


考虑不同充电策略的锂电池健康状态区间估计
收稿日期: 2022-09-05
修回日期: 2023-01-10
录用日期: 2023-03-03
网络出版日期: 2023-05-04
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(51409095);河南工业大学粮食信息处理与控制教育部重点实验室开放基金(KFJJ-2016-110)
Interval Estimation of State of Health for Lithium Batteries Considering Different Charging Strategies
Received date: 2022-09-05
Revised date: 2023-01-10
Accepted date: 2023-03-03
Online published: 2023-05-04
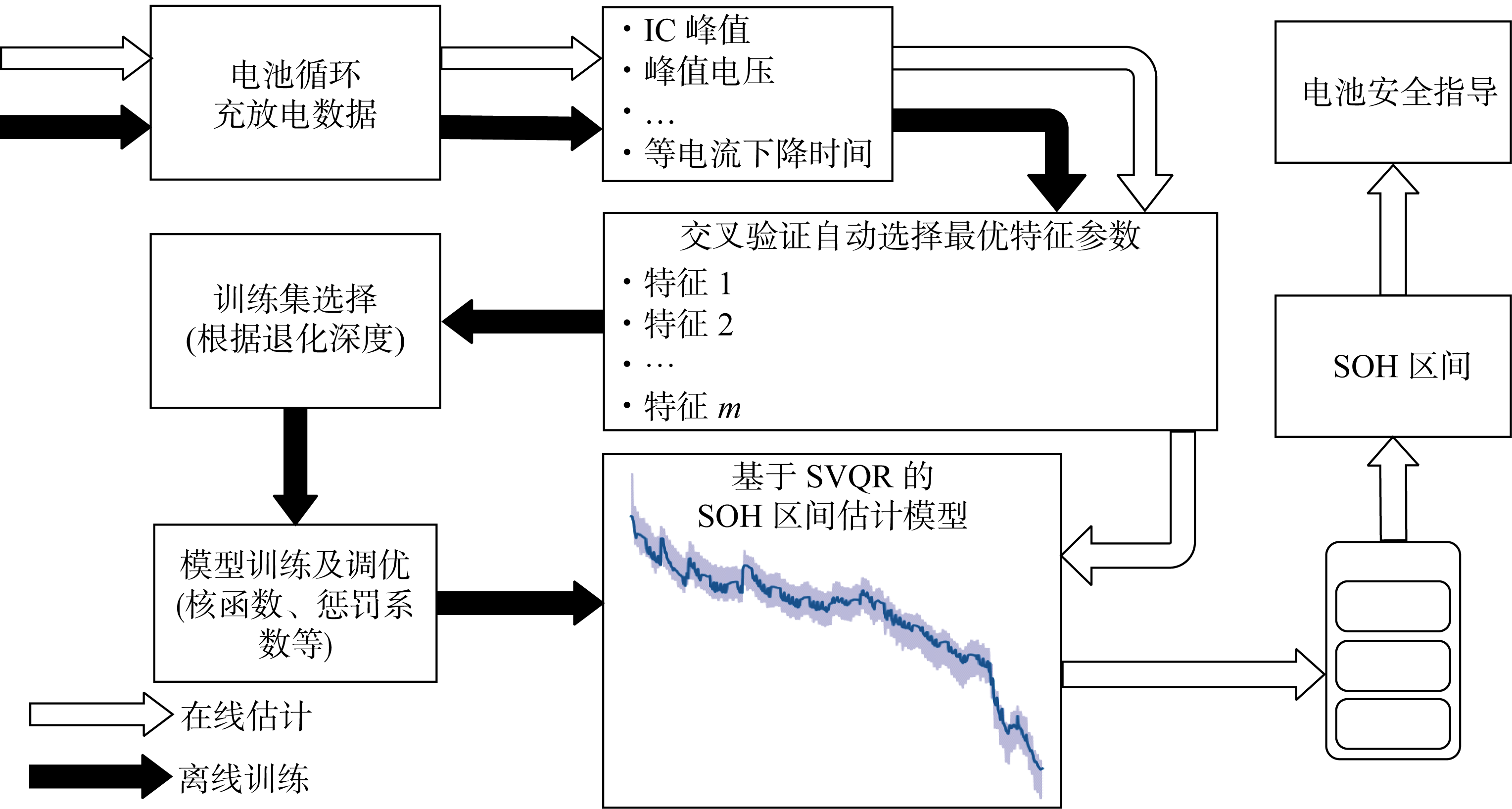
评估锂离子电池健康状态(SOH)对于电池使用、维护、管理和经济性评价都有十分重要的意义,但当前锂电池SOH估计方法多针对特定充电策略,采用确定性估计模型,无法反映电池退化过程中的随机性、模糊性等不确定性信息.为此,提出一种适用于不同充电策略的锂电池SOH区间估计方法.该方法针对不同充电策略的电池循环充放电数据提取多个特征参数,通过交叉验证自动选择针对特定充电策略的最优特征参数组合.另外,考虑到锂电池全生命期循环次数有限,属于小样本问题,提出集成支持向量回归与分位数回归优势的支持向量分位数回归模型(SVQR)进行锂电池SOH区间估计.选用放电程度较深的锂电池充放电循环数据作为训练集,对SVQR模型进行离线训练,训练好的模型用于不同充电策略下锂电池SOH在线估计.采用具有不同充电策略的数据集验证所提方法,实验结果表明:所提方法适用于不同充电策略,且估计结果优于分位数回归法、分位数回归神经网络法和高斯过程回归法.
张孝远 , 张金浩 , 杨立新 . 考虑不同充电策略的锂电池健康状态区间估计[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2024 , 58(3) : 273 -284 . DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2022.347
State of health (SOH) estimation of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries is of great importance for battery use, maintenance, management, and economic evaluation. However, the current SOH estimation methods for Li-ion batteries are mainly targeted at specific charging strategies by using deterministic estimation models, which cannot reflect uncertain information such as randomness and fuzziness in the battery degradation process. To this end, a method for estimating the SOH interval of Li-ion batteries applicable to different charging strategies is proposed, which extracts multiple feature parameters from the cyclic charging and discharging data of batteries with different charging strategies, and automatically selects the optimal combination of feature parameters for a specific charging strategy by using the cross-validation method. In addition, considering the limited number of cycles in the whole life cycle of Li-ion batteries as a small sample, support vector quantile regression (SVQR), which integrates the advantages of support vector regression and quantile regression, is proposed for the estimation of SOH interval of lithium-ion batteries. Li-ion battery charge/discharge cycle data with deep discharge degree is selected as the training set for offline training of the SVQR model, and the trained model is used for online estimation of the SOH of Li-ion batteries of different charging strategies. The proposed method is validated using three datasets with different charging strategies. The experimental results show that the proposed method is applicable to different charging strategies and the estimation results are better than those of quantile regression, quantile regression neural network and Gaussian process regression.

| [1] | 孙丙香, 任鹏博, 陈育哲, 等. 锂离子电池在不同区间下的衰退影响因素分析及任意区间的老化趋势预测[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(3): 666-674. |
| SUN Bingxiang, REN Pengbo, CHEN Yuzhe, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of degradation under different interval stress and prediction of aging trend in any interval for lithium-ion battery[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(3): 666-674. | |
| [2] | 杨胜杰, 罗冰洋, 王菁, 等. 基于容量增量曲线峰值区间特征参数的锂离子电池健康状态估算[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(11): 2277-2287. |
| YANG Shengjie, LUO Bingyang, WANG Jing, et al. State of health estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on peak region feature parameters of incremental capacity curve[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(11): 2277-2287. | |
| [3] | 卢地华, 陈自强. 基于双充电状态的锂离子电池健康状态估计[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2022, 56(3): 342-352. |
| LU Dihua, CHEN Ziqiang. State of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on dual charging state[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2022, 56(3): 342-352. | |
| [4] | 李建林, 李雅欣, 陈光, 等. 退役动力电池健康状态特征提取及评估方法综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(4): 1332-1347. |
| LI Jianlin, LI Yaxin, CHEN Guang, et al. Research on feature extraction and SOH evaluation methods for retired power battery[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(4): 1332-1347. | |
| [5] | 张立强. 锂离子电池多物理模型参数辨识及健康特征提取[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015. |
| ZHANG Liqiang. Parameter identification and health feature extraction of multi-physical model of lithium-ion battery[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015. | |
| [6] | 王震坡, 王秋诗, 刘鹏, 等. 大数据驱动的动力电池健康状态估计方法综述[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59(2): 151-168. |
| WANG Zhenpo, WANG Qiushi, LIU Peng, et al. Review on techniques for power battery state of health estimation driven by big data methods[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(2): 151-168. | |
| [7] | 李凯铨, 汪玉洁. 锂离子电池的健康状态估计综述[C]// 系统仿真技术及其应用. 安徽: 中国科学技术大学, 2021: 330-333. |
| LI Kaiquan, WANG Yujie. A review of the estimation of the state of health of lithium-ion batteries[C]// System Simulation Technology & Its Application. Anhui, China: University of Science and Technology of China, 2021: 330-333. | |
| [8] | OSPINA AGUDELO B, ZAMBONI W, MONMASSON E. Application domain extension of incremental capacity-based battery SoH indicators[J]. Energy, 2021, 234: 121224. |
| [9] | SHE C Q, WANG Z P, SUN F C, et al. Battery aging assessment for real-world electric buses based on incremental capacity analysis and radial basis function neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(5): 3345-3354. |
| [10] | 徐宏东, 高海波, 徐晓滨, 等. 基于证据推理规则CS-SVR模型的锂离子电池SOH估算[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2022, 56(4): 413-421. |
| XU Hongdong, GAO Haibo, XU Xiaobin, et al. State of health estimation of lithium-ion battery using a CS-SVR model based on evidence reasoning rule[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2022, 56(4): 413-421. | |
| [11] | WANG Z K, ZENG S K, GUO J B, et al. State of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on the constant voltage charging curve[J]. Energy, 2019, 167: 661-669. |
| [12] | 石伟杰, 王海民. 基于锂离子电池热特性的SOH在线诊断模型研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2020, 41(8): 206-216. |
| SHI Weijie, WANG Haimin. On-line diagnosis model of SOH based on thermal characteristics of lithium-ion battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2020, 41(8): 206-216. | |
| [13] | 王萍, 弓清瑞, 张吉昂, 等. 一种基于数据驱动与经验模型组合的锂电池在线健康状态预测方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(24): 5201-5212. |
| WANG Ping, GONG Qingrui, ZHANG Ji'ang, et al. An online state of health prediction method for lithium batteries based on combination of data-driven and empirical model[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(24): 5201-5212. | |
| [14] | 刘金枝, 杨鹏, 李练兵. 一种基于能量建模的锂离子电池电量估算方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2015, 30(13): 100-107. |
| LIU Jinzhi, YANG Peng, LI Lianbing. A method to estimate the capacity of the lithium-ion battery based on energy model[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(13): 100-107. | |
| [15] | ROMAN D, SAXENA S, ROBU V, et al. Machine learning pipeline for battery state-of-health estimation[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2021, 3(5): 447-456. |
| [16] | LI K W, WANG R, LEI H T, et al. Interval prediction of solar power using an improved bootstrap method[J]. Solar Energy, 2018, 159: 97-112. |
| [17] | LI H, PAN D H, PHILIP CHEN C L. Intelligent prognostics for battery health monitoring using the mean entropy and relevance vector machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, & Cybernetics: Systems, 2014, 44(7): 851-862. |
| [18] | 曹孟达. 卫星电源部件在轨退化状态评估方法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2019. |
| CAO Mengda. Research on evaluation method of on-orbit degradation state of satellite power components[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2019. | |
| [19] | 魏中宝, 钟浩, 何洪文. 基于多物理过程约束的锂离子电池优化充电方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59(2): 223-232. |
| WEI Zhongbao, ZHONG Hao, HE Hongwen. Multiphysics-constrained optimal charging of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(2): 223-232. | |
| [20] | 吴晓刚, 崔智昊, 孙一钊, 等. 电动汽车大功率充电过程动力电池充电策略与热管理技术综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(6): 2218-2234. |
| WU Xiaogang, CUI Zhihao, SUN Yizhao, et al. Summary of charging strategy and thermal management technology of power battery in high-power charging process of electric vehicle[J]. Energy Storage Science & Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2218-2234. | |
| [21] | 郭剑成, 王惜慧, 岑海林. 一种基于温度变化的动力电池智能充电策略[J]. 电源技术, 2022, 46(5): 518-522. |
| GUO Jiancheng, WANG Xihui, CEN Hailin. An intelligent charging strategy of power battery based on temperature change[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 46(5): 518-522. | |
| [22] | KOENKER R, BASSETT G. Regression quantiles[J]. Econometrica, 1978, 46(1): 33-50. |
| [23] | CRISTIANINI N, SHAWE-TAYLOR J. An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000. |
| [24] | TAKEUCHI I, FURUHASHI T. Non-crossing quantile regressions by SVM[C]// 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2004: 401-406. |
| [25] | SHIM J, KIM Y, LEE J, et al. Estimating value at risk with semiparametric support vector quantile regression[J]. Computational Statistics, 2012, 27(4): 685-700. |
| [26] | YUAN M. GACV for quantile smoothing splines[J]. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2006, 50(3): 813-829. |
| [27] | HE W, WILLIARD N, OSTERMAN M, et al. Prognostics of lithium-ion batteries based on Dempster-Shafer theory and the Bayesian Monte Carlo method[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(23): 10314-10321. |
| [28] | BIRKL C. Diagnosis and prognosis of degradation in lithium-ion batteries[D]. Oxford, UK: University of Oxford, 2017. |
| [29] | SEVERSON K A, ATTIA P M, JIN N, et al. Data-driven prediction of battery cycle life before capacity degradation[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(5): 383-391. |
| [30] | LIAN C, ZHU L Z, ZENG Z G, et al. Constructing prediction intervals for landslide displacement using bootstrapping random vector functional link networks selective ensemble with neural networks switched[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 291: 1-10. |
| [31] | LIAN C, ZENG Z G, WANG X P, et al. Landslide displacement interval prediction using lower upper bound estimation method with pre-trained random vector functional link network initialization[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 130: 286-296. |
| [32] | 何耀耀, 刘瑞, 撖奥洋. 基于实时电价与支持向量分位数回归的短期电力负荷概率密度预测方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(3): 768-775. |
| HE Yaoyao, LIU Rui, HAN Aoyang. Short-term power load probability density forecasting method based on real time price and support vector quantile regression[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(3): 768-775. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |