


卫星对空中动态目标凝视成像姿态规划方法
收稿日期: 2022-10-28
修回日期: 2022-12-13
录用日期: 2023-02-01
网络出版日期: 2023-03-10
基金资助
国家自然科学基金企业联合基金重点项目(U20B2054)
Attitude Planning Method of Satellite Staring Imaging to Aerial Dynamic Target
Received date: 2022-10-28
Revised date: 2022-12-13
Accepted date: 2023-02-01
Online published: 2023-03-10
杜宁 , 吴树范 , 陈占胜 , 陈文晖 , 王世耀 , 徐家国 , 秦栋栋 . 卫星对空中动态目标凝视成像姿态规划方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2024 , 58(4) : 411 -418 . DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2022.425
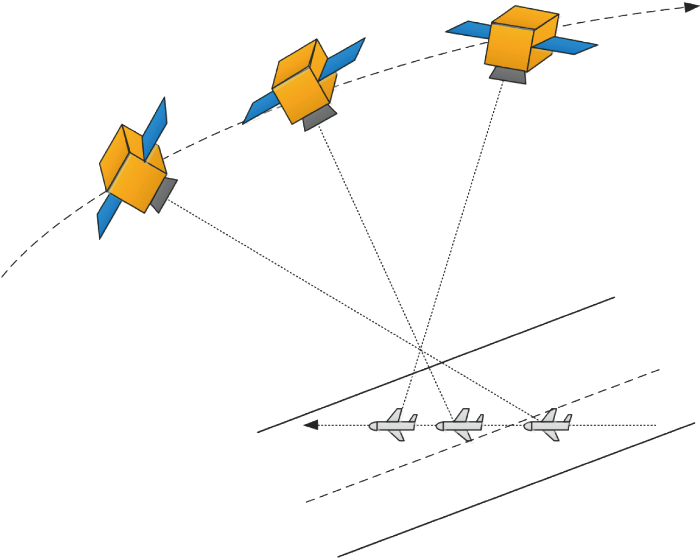
Aimed at the staring imaging requirements of the low earth orbit (LEO) satellite array camera for aerial dynamic targets, a method for target position estimation and staring attitude planning based on image miss-distance of the satellite platform is proposed. Based on the prior knowledge of the flying altitude of the aerial dynamic target, taking the latitude and longitude change rate of the target geography as the state quantity and the central pixel value of the target as the observation, an extended Kalman filter (EKF) is designed to realize the accurate smooth estimation and prediction of the geographical latitude and longitude of the target. On this basis, the attitude and angular velocity of the satellite are planned, the influence of target pixel noise and delay on attitude stability is avoided, and the position estimation of a single satellite to target is realized. The effectiveness of the proposed method is illustrated by a numerical simulation.
| [1] | XU J, LIANG Y H, LIU J, et al. Multi-frame super-resolution of gaofen-4 remote sensing images[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(2142): 1-15. |
| [2] | 刘刚, 于淼. 静止轨道光学成像卫星研究现状及建议[J]. 飞控与探测, 2020, 3(5): 21-26. |
| LIU Gang, YU Miao. Status and development trends of high-resolution geostationary optical imaging satellite[J]. Flight Control & Detection, 2020, 3(5): 21-26. | |
| [3] | 黄丽霞, 彭鑫, 刘书豪, 等. 高轨光学成像卫星动目标跟踪策略设计与仿真[J]. 航天器工程, 2018, 27(4): 10-16. |
| HUANG Lixia, PENG Xin, LIU Shuhao, et al. Design and simulation for moving target tracking strategy of high orbit optical imaging satellite[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2018, 27(4): 10-16. | |
| [4] | ZHANG R, ZHANG X Y, XIAO L L, et al. Recognition of aircraft activities at airports on video micro-satellites: Methodology and experimental validation[J]. Aerospace, 2022, 9(414): 1-19. |
| [5] | ZHANG X Y, XIANG J H. Tracking imaging feedback attitude control of video satellite[C]// 2016 Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Automation. Hong Kong, China: Electrical Engineering and Automation, 2017: 729-737. |
| [6] | PEI W J. Staring imaging attitude tracking control laws for video satellites based on image Information by hyperbolic tangent fuzzy sliding mode control[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2022, 2022: 8289934-1-13. |
| [7] | 黄家明, 陈寰, 史庆杰, 等. 基于FPGA的红外目标识别神经网络加速器设计[J]. 飞控与探测, 2020, 3(6): 66-75. |
| HUANG Jiaming, CHEN Huan, SHI Qingjie, et al. An infrared object detection neural network accelerator based on FPGA[J]. Flight Control& Detection, 2020, 3(6): 66-75. | |
| [8] | JIANG L, YANG X B. Study on enlarging the searching scope of staring area and tracking imaging of dynamic targets by optical satellites[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(4): 5349-5358. |
| [9] | YANG Y, HOU Q Y, ZHANG J X, et al. Mission scheduling optimization of multi-optical satellites for multi-aerial targets staring surveillance[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2020, 357: 8657-8677. |
| [10] | LIAN Y J, GAO Y D, ZENG G Q. Staring imaging attitude control of small satellites[J]. Journal of Guidance Control and Dynamics, 2017, 40(5): 1275-1282. |
| [11] | LI P Y, DONG Y F, LI H J. Staring imaging real-time optimal control based on neural network[J]. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering Volume, 2020, 2020: 8822223-1-14. |
| [12] | FELICETTI L, EMAMI M R. Image-based attitude maneuvers for space debris tracking[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2018, 76: 58-71. |
| [13] | WU Y H, HAN F, ZHENG M H, et al. Attitude tracking control for a space moving target with high dynamic performance using hybrid actuator[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2018, 78: 102-117. |
| [14] | 张宇, 夏鲁瑞, 蔡博宇. 基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的空间目标双星定位方法[J]. 上海航天, 2020, 37(1): 38-43. |
| ZHANG Yu, XIA Lurui, CAI Boyu. A novel bi-satellite positioning method for spatial targets based on the unscented Kalman filter[J]. Aerospace Shanghai (Chinese & English), 2020, 37(1): 38-43. | |
| [15] | WANG C J, WANG W H, CHEN Z P. Single-satellite positioning algorithm based on direction-finding[C]// 2017 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium—Spring. St Petersburg, Russia: IEEE, 2017: 2533-2538. |
| [16] | 于大腾, 王华, 尤岳, 等. 基于单星观测的弹道导弹参数估计方法综述[J]. 现代防御技术, 2014, 42(2): 62-68. |
| YU Dateng, WANG Hua, YOU Yue, et al. Review for the method of single satellite early warning ballistic missile parameter estimation[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2014, 42(2): 62-68. | |
| [17] | KYUJIN M, HOJUN K, CHANG K R. Trajectory estimation for a ballistic missile in ballistic phase using IR images[C]// 2018 9th International Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2018: 173-177. |
| [18] | SHYAM B, JOSEPH E F, STEPHEN P S. Autonomous nucleus tracking for comet/asteroid encounters: The STARDUST example[C]// 1998 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings. Snowmass, CO, USA: IEEE, 1998: 353-365. |
| [19] | BONG W. Rapid multitarget acquisition and pointing control of agile spacecraft[J]. Journal of Guidance Control and Dynamics, 2002, 25(1): 96-104. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |