻巧价廉、结构紧凑,被广泛应用于智能轮胎中,但加速度噪声信号干扰大、加速度信号种类冗杂,特征信息提取较为困难.而应变传感器同样具有轻巧、紧凑、价廉的优点,且信号更单一纯粹,随着柔性传感技术的发展,应变传感器在智能轮胎中的应用获得了更大的空间.
1 重载轮胎有限元模型
随着计算机技术的飞速发展,有限元分析技术成为轮胎结构力学性能设计和分析的重要手段.利用计算机的技术优势能精确描述各种复杂工况下轮胎的形变、受力,准确表达轮胎的力学特性.
1.1 有限元模型的建立
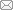
轮胎有限元模型如图1所示.利用AutoCAD软件完成重载轮胎二维结构模型的绘制和建立后,选用HyperMesh软件对轮胎的二维结构模型进行网格划分,如图1(a)所示,完成轮胎二维有限元建模的其余前处理步骤[13].再参照中心参考点,通过inp文件命令编辑将轮胎二维有限元模型旋转为轮胎三维模型.考虑到轮胎不同部位在运行过程中的应力分布和应变程度存在较大梯度,对轮胎分析结果影响也有较大差异,若旋转步长采用单一尺寸,能够以恒定的采样频率获取节点信号,一定程度上提高了模型的计算精度,且避免了步长变化导致的应力突变.在有限元仿真中,网格越精细,仿真精度越高,但却增加了计算量、资源消耗和降低了收敛率.由于轮胎应变的主要变化区域是在接地区前后,所以对于非接地区的形变与应变的精度要求不高.由二维模型旋转生成三维模型时,采用变旋转步长方法,如图1(b)所示,仅对接地区域附近进行网格细化.在减少计算成本、节省资源的同时,更真实地模拟轮胎接地区的实际行为,提高了接地区应变信号的精度.
图1
1.2 模型验证
轮胎垂向刚度是表征轮胎特性的重要参数,对车辆的承载能力和平顺性有着重要影响.而轮胎的接地印记特性直接影响轮胎的使用寿命、磨损状况和轮胎力特性,对车辆的安全性也有重要影响.
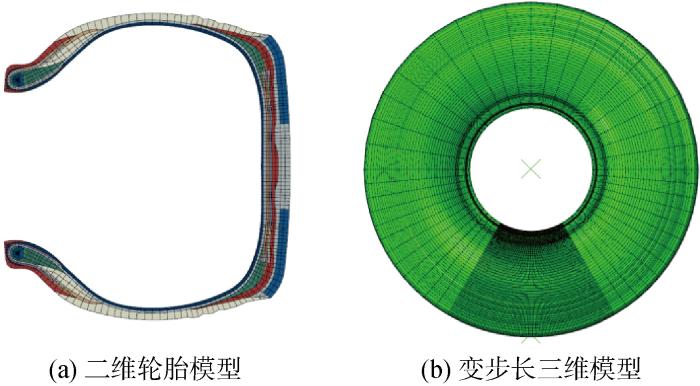
利用重载轮胎力学振动实验系统进行重载轮胎加载实验,如图2所示,获取重载轮胎不同静载荷下接地印记形状和轮胎下沉量,实验系统如图2(a)所示.对比有限元仿真结果进行接地印记特性和垂向刚度验证,结果如图2(b)、2(c)所示.图中:F为加载力;ΔH为下沉量.由图可知,各载荷下实验与仿真的轮胎接地印记形状均对应相似;轮胎下沉量随载荷增大,变化趋势一致,误差最大为7.79%.
图2
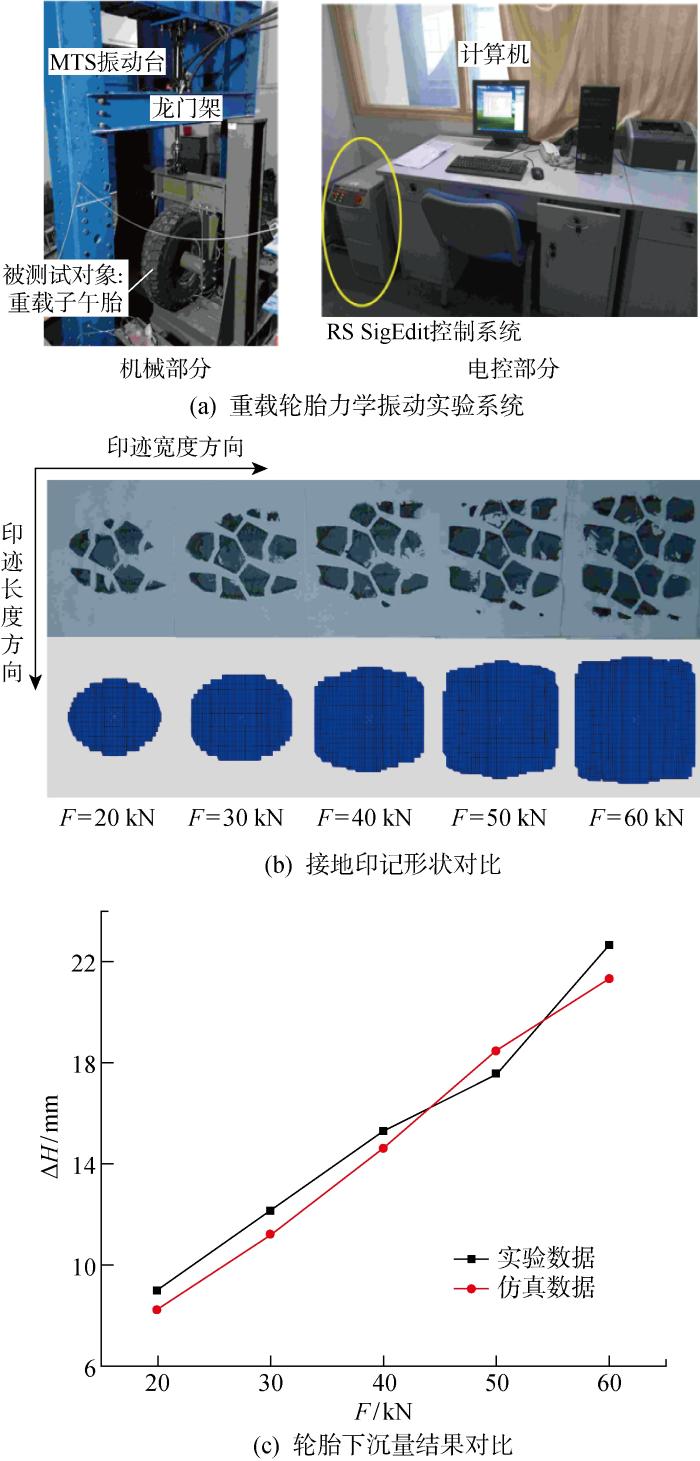
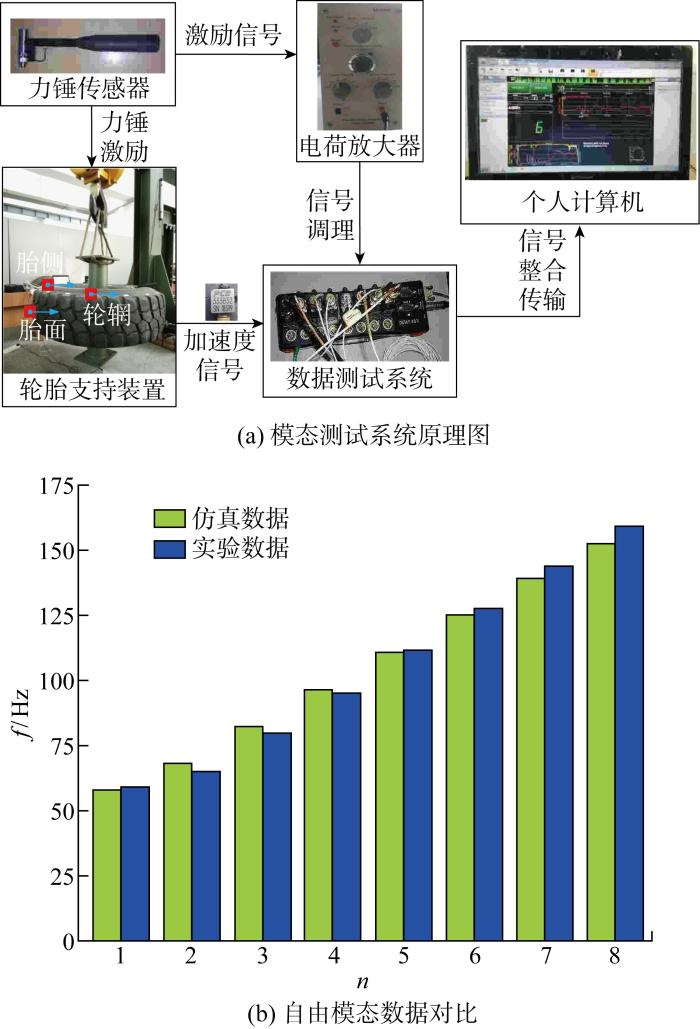
轮胎的模态参数可以表征其振动特性,与轮胎的充气压力和约束条件有直接关系.本文搭建重载轮胎模态测试系统如图3所示.图中:f为频率;n为阶次.模态测试系统包括:轮胎支撑装置、力锤及电荷放大器、数据测试系统和个人计算机.利用模态测试系统对轮辋自由状态下的轮胎进行力锤锤击实验,提取了轮胎前8阶径向振动模态振型.对比实验测试模态结果和有限元仿真的解析模态结果,发现两者振型顺序一致,同振型对应的特征频率误差最大为5.49%.
图3
上述实验结果表明:所建轮胎有限元模型的垂向刚度和模态参数同实胎具有较好的一致性,能够可靠反映轮胎的真实力学特性,模型的精度和真实性满足后续研究的条件.
2 轮胎垂向力与周向应变的关系
车辆运行过程中,只有轮胎胎面与地面是直接接触的,在胎面上安装传感器获取的信号能最直观地反映轮胎的形变与受力.但胎面上的传感器信号对外界干扰因素响应较大,信号曲线特征杂乱,且传感器安装难度较大.目前多数学者选择将传感器安装在内衬层上,王国林等[14]采用基于方差的全局灵敏度分析法研究了内衬层轮胎力敏感区域,其中胎冠区对于周向应变的响应最为灵敏.考虑到静载和直线滚动下轮胎的受力和形变关于胎面中心线对称,选择胎面中心点作为应变传感器安装点.
2.1 重载轮胎静载接地特性分析
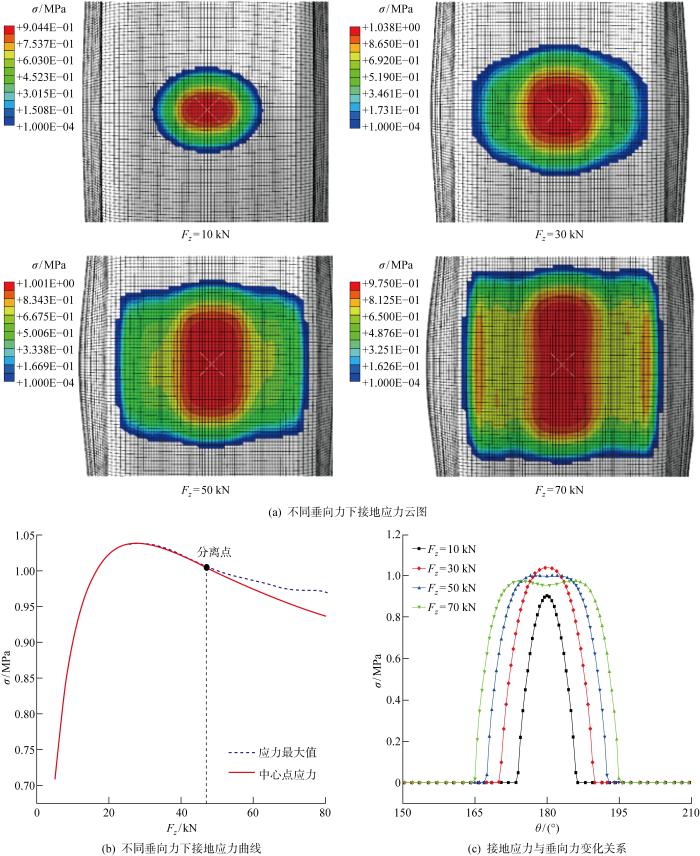
利用轮胎有限元模型对不同垂向力Fz下的静载工况进行仿真,对轮胎接地胎面中心线接地应力σ进行提取分析,结果如图4所示.图中:θ为测量点位与穿过有限元模型中心的横轴方向之间的角度.
图4
图4
静载荷对接地特性的影响规律
Fig.4
Effect of static load on tire grounding characteristics
从图4可以看出:随垂向力增大,接地印记形状从椭圆形向矩形转变,轮胎接地印记长度持续增加,接地宽度在增长至接近胎面宽度后基本不再变化;接地区中心点接地应力和接地应力最大值均先快速增大后缓慢减小,Fz=28 kN时接地应力达到最大值;当Fz>47 kN时,接地应力最大值和中心点接地应力开始出现显著差值,接地应力曲线由上凸抛物线变为马鞍形,接地应力最大值点由中心点向两侧偏移.
通过接地应力曲线提取轮胎前后接地角ϕf和ϕr,结合接地长度计算公式求解各垂向力下的接地长度:
式中:R为轮胎充气后自由状态半径;静载状态前后接地角相等,ϕf=ϕr.
与有限元仿真值进行对比,结果如图5所示.接地长度的公式计算结果与仿真结果误差最大为1.3%,一致性较高;随着垂向力从5 kN增大到80 kN,接地长度和接地角不断增大,但增长幅度不断减小.
图5
2.2 重载轮胎静载周向应变分析
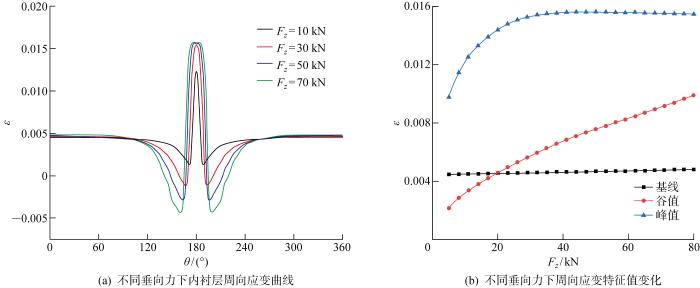
通过有限元仿真对0.8 MPa标准胎压、不同静载荷工况轮胎的内衬层周向应变曲线进行仿真分析,结果如图6所示.图中:ε为周向应变.可以看出:垂向力由5 kN增大到80 kN过程中,由于非接地区的作用力基本不变,导致周向应变曲线基线值无明显变化;随垂向力增大,曲线谷值和谷值间距角均呈现降幅增长.
图6
2.3 基于内衬层周向应变的接地角估计
通过上述分析可以发现,轮胎内衬层周向应变曲线的相邻谷值的间距角度、轮胎接地角、接地印记长度随垂向力均呈正相关,且三者曲线趋势相似.本文认为,轮胎接地角与周向应变曲线谷值间距角密切相关,可通过周向应变曲线特征参量表征轮胎接地角.
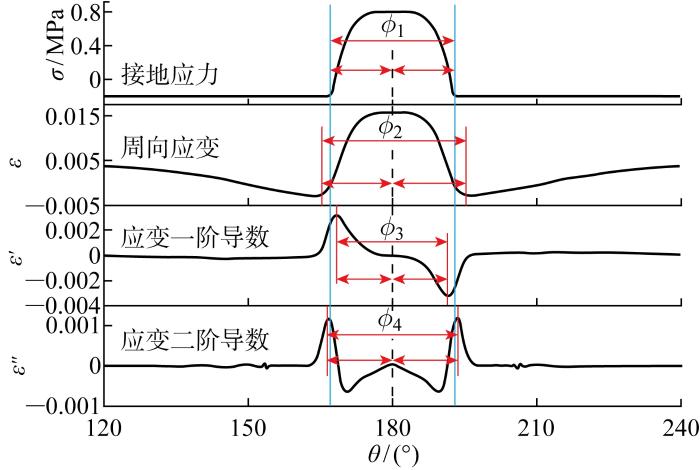
图7
图7
内衬层周向应变曲线特征点角度差与接地角对比图
Fig.7
Comparison of characteristic point angle difference and contact angle of circumferential strain curve of tire inner liner
表1 不同垂向力下应变曲线特征点间距角
Tab.1
| Fz/kN | ϕ1/(°) | ϕ2/(°) | ϕ3/(°) | ϕ4/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 13 | 17 | 11 | 13 |
| 20 | 17 | 22 | 14 | 18 |
| 30 | 20 | 26 | 17 | 21 |
| 40 | 23 | 29 | 20 | 24 |
| 50 | 26 | 32 | 23 | 27 |
| 60 | 28 | 35 | 26 | 29 |
| 70 | 31 | 38 | 28 | 32 |
由表1可见,周向应变曲线谷值间距角和应变二阶导数峰值间距角均大于接地角,应变一阶曲线峰谷值间距角小于接地角,且随垂向力增大,误差角度越大.单靠一类应变曲线难以准确表征接地角,考虑选用多类间距角均值作为接地角表征指标.由于接地角夹在应变零阶、二阶与一阶特征点间距角之间,提出均值表征指标CA1、CA2、CA3,与接地角误差分别为δ1、δ2、δ3,则有:
表2 不同表征指标误差结果
Tab.2
| Fz/kN | δ1/% | δ2/% | δ3/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 7.69 | 7.69 | 5.12 |
| 20 | 5.88 | 6.67 | 5.88 |
| 30 | 7.50 | 5.00 | 6.67 |
| 40 | 6.52 | 4.34 | 5.79 |
| 50 | 5.77 | 3.85 | 5.12 |
| 60 | 8.93 | 1.78 | 7.14 |
| 70 | 6.45 | 3.22 | 5.38 |
3 垂向力估计模型
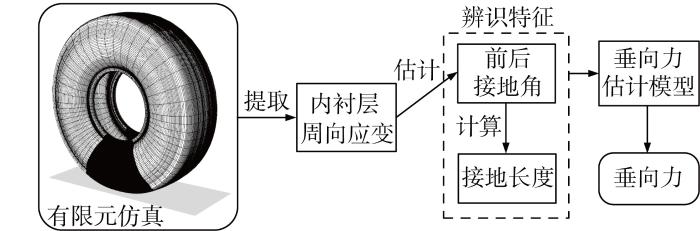
通过上述分析发现,垂向力与接地角之间关系密切,且已有学者通过柔性环模型建立了接地角与垂向力的关系方程.但通过数学方程计算垂向力所需轮胎参数较多、公式较为复杂,且公式本身存在误差和参数获取过程的误差,会造成垂向力估计精度下降.采用建立黑盒系统的方法,在确立接地角、接地长度与垂向力的输入输出关系后,通过有限元仿真获取数据集,建立估计模型对垂向力进行预测,垂向力估计流程图如图8所示.
图8
3.1 基于灰狼支持向量回归机的垂向力估计模型
GWO算法是Mirjalili等[17]受灰狼群捕猎行为提出的优化搜索算法,具有良好的收敛性能、参数少、易实现等优点.GWO算法优化过程包括主要狼群等级分层、搜索包围猎物和狩猎攻击猎物.
(1) 狼群等级分层.在搜索空间随机生成狼群后,将狼群中适应度最好的3匹灰狼依次标记为α、β和δ,余下的均划分为ω,每次迭代后重复分级过程.
(2) 搜索包围猎物.灰狼在攻击猎物前先对猎物的位置进行确定,通过协同系数向量μ和B、随机向量r1和r2调整对猎物的搜索模式和搜索方向.|μ|>1时,狼群外散进行全局搜索;|μ|<1时,狼群对某区域进行局部搜索.
式中:D为当前狼与猎物之间的距离;Xp(t)为第t代猎物位置向量;X(t)为第t代当前狼位置向量;整个迭代过程中a由2线性降到0;r1和r2为[0,1]中的随机向量.
(3) 狩猎.灰狼群在迭代后,α、β和δ3匹狼与猎物距离最近,3匹狼利用自身与猎物间的距离联合指导其他ω狼调整位置围剿猎物.
式中:k=α,β,δ;i=1,2,3;Xp(t+1)为第t+1代猎物位置向量;Xi定义了ω狼朝高等级狼前进的方向和步长;Xp(t+1)定义了ω狼的最终位置.
选用支持向量回归机建立轮胎垂向力估计模型,利用灰狼算法实现对SVR参数C和γ进行寻优,以实现对轮胎垂向力的预测.
3.2 特征集获取与模型训练
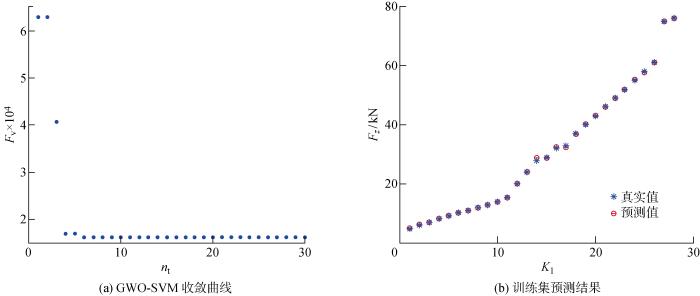
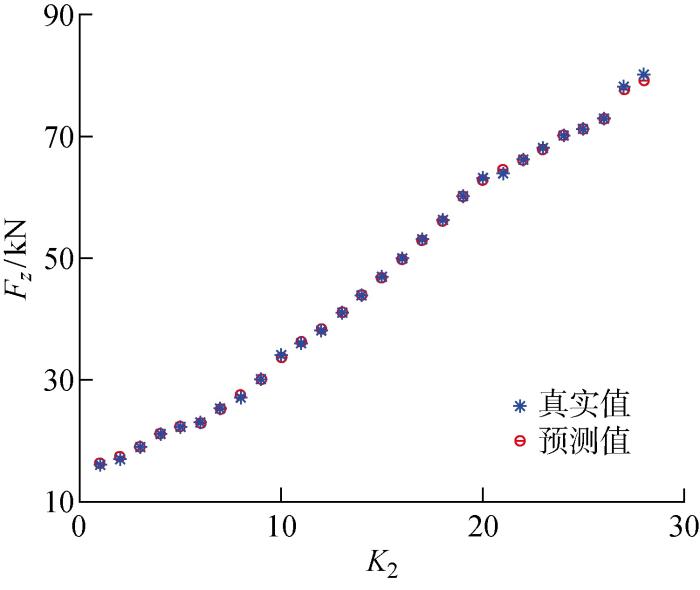
根据垂向力与接地角、接地长度的关系,将接地角ϕ、接地长度L作为估计模型的特征参数.通过有限元对轮胎模型进行5 kN到80 kN静载工况的仿真计算,提取内衬层周向应变,结合接地角表征指标CA2和式(1)求解接地角和接地长度.总共采集了56个样本,选取28个作为训练集,用于垂向力估计模型的训练,其余的作为测试集来检验模型的训练效能.基于灰狼算法对支持向量机参数C、γ寻优过程的适应度变化曲线和训练集预测结果如图9所示.图中:Fv为适应度;nt为迭代次数;K1为训练集样本编号.可以看出,适应度迅速下降并稳定在了0.000 16附近,收敛性良好,能够较好获取参数最优解;模型训练集均方根误差为 0.258 7 kN,平均绝对误差为1.06%.
图9
3.3 垂向力预测结果
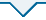
模型测试结果如图10所示.图中:K2为测试集样本编号.测试集均方根误差为 0.289 4 kN,最大绝对误差为1.79%,决定系数达到99.985%,具有良好的估计精度.可以认为本文所提出的基于周向应变曲线获取接地参数进行垂向力估计的方法是可行的.
图10
4 结语
建立了16.00R20重载轮胎有限元模型,通过加载实验和模态实验对模型进行了垂向刚度和振动特性的双重验证;利用有限元仿真分析了载荷对轮胎接地特性和内衬层周向应变曲线的影响;提出了接地角均值表征指标,对比有限元仿真结果验证了指标可靠性;以接地角、接地长度估算值作为辨识特征,结合灰狼优化算法和支持向量回归机建立了垂向力估计模型.结果表明:接地角、接地长度随垂向力增大降幅增长;周向应变曲线的极值点间距对垂向力变化响应较敏感,垂向力越大,间距越大;采用周向应变零阶、一阶、二阶导数特征点间距角均值作为轮胎接地角表征指标的估计误差均在8%以内,用一阶与二阶间距角均值作为表征指标效果最好;以轮胎接地角和接地长度作为支持向量机的输入特征的垂向力估计模型估测垂向力误差在1.8%以内,能对垂向力进行准确估计.
参考文献
轮胎稳态运动学与六分力预报I: 理论与方法[J]
提出一种新的轮胎运动学描述和六分力预报理论。滚动接触是汽车轮胎力学、轮轨动力学的核心问题,由于涉及刚体转动与有限变形,滚动接触运动学与动力学的描述与求解非常困难。用拉格朗日—欧拉混合描述法分析大变形滚动接触结构的速度场、加速度场和接触变形。以车轮定位角为卡尔丹角,用拉格朗日描述,得到了包含刚体转动和弹性变形的轮胎速度场。而接触区域的变形和受力用欧拉描述,通过欧拉网格和拉格朗日网格的信息传递,完成滚动结构动力学分析。所提出的理论可以退化到Fiala模型,并可以从理论上解释子午线轮胎的伪侧偏和伪侧倾现象。基于所建立的运动学理论和非线性有限元,建立轮胎六分力预报方法。针对某轿车子午线轮胎,分析轮胎接地面滑移速度、接地面积、接地压力、侧向剪力分布等随着侧偏角的变化规律,并研究该轮胎侧偏力和回正力矩随着胎面刚度和摩擦因数的参数敏感性。结果表明轮胎侧偏刚度和回正刚度主要受结构刚度控制,而峰值侧偏力和峰值回正力矩主要受摩擦因数控制。将利用所建立的方法和试验,探讨带束层结构对大规格子午线轮胎侧偏特性的影响规律,进一步验证所提出的理论和方法的正确性。所提出的理论和方法开辟了直接从轮胎设计预报轮胎六分力的新途径。
Theory and method of tire rolling kinematics and prediction of tire forces and moments[J]
A new method to describe the tire rolling kinematics and calculate the tire forces and moments is presented. The rolling contact is the core problem of tire/vehicle mechanics as well as wheel/track dynamics. It is extremely difficult to model rolling contact because of the rigid body rotation and the finite deformation occurred. The mixed Lagrange-Euler method is introduced to deal with the calculation of the velocity, acceleration, and contact deformation of rolling contact structure. By using Lagrange framework, the tire velocity and acceleration which include the rigid body rotation and elastic deformation can be obtained by treating the wheel position angles as Cardanic angles, while the Euler method is used to analyze the deformation and forces in the contact area. The dynamic analysis of the rolling structure is thus performed by transferring information between these two kinds of grids in the contact area. Not only can the presented principle be degenerated into Fiala tire model but it can explain the tire ply steer and ply camber phenomenon as well. The method to predict the tire forces and moments is built up by using the proposed kinematic theory and nonlinear finite element method. The detailed analysis of the slipping velocity, contact forces, contact areas, lateral forces of a radial tire have been performed. Study on the parametric sensitivity of the tire lateral forces and self-aligning torque on the tread stiffness and friction coefficient is also carried out. The results show that the tire cornering stiffness and self-aligning stiffness are mainly controlled by the structure stiffness, while the peak lateral force and peak self-aligning torque are mainly controlled by the friction coefficient. The effect of the belt structure to the cornering properties of the large radial tires will be studied by using related experiments and simulations, to verify the principles and methods mentioned above. The proposed methodology provides a new tool to predict tire forces and moments.
Modeling and validation of off-road vehicle ride dynamics
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.ymssp.2011.11.006 URL [本文引用: 1]
Comprehensive tire-road friction coefficient estimation based on signal fusion method under complex maneuvering operations
[J].
Optimizing tire vertical stiffness based on ride, handling, performance, and fuel consumption criteria
[J].
DOI:10.1115/1.4031459
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Researchers mostly focus on the role of suspension system characteristics on vehicle dynamics. However tire characteristics are also influential on the vehicle dynamics behavior. In this paper, the effects of tire vertical stiffness on the ride, handling, accelerating/braking performance, and fuel consumption of a vehicle are analytically investigated. Furthermore, a method for determining the optimum vertical stiffness of tires is presented. For these purposes, first an appropriate mathematical criterion for the ride, handling, accelerating/braking performance, and fuel consumption is developed. Next, to achieve the optimum tire characteristic, a performance index, which contains all of the above-mentioned criteria, is defined and optimized. In the proposed performance index, the tire vertical stiffness is a design variable and its optimization provides a compromise among ride, handling, accelerating/braking performance, and fuel consumption of the vehicle. Last, the analytical optimization results are confirmed by performing precise numerical simulations.
Tire model application and parameter identification—A literature review
[J].DOI:10.4271/2014-01-0872 URL [本文引用: 1]
Tire grip identification based on strain information: Theory and simulations
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.ymssp.2013.06.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
Longitudinal tire dynamics model for transient braking analysis: ANCF-LuGre tire model
[J].
DOI:10.1115/1.4028335
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In this investigation, the flexible tire model based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation (ANCF) is integrated with LuGre tire friction model for evaluation of the longitudinal tire dynamics under severe braking scenarios. The ANCF-LuGre tire model developed allows for considering the nonlinear coupling between the dynamic structural deformation of the tire and its transient tire force distribution in the contact patch using general multibody dynamics computer algorithms. To this end, the contact patch obtained by the ANCF elastic ring tire model is discretized into small strips and the state of friction at each strip is defined by the differential equation associated with the discretized LuGre friction parameters. The normal contact pressure distribution predicted by the ANCF elastic ring elements that are in contact with the road surface are mapped onto the LuGre strips in the contact patch to evaluate the tangential tire force distribution and then the tire forces evaluated at LuGre strips are fed back to the generalized tangential contact forces of the ANCF elastic ring tire model. By doing so, the structural deformation of the ANCF elastic ring tire model is dynamically coupled with the LuGre tire friction in the final form of the governing equations. Furthermore, the systematic and automated parameter identification procedure for the LuGre tire force model is developed. It is shown that use of the proposed procedure with the modified friction curve proposed for wet road conditions leads to accurate prediction of the LuGre model parameters for measured tire force characteristics under various loading and speed conditions. Several numerical examples are presented in order to demonstrate the use of the in-plane ANCF-LuGre tire model for the longitudinal transient dynamics of tires under severe braking scenarios.
内嵌加速度计的智能轮胎纵/垂向力估计算法
[J].
Estimation algorithm for longitudinal and vertical forces ofsmart tire with accelerometer embedded
[J].
应用模型的智能轮胎垂向力估计算法
[J].
Vertical force estimation algorithm of intelligent tires based on physical model
[J].
平面单元和壳单元在复合有限条法中模拟加劲肋的应用
[J].
Application of plane elements and shell elements in imitating ribs of members in compound strip method
[J].
智能轮胎力的敏感响应区域及变量
[J].
Force-sensitive response area and variable of intelligent tire
[J].
基于支持向量机回归的曲面零件涡流测距标定方法
[J].
Eddy current distance measurement calibration method for curved surface parts based on support vector machine regression
[J].
基于证据推理规则CS-SVR模型的锂离子电池SOH估算
[J].
State of health estimation of lithium-ion battery using a CS-SVR model based on evidence reasoning rule
[J].
Greywolf optimizer
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007 URL [本文引用: 1]